bot-context
A easy and powerful way to maintain conversational context in chat bots. Using function closures. Blog post
Core Concept
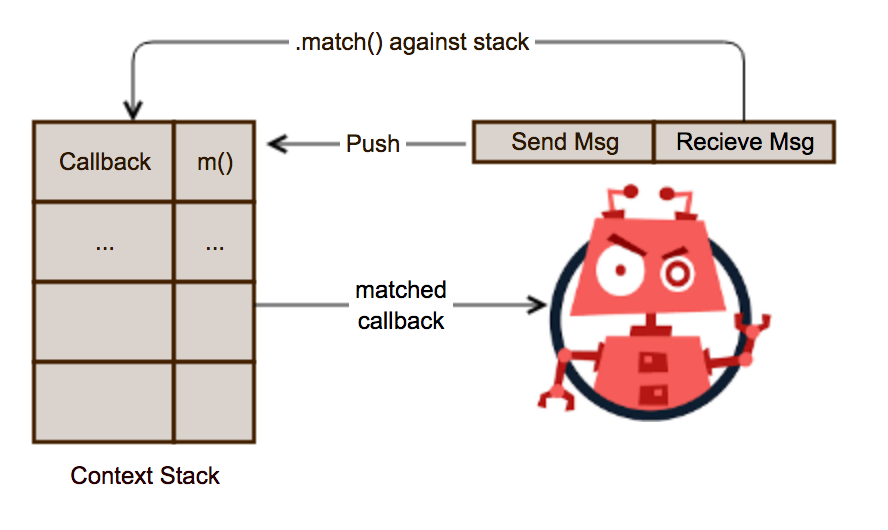
Here we introduce a reactive approach to maintaining the context of conversations.
- Whenever the bot sends a message, set(push) a context(callback) on the stack.
- Whenever the bot recieves a message, match the message in FIFO order to
the items on the stack. And call the callback.
The elegant trick here is that when a callback is pushed on the stack, it captures the closure state of the callback function being pushed.
So when we match the context stack on recieving a message, the closure variables and data are maintained, allowing time travel!
Usage
$ npm i bot-context
This is a very basic pizza delivery bot, to demonstrate the usage of bot-context.
// The message recieving module.
let context = require('bot-context');
function onMessageRecieved(message, userId) {
let ctx = botContext.getOrCreate(userId);
if(!ctx.isSet()) {
init(userId); // initialize the actions.
}
ctx.match(message, function(err, match, contextCb) {
if(!err) contextCb(userId, match);
});
}The set of actions to send the message:
function init(userId) {
let ctx = botContext.getOrCreate(userId);
ctx.set(
/.*/, // The base matcher to match anything.
(match) => getPizzaType(userId));
}
function getPizzaType(userId) {
let ctx = botContext.getOrCreate(userId);
ctx.set(
/(chicken|cheese|veggie)/,
(match) => getDeliveryAddress(userId, match)
);
sendMessage(userId, "What kind of pizza do you want ?");
}
function getDeliveryAddress(userId, pizzaType) {
let address = userDataService.getAddress(userID);
let ctx = botContext.getOrCreate(userId);
if(address) {
ctx.set(/(yes|no)/, (reponse) => {
if(response === 'yes') {
userDataService.clearAddress(userId);
getDeliverAddress(userId, pizzaType);
} else {
end(userId, pizzaType, address);
}
});
sendMessage(userId, 'Would you like to change your address ?');
return;
}
ctx.set(
validateAddressUsingGoogleAPI, // Can use some async API method
(address) => end(userId, pizzaType, address)
); // Note that pizzaType is now a closure variable.
sendMessage(userId, `Please enter the delivery Address.`);
}
function end(userId, pizzaType, address) {
sendMessage(userId, `Thank you, a ${pizzaType} pizza, will be` +
+ `delivered to ${address} in 30 mins.`);
} Now, if a user after putting his address changes his mind to another pizza type, by just typing the type of the pizza.
Webhooks
WYSIWYG bot creators are the latest hot stuff. Almost all of them allow integration with external
tools via http webhooks.
bot-context can easily be used with such bot tools. Please see the example,
on how could you setup bot-context as a webservice.
API
var contextMap = require('bot-context');
returns an instance of the ContextMap, the following methods are available on it.
ContextMap extends Map
A map to hold contexts for all users/keys
getOrCreate(uKey: string): Context
Get Or Creates a context given the key.
Parameters
uKeyunique key to identify a user. string
Returns Context
Context
A context uniqiue for each user. The following methods are available on the context.
set(matchRegex|matcherFn, contextCallback)
Set the current context.
Parameters
matchRegex|matchFn(RegExp | Function) Used to match the inputcontextCallbackCallback which is stored in the stack, it can hold references to closure vars.
matcherFn(inputText, callback)
Matcher method called when matching contexts. It is called with the following params.
Parameters
contextCallback
Context callback set in the context stack.
Returns, is there any context set.
match(inputText: string, contextMatchedCallback)
Match an input text to the collection of currently set contexts.
Parameters
inputTextstring textcontextMatchedCallbackThe callback to be called if matched.
contextMatchedCallback
Callback called when a context is matched, with the following values.
Parameters
err(string | null) Error if anymatchany the match returned from the matchFn or regexcontextCallbackthe callback which was previously set to the context stack.