Logquacious (lq) is a fast and simple log viewer written by Square.
It currently only supports talking to ElasticSearch, however the storage/indexing backend is pluggable. If you are interested in contributing more backends, open a pull request!
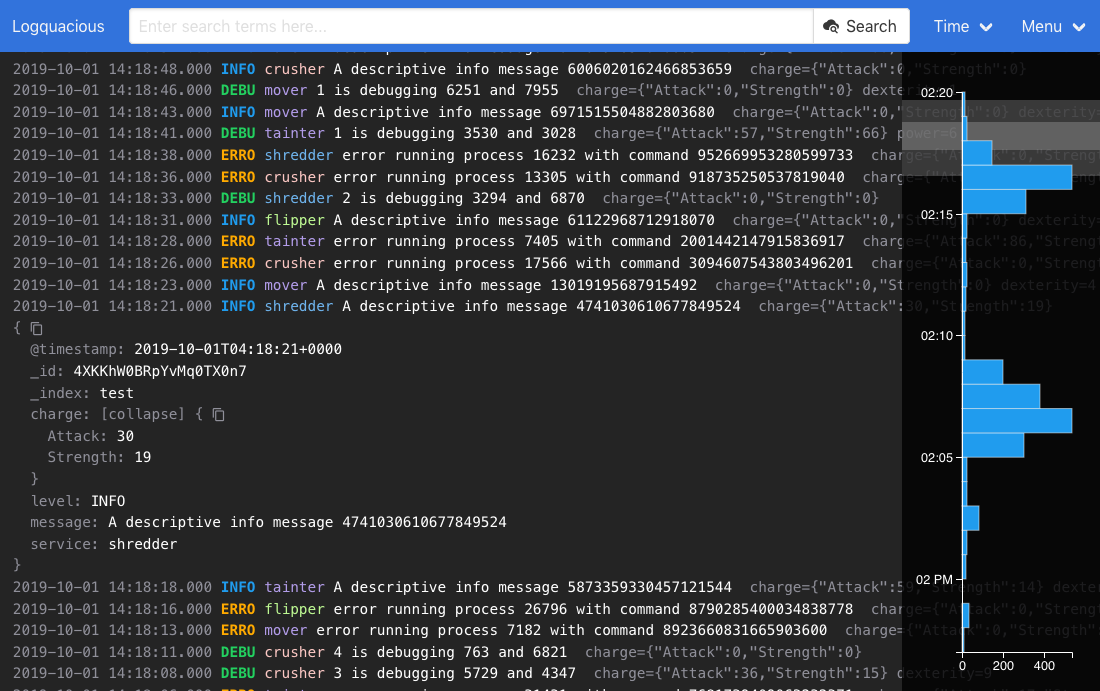
There are more screenshots to see other parts of the UI.
- Fields, filters and data sources are customisable, see config.example.ts.
- Interactive histogram.
- Time picker.
- URLs can be shared.
- Expandable log entries:
- Multiple levels of JSON objects can be expanded.
- Click on a value to add as a filter.
- Can copy the whole JSON payload, or a single value by pressing the copy icon.
- Customise log direction.
- Customise light and dark theme.
- Real time tailing.
- Show log context around an entry.
The local demo runs a basic web server which serves Logquacious. It also runs an instance of ElasticSearch with a script to generate demo log entries.
You'll need docker and docker-compose installed, then run:
cd demo
docker-compose up
Wait a while, then visit http://localhost:2015/ in your browser.
You should be presented with the Logquacious UI and a few logs that are continuously generated in the background.
Coming soon: image to live on Docker Hub.
You will need docker installed.
Build the image:
docker build -f docker/Dockerfile -t logquacious .You can configure the instance via command line arguments or environment variables (e.g. ES_URL):
# docker run logquacious --help
Usage: lq-startup
Flags:
--help Show context-sensitive help.
--es-proxy Use a reverse proxy for ElasticSearch to avoid
needing CORS. (ES_PROXY)
--es-url=STRING ElasticSearch host to send queries to, e.g.:
http://my-es-server:9200/ (ES_URL)
--es-index="*" ElasticSearch index to search in. (ES_INDEX)
--timestamp-field="@timestamp"
The field containing the main timestamp entry.
(TIMESTAMP_FIELD)
--level-field="level" The field containing the log level. (LEVEL_FIELD)
--service-field="service" The field containing the name of the service.
(SERVICE_FIELD)
--message-field="message" The field containing the main message of the log
entry. (MESSAGE_FIELD)
--ignored-fields=_id,_index,...
Do not display these fields in the collapsed log
line. (IGNORED_FIELDS)For example:
- ElasticSearch service is at
192.168.0.1 - The ElasticSearch indexes start with
logs- - The message field is
text - You want the host to listen on port
8080(internally it's always port2015).
docker run -p 0.0.0.0:8080:2015 logquacious \
--es-url="http://192.168.0.1:9200" \
--es-index="logs-*" \
--message-field="text"
2019/10/01 05:28:07 Variables for this docker image looks like this:
{ESProxy:true ESURL:http://192.168.0.1:9200 ESIndex:logs-* TimestampField:@timestamp LevelField:level ServiceField:service MessageField:text IgnoredFields:[_id _index] IgnoredFieldsJoined:}
2019/10/01 05:28:07 Successfully generated/lq/Caddyfile
2019/10/01 05:28:07 Successfully generated/lq/config.json
2019/10/01 05:28:07 Running caddy...
Activating privacy features... done.
Serving HTTP on port 2015
http://:2015http://localhost:8080/ should work in this example.
- Install Node.js
git clone https://github.com/square/logquacious
cd logquacious
npm install
npm run buildnpm run buildwill generate adistdirectory containing all the files needed for a web server, including anindex.htmlfile.
Configure Logquacious in config.ts.
Setting up a web server if you don't already have one:
- Install Caddy:
curl https://getcaddy.com | bash -s personal - Create a
Caddyfileto listen on port 2015 with http, also to talk to your ElasticSearch server:
:2015
proxy /es my-elastic-search-hostname:9200 {
without /es
}
- Run
caddyin the same directory as theCaddyfile - Point your browser at
http://localhost:2015/. The ElasticSearch endpoint should be working athttp://localhost:2015/es/.
The development workflow is very similar to the "From Source" set up above. You can run a self reloading development server instead of npm run build.
You can either set up CORS on ElasticSearch or reverse proxy both the hot server and ElasticSearch. To do this, create Caddyfile in the root of the project:
:2015
# Redirect all /es requests to the ElasticSearch server
proxy /es my-elastic-search-hostname:9200 {
without /es
}
# Redirect all other requests to parcel's development server.
proxy / localhost:1234
To run the parcel development server:
npm run hot
Run caddy. You should be able to hit http://localhost:2015/ and when you make any code changes the page should refresh.
There are tests which are executed with npm test.
The top level structure of the json configuration is as follows:
{
"dataSources": [],
"fields": {
"name-of-field-configuration": [],
},
"filters": []
}Contains the URL, index, etc for querying ElasticSearch. An example:
"dataSources": [
{
"id": "elasticsearch-server",
"type": "elasticsearch",
"index": "{{.ESIndex}}",
"urlPrefix": "{{if .ESProxy}}/es{{else}}{{.ESURL}}{{end}}",
"fields": "main"
}
]id is a reference that can be used to create a data source filter. (See below). If you only have one data source, you don't need to create a data source filter.
type must be elasticsearch until more data sources are implemented.
index is the ElasticSearch index to search in. You can use an asterisk as a wildcard. This corresponds to the URL in a query request, e.g. http://es:9200/index/_search
urlPrefix is the URL to connect to your ElasticSearch server, without a trailing slash. This will resolve to urlPrefix/index/_search.
fields is a reference to the key of the fields in the top level of the json configuration.
Configures how log entries are shown in the UI. You're able to transform, add classes, ignore fields, etc.
Here is an example:
"fields": {
"main": {
"collapsedFormatting": [
{
"field": "@timestamp",
"transforms": [
"timestamp"
]
},
{
"field": "message",
"transforms": [
{
"addClass": "strong"
}
]
}
],
"collapsedIgnore": ["_id", "_index"]
}
}This configuration will do the following:
- It is called
mainwhich is thefieldsreference used indataSources. - Place the
@timestampfield at the start of each line and format it. - Place the
messagefield afterwards and make it stand out. - All other fields in the log entry will be shown afterwards in the default grey colour, except
_idand_index.
If you want to see an example of many transforms check out the example config.
There is a menu drop down that is enabled when you use filters. It is between the search button and the time drop down.
You are able to customise it to have values you can filter on, e.g.:
"filters": [
{
"id": "region",
"urlKey": "r",
"title": "Region",
"default": "ap-southeast-2",
"type": "singleValue",
"items": [
{
"title": "All Regions",
"id": null
},
{
"title": "Sydney",
"id": "ap-southeast-2"
},
{
"title": "London",
"id": "eu-west-2"
}
]
}
]This singleValue filter allows you filter log entries based on region equalling ap-southeast-2 for example. This is identical to searching for region:ap-southeast-2 in the search field.
The urlKey is what is used in the URL for this filter. For example the URL might look like: http://localhost:2015/?q=my+search&r=ap-southeast-2
title is shown as the the name of the field/value in the search drop down menu.
The null value signifies that the filter was not selected, so it does not filter on that key in that case.
Another type of filter is a dataSource filter for when you have multiple ElasticSearch instances.
The id of each item must point to the id of a data source.
You can see an example of this in the example config under the env filter.
If you want to be able to communicate to ElasticSearch on a different host and port to Logquacious, you will need to configure ElasticSearch to respond with the correct CORS headers.
For example, you are running https://lq.mycompany.com/ which serves the static content. You will need to set these configuration options in ElasticSearch:
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "https://lq.mycompany.com/"
See the ElasticSearch documentation on the http configuration options for more information.