This is the repository corresponding to a master thesis developed by Adrian Garcia Espinosa. This master thesis was developed in at the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne having as advisors; Arsany Guirguis, Prof. Rachid Guerraoui and Álvaro Carrera Barroso.
- In-Network computing
- Distributed Machine Learning
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Vagrant: enables the configuration and management of Virtual Machines. Vagrant was used to manage a VM that contains the needed dependencies for deploying and testing the implementation [41].
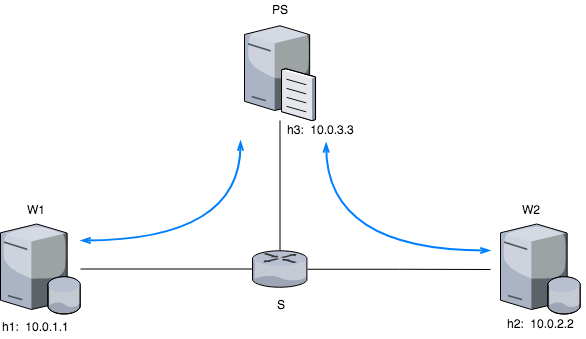
- Mininet: as it has been detailed on the background section (2), mininet was used to deploy the different setups with the corresponding topologies.
- P4: also been detailed on the background section (2). P4 us a domain specific language, very limited and used for programming on programmable switches.
- Python: it is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. All the workers and parameter server logic has been developed with python. Not only the communication logic but also the ML modules.
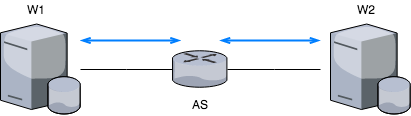
In order to be able to compare the performance and functioning of the system, two deployments will be tested trying to use in both the closest environment setup possible: