This will work with GitHub codespaces (either in browser or via your local VSCode - requires a VSCode extension).
This uses the sample Python devcontainer as inspiration. Lots more sample environments here.
Also interesting (but untested) is https://github.com/loft-sh/devpod which promises to read this file but spin up on local machines / any cloud.
Don't forget to delete your codespace after use, see below!
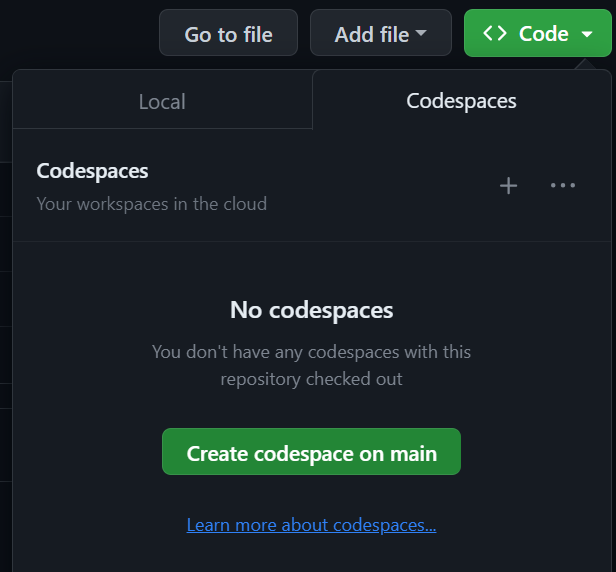
To launch a new codespace, click the Code button, change to the Codespaces tab and click Create codespace on main.
The random, two word name for the codespace will be generated. In this case "probable winner".
The codespace will begin creation in a new browser window. Wait until the codespace is running.
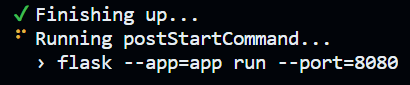
You should see this command in the terminal. Leave it running.
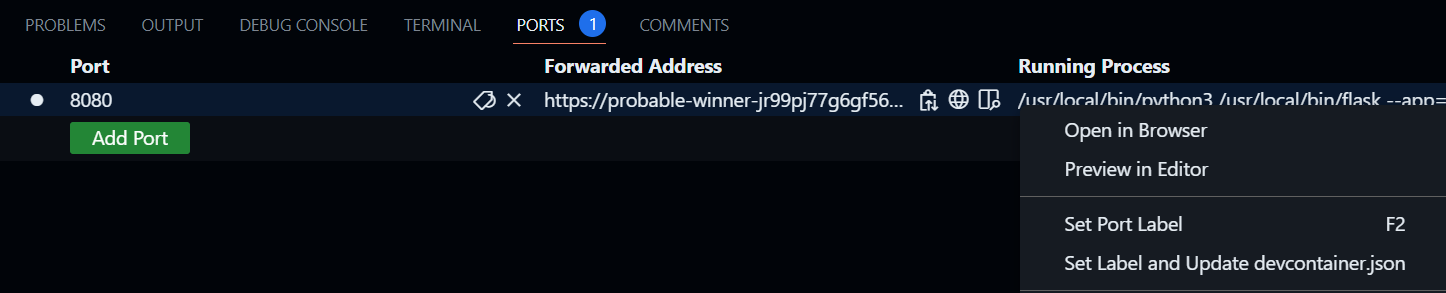
Toggle over to the Ports tab and right click the row for port 8080.
Choose Open in browser
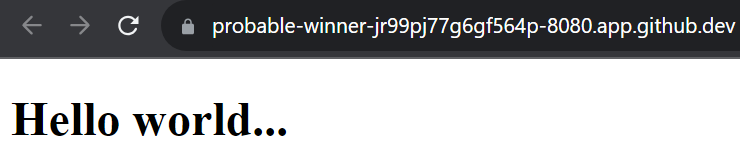
The demo application should be displayed.
The codespace template is found in .devcontainer/devcontainer.json.
In this example, a custom container is built from the Dockerfile (but you can also reference an existing image).
After the container is built and running, the postStartCommand (see .devcontainer/devcontainer.json) is used to run a flask web application server automatically for you.
The forwardPorts directive in .devcontainer/devcontainer.json is used to privately (only to your GitHub user) expose port 8080 and make the application available.
Go to https://github.com/codespaces and delete your codespace to avoid unneccessary charges!