This repository contains code to instantiate and deploy a text generation model. This model recognizes a text file as an input and outputs a string. The model was trained on the One Billion Word Benchmark (http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.3005) data set. The input to the model is a simple text file, and the output is a string containing the words that are predicted to follow. The model has a vocabulary of approximately 800,000 words.
The model files are hosted on IBM Cloud Object Storage. The code in this repository deploys the model as a web service in a Docker container. This repository was developed as part of the IBM Code Model Asset Exchange and the public API is powered by IBM Cloud.
| Domain | Application | Industry | Framework | Training Data | Input Data Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | Text generation | Multi | TensorFlow | 1 Billion Word Language Model Benchmark | text file |
Rafal Jozefowicz, Oriol Vinyals, Mike Schuster, Noam Shazeer: “Exploring the Limits of Language Modeling”, 2016; arXiv:1602.02410.
| Component | License | Link |
|---|---|---|
| This repository | Apache 2.0 | LICENSE |
| Pretrained weights | Apache 2.0 | LICENSE |
| Training Data | 1 Billion Word Language Model Benchmark |
Note: this model can be very memory intensive. If you experience crashes (such as the model API process terminating with a Killed message), ensure your docker container has sufficient resources allocated (for example you may need to increase the default memory limit on Mac or Windows).
docker: The Docker command-line interface. Follow the installation instructions for your system.- The minimum recommended resources for this model is 8 GB Memory and 4 CPUs.
To run the docker image, which automatically starts the model serving API, run:
$ docker run -it -p 5000:5000 codait/max-news-text-generator
This will pull a pre-built image from Docker Hub (or use an existing image if already cached locally) and run it. If you'd rather checkout and build the model locally you can follow the run locally steps below.
You can deploy the model-serving microservice on Red Hat OpenShift by following the instructions for the OpenShift web console or the OpenShift Container Platform CLI in this tutorial, specifying codait/max-news-text-generator as the image name.
You can also deploy the model on Kubernetes using the latest docker image on Docker Hub.
On your Kubernetes cluster, run the following commands:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/MAX-News-Text-Generator/master/max-news-text-generator.yaml
The model will be available internally at port 5000, but can also be accessed externally through the NodePort.
A more elaborate tutorial on how to deploy this MAX model to production on IBM Cloud can be found here.
Clone this repository locally. In a terminal, run the following command:
$ git clone https://github.com/IBM/MAX-News-Text-Generator.git
Change directory into the repository base folder:
$ cd MAX-News-Text-Generator
To build the docker image locally, run:
$ docker build -t max-news-text-generator .
All required model assets will be downloaded during the build process. Note that currently this docker image is CPU only (we will add support for GPU images later).
To run the docker image, which automatically starts the model serving API, run:
$ docker run -it -p 5000:5000 max-news-text-generator
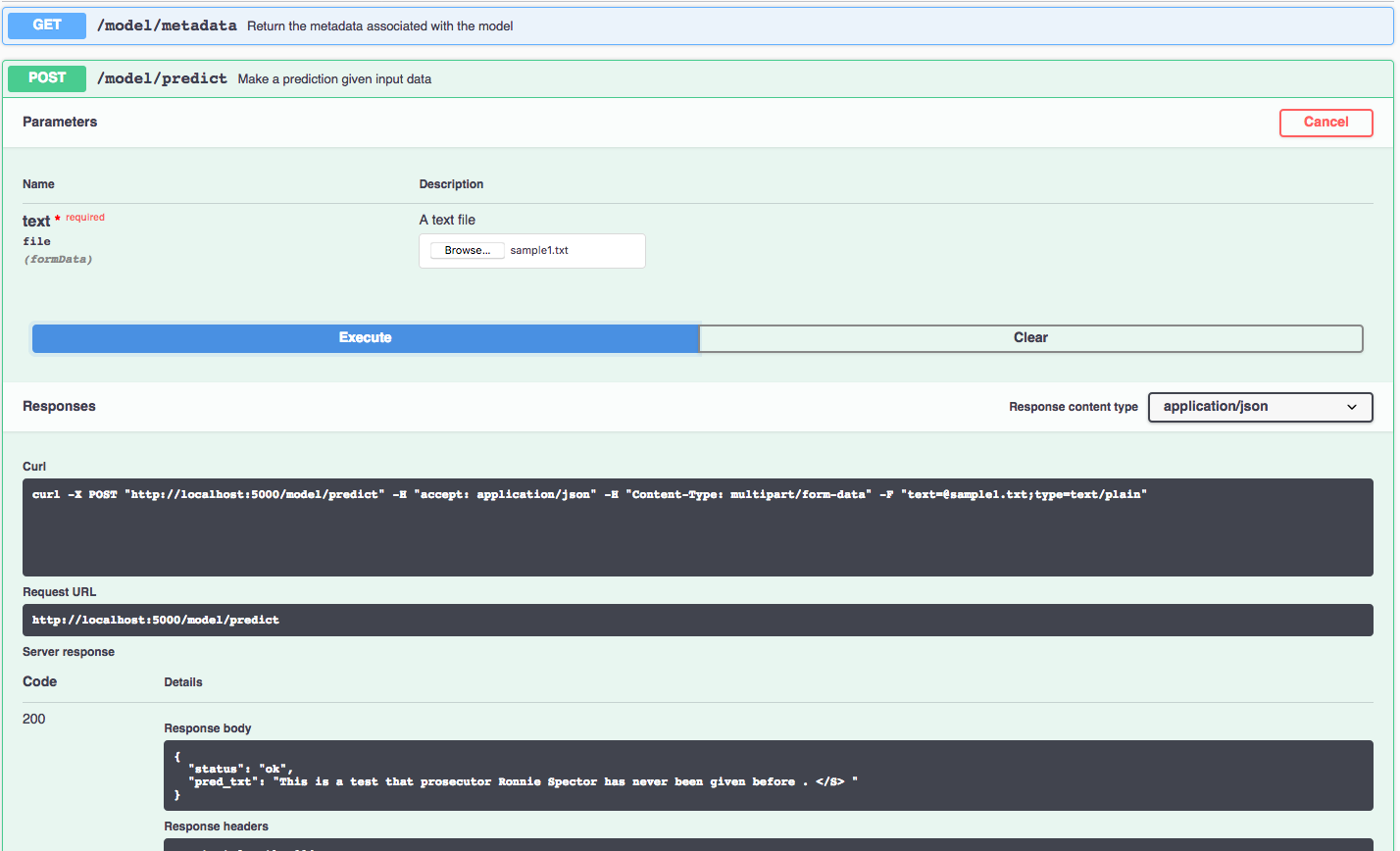
The API server automatically generates an interactive Swagger documentation page. Go to http://localhost:5000 to load
it. From there you can explore the API and also create test requests.
Use the model/predict endpoint to load some seed text (you can use one of the test files from the samples folder)
and get predicted output from the API.
You can also test it on the command line, for example:
$ curl -F "text=@samples/sample1.txt" -XPOST http://localhost:5000/model/predict
You should see a JSON response like that below:
{"status": "ok", "pred_txt": "This is a test rather than an alternative view . </S> "}To run the Flask API app in debug mode, edit config.py to set DEBUG = True under the application settings. You will then need to rebuild the docker image (see step 1).
To stop the docker container type CTRL + C in your terminal.