- Installing TAP on Docker Desktop requires sufficient resources in CPU and memory. These installation scripts have been tested on Docker resources with 8 cpus and 16 GB of RAM.
- Installation process may be slow on Docker Desktop due to limited resources and enough time must be given to complete the installation( sometimes 10 minutes or more ). Have noticed that if there are too many applications running along with Docker then the installation is very, very slow and times out
- The container registry used for installation on Docker Desktop is Harbor.
In order to complete the installation, please ensure you have:
- Account created in Tanzu Network. Information on creating a Tanzu Network account can be found here
pivnetCLI API Token for login. Information on generating apivnettoken for login can be found here
For Docker Desktop:
- Docker Desktop installed in your local workstation. Scripts were tested on Docker Desktop v4.5.0 with Docker Engine v20.10.12
- Kubernetes enabled in Docker Desktop ( Kubernetes version v1.22.5 ).
- Harbor container registry account. Can request for a corporate harbor account on the Self Service Portal. Requires VMware VPN connection
- Create Robot Account for Harbor container registry
For GCP:
- Google Cloud Account
gcloudCLI installed and configured with project/region Refer to instructions here- Create a service account in Google Cloud IAM with permission for GKE clusters, compute instance,Container registry(admin privileges for these resources). Create a key file for this service account and download it to the local system.
- The script creates a jump host on GCP, from where the installation is done on the GKE cluster
-
Create an environment configuration file with the name
.envat the root of the project folder using the template fileenv.sample.$ cp .env.sample .env
-
Edit the configuration file and provide all required values. Description of each variable is provided below:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| K8_CLUSTER | Target K8 Cluster where TAP will be installed. Must be either docker-desktop or gke |
| PIVNET_API_TOKEN | API token to access the Tanzu Network account. Refer to pre-requisite section above on how to generate an API token |
| TANZUNET_REGISTRY | Static text - registry.tanzu.vmware.com |
| TANZUNET_USERNAME | User name to access Tanzu Network. Refer to pre-requisite section above on how to create a Tanzu Net account |
| TANZUNET_PASSWORD | Password to access Tanzu Network |
| CONTAINER_REGISTRY_HOSTNAME | Container registry to host the Tanzu Build Service dependencies, supply chain artefacts and workload images . Must have write access and space of 10GB. |
| CONTAINER_REGISTRY_USERNAME | Username for the CONTAINER_REGISTRY_HOSTNAME container repository provided above. Note if you are using robot account for Harbor repository, it should be enclosed in single quotes to avoid unnecessary command substitution. For e.g. CONTAINER_REGISTRY_USERNAME='robot$demo+admin'. For Google cloud this is always _json_key |
| CONTAINER_REGISTRY_PASSWORD | Password for the CONTAINER_REGISTRY_HOSTNAME container repository provided above. For GKE this is the path to the Google Cloud JSON credentials file |
| CONTAINER_REPOSITORY | Name of the repository in the CONTAINER_REGISTRY_HOSTNAME. For Harbor and Google Cloud, this is the project name |
| CATALOG_GUI_GIT_URL | Path to the catalog-info.yaml catalog definition file. For e.g. If the catalog is hosted on Github, then the path will be the full URL of the catalog-info.yaml file as https://github.com/<git_user>/<git_repo>/blob/main/catalog-info.yaml |
| INGRESS_DOMAIN | Subdomain of your choice that is the value of the same name passed to the tap-gui package. via the tap-values.yaml. To simplify DNS for our local(Docker Desktop) installation , we set our ingress-domain to 127-0-0-1.nip.io. This will automatically route requests to localhost and does not require any entries to be made to /etc/hosts file |
| DEVELOPER_NAMESPACE | Kubernetes namespace which holds all resources for workload per developer |
| DEFAULT_WORKLOAD_NAME | Default workload name used if not specified when creating workloads on TAP. Default value sample-app |
| GCP_REGION | Google Cloud Region where all GCP resources (GKE,Jump Host) are created |
| GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME | Google IAM Service account with privileges for GKE, Compute, Container Registry. The key file associated with this account must be provided in CONTAINER_REGISTRY_PASSWORD |
-
To be run on GCP only: Setup the Google Cloud environment by creating the GKE cluster and jump host.
./install/configure-tap-gcp-env.sh
This will create the GKE cluster with the name
tap-clusterand a jump host with the nametap-jump. copy over the service account json key to the jump host and then supply it as a path value in the environment file for CONTAINER_REGISTRY_PASSWORD As part of this script, the project files are also copied over to the jump host, from where the scripts can be run directly from the jump host. -
To be run on GCP only: SSH into the GCP jump host by using
gcloud compute ssh tap-jump
Navigate to the root of the project after logging into the jump host and run all the commands below from the jump host
-
Run the following command from the root of the project folder to configure the install environment
./install/00-install-tools.sh
This script will download the
piventCLI if not installed previously and login using thePIVNET_API_TOKENprovided in the environment configuration file. It will also downloadjq,curlandkubectlA sample output is shown below where thepivnetCLI has been succesfully authenticated with the provided tanzu net credentialsLogged-in successfully
-
Run the following command from the root of the project folder to install Tanzu Cluster Essentials
sudo ./install/01-install-tanzu-cluster-essentials.sh
A sample output is shown below where the Tanzu Cluster Essentials is successfully deployed.
3:35:50PM: ^ Waiting for generation 2 to be observed 3:35:50PM: L ok: waiting on replicaset/secretgen-controller-545c98d48 (apps/v1) namespace: secretgen-controller 3:35:50PM: L ongoing: waiting on pod/secretgen-controller-545c98d48-tj2lx (v1) namespace: secretgen-controller 3:35:50PM: ^ Pending: ContainerCreating 3:35:51PM: ok: reconcile deployment/secretgen-controller (apps/v1) namespace: secretgen-controller 3:35:51PM: ---- applying complete [12/12 done] ---- 3:35:51PM: ---- waiting complete [12/12 done] ---- Succeeded
-
Run the following command from the root of the project folder to install Tanzu CLI
sudo ./install/02-install-tanzu-cli.sh
A sample output is shown below which lists the Tanzu CLI plugins are installed on the platform
✔ successfully installed 'all' plugin NAME DESCRIPTION SCOPE DISCOVERY VERSION STATUS login Login to the platform Standalone default v0.11.1 not installed management-cluster Kubernetes management-cluster operations Standalone default v0.11.1 not installed package Tanzu package management Standalone default v0.11.1 installed pinniped-auth Pinniped authentication operations (usually not directly invoked) Standalone default v0.11.1 not installed secret Tanzu secret management Standalone default v0.11.1 installed services Discover Service Types and manage Service Instances (ALPHA) Standalone v0.1.1 installed accelerator Manage accelerators in a Kubernetes cluster Standalone v1.0.1 installed apps Applications on Kubernetes Standalone v0.4.1 installed
-
Configure Tanzu Repository
./install/03-configure-tap-repository.sh
A sample output is shown below where the Tanzu repository is reconciled successfully.
Added package repository 'tanzu-tap-repository' in namespace 'tap-install' \ Retrieving repository tanzu-tap-repository... NAME: tanzu-tap-repository VERSION: 1747145 REPOSITORY: registry.tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu-application-platform/tap-packages TAG: 1.0.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded REASON:
-
Install TAP
./install/04-install-tap.sh
Note: This may take some time to complete the installation. You will continue to see a message as below when the reconciliation is in progress
/ Waiting for 'PackageInstall' reconciliation for 'tap' | 'PackageInstall' resource install status: ReconcilingIf the TAP installation script has failed reconciliation you can see the error message as below
/ Waiting for 'PackageInstall' reconciliation for 'tap' / 'PackageInstall' resource install status: Reconciling Please consider using 'tanzu package installed update' to update the installed package with correct settings Error: timed out waiting for the condition Error: exit status 1 ✖ exit status 1The reconciliation process continues in the background without any user interaction. You could verify the status of the package reconciliation as described in the next step.
-
Verify TAP installation
./install/05-verify-tap-install.sh
A sample output is shown below where some of the TAP packages have failed reconciliation
NAME PACKAGE-NAME PACKAGE-VERSION STATUS accelerator accelerator.apps.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.1 Reconcile succeeded appliveview run.appliveview.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.2-build.2 Reconcile succeeded appliveview-conventions build.appliveview.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.2-build.2 Reconcile failed: Error (see .status.usefulErrorMessage for details) buildservice buildservice.tanzu.vmware.com 1.4.2 Reconcile succeeded cartographer cartographer.tanzu.vmware.com 0.2.1 Reconcile succeeded cert-manager cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+tap.1 Reconcile succeeded cnrs cnrs.tanzu.vmware.com 1.1.0 Reconcile failed: Error (see .status.usefulErrorMessage for details)You can further look at the error message for each package failure by running the below command and providing the package name which has failed reconciliation as an argument
./install/05-verify-tap-install.sh cnrs
The below sample shows the installation details for the package
cnrs| Retrieving installation details for cnrs... NAME: cnrs PACKAGE-NAME: cnrs.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 1.1.0 STATUS: Reconcile failed: Error (see .status.usefulErrorMessage for details) CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileFailed True Error (see .status.usefulErrorMessage for details)}] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE: kapp: Error: waiting on reconcile deployment/imc-dispatcher (apps/v1) namespace: knative-eventing: Finished unsuccessfully (Deployment is not progressing: ProgressDeadlineExceeded (message: ReplicaSet "imc-dispatcher-5987767d76" has timed out progressing.))The package reconciliation failure could be because of client-side throttling of Kubernetes. You can continue to wait until all packages have been reconciled successfully
A sample output is shown below where the TAP packages have been reconciled successfully.
| Retrieving installed packages... NAME PACKAGE-NAME PACKAGE-VERSION STATUS accelerator accelerator.apps.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.1 Reconcile succeeded appliveview run.appliveview.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.2-build.2 Reconcile succeeded appliveview-conventions build.appliveview.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.2-build.2 Reconcile succeeded buildservice buildservice.tanzu.vmware.com 1.4.2 Reconcile succeeded cartographer cartographer.tanzu.vmware.com 0.2.1 Reconcile succeeded cert-manager cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+tap.1 Reconcile succeeded cnrs cnrs.tanzu.vmware.com 1.1.0 Reconcile succeeded contour contour.tanzu.vmware.com 1.18.2+tap.1 Reconcile succeeded conventions-controller controller.conventions.apps.tanzu.vmware.com 0.5.0 Reconcile succeeded developer-conventions developer-conventions.tanzu.vmware.com 0.5.0 Reconcile succeeded fluxcd-source-controller fluxcd.source.controller.tanzu.vmware.com 0.16.1 Reconcile succeeded ootb-delivery-basic ootb-delivery-basic.tanzu.vmware.com 0.6.1 Reconcile succeeded ootb-supply-chain-basic ootb-supply-chain-basic.tanzu.vmware.com 0.6.1 Reconcile succeeded ootb-templates ootb-templates.tanzu.vmware.com 0.6.1 Reconcile succeeded service-bindings service-bindings.labs.vmware.com 0.6.0 Reconcile succeeded services-toolkit services-toolkit.tanzu.vmware.com 0.5.0 Reconcile succeeded source-controller controller.source.apps.tanzu.vmware.com 0.2.0 Reconcile succeeded spring-boot-conventions spring-boot-conventions.tanzu.vmware.com 0.3.0 Reconcile succeeded tap tap.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.1 Reconcile succeeded tap-gui tap-gui.tanzu.vmware.com 1.0.2 Reconcile succeeded tap-telemetry tap-telemetry.tanzu.vmware.com 0.1.3 Reconcile succeeded tekton-pipelines tekton.tanzu.vmware.com 0.30.0 Reconcile succeededAfter all packages have been reconciled succesfully, you can deploy workloads using TAP. Refer to the workload documentation in this project
-
In case you need to manually start reconciliation of a package that has failed:
./install/06-manual-tap-reconciliation.sh
-
In case of any changes to the
tap-values.yaml, you can re-apply the configuration by using:./install/07-update-tap-install.sh
- Setup Developer workspace
./workloads/01-setup-dev-namespace.shThis script will create a separate namespace for the developer to run workloads using the name DEVELOPER_NAMESPACE defined in the environment configuration. It also configures the RBAC, secrets to deploy workloads
A sample partial output is shown below where the Developer namespace and RBAC is created successfully.
secret/tap-registry created
serviceaccount/default configured
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/default created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/default created
-
Create workload
./workloads/02-workload-create.sh sample-app
Note: The argument provided above to the script is the name of the workload.
The following output is generated which also contains the workload yaml.
+ tanzu apps workload create sample-app --git-repo https://github.com/sample-accelerators/tanzu-java-web-app --git-branch main --type web --label app.kubernetes.io/part-of=sample-app --namespace dev1 --yes Create workload: 1 + |--- 2 + |apiVersion: carto.run/v1alpha1 3 + |kind: Workload 4 + |metadata: 5 + | labels: 6 + | app.kubernetes.io/part-of: sample-app 7 + | apps.tanzu.vmware.com/workload-type: web 8 + | name: sample-app 9 + | namespace: dev1 10 + |spec: 11 + | source: 12 + | git: 13 + | ref: 14 + | branch: main 15 + | url: https://github.com/sample-accelerators/tanzu-java-web-app Created workload "sample-app"
This should take a very long time on Docker Desktop due to limited resource capacity (sometimes over 10 mins)
-
Tail the logs generated by the workload
./workloads/03-workload-tail.sh sample-app
Note: The argument provided below to the script is the name of the workload that is used in the above step.
The output from the command will display all the current tasks that are being run as part of the supply chain
-
Check the status of the workload
./workloads/04-workload-status.sh sample-app
lastTransitionTime: "2022-02-23T05:07:26Z" message: "" reason: Ready status: "True" type: Ready Workload pods NAME STATUS RESTARTS AGE sample-app-build-1-build-pod Succeeded 0 13m sample-app-config-writer-px56g-pod Succeeded 0 6m48s Workload Knative Services NAME READY URL sample-app Ready http://sample-app.dev1.tap.ahmedmq.co.inNotice the status of the
sample-appis 'Ready' and the URL of the workload which is formed of the DEFAULT_WORKLOAD_NAME, DEVELOPER_NAMESPACE and INGRESS_DOMAIN defined in the configuration file
-
Configure DNS to route traffic to the envoy load balancer. This needs to be done for GCP only, for Docker-desktop we have configured the
127-0-0-1.nip.iodomainObtain the external IP of the envoy load balancer
kubectl get service envoy -n tanzu-system-ingressNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE envoy LoadBalancer 10.24.5.113 34.100.181.55 80:31593/TCP,443:31440/TCP 46m -
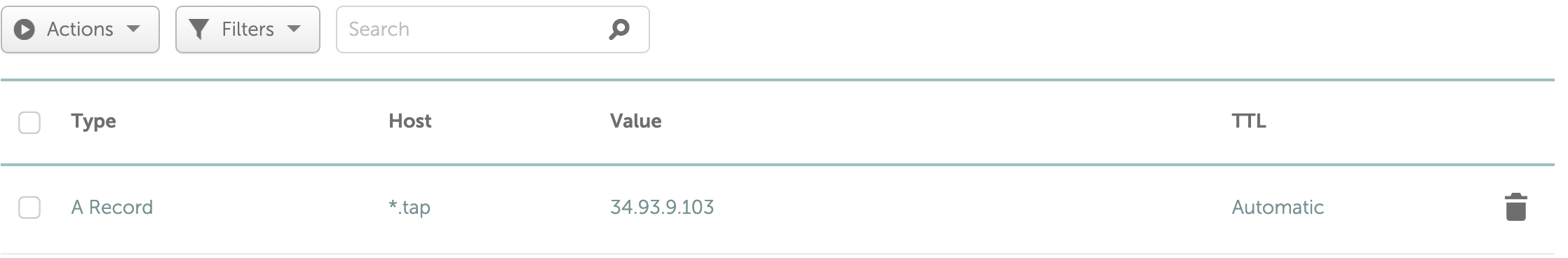
Create a wildcard DNS record for the domain you have provided in the environment configuration(INGRESS_DOMAIN). A sample is shown below
-
Run command to
curlto the workload url and check the response./workloads/05-workload-test.sh sample-app
Below is a sample output from the
curlcommand to the workload url, which executes every 2 seconds.Greetings from Spring Boot + Tanzu! Greetings from Spring Boot + Tanzu! Greetings from Spring Boot + Tanzu! Greetings from Spring Boot + Tanzu! Greetings from Spring Boot + Tanzu!The URL of the workload can be been seen in the output of the workload status command in the previous step. Alternatively, you can open the browser and enter the URL to access the workload
-
After completing the above steps, you can clean up by deleting the workload
./workloads/06-workload-delete.sh
A sample output below shows the workload is successfully deleted
+ tanzu apps workload delete sample-app --namespace dev1 --yes Deleted workload "sample-app"The namespace and workload name in the above output is picked up from DEVELOPER_NAMESPACE and DEFAULT_WORKLOAD_NAME defined in the environment configuration file
-
Finally, we can clean up the whole TAP installation by running the following command. Note, alternatively the quicker way is deleting the cluster or resetting Kubernetes in Docker desktop and then executing this step.
sudo ./install/08-uninstall-all.sh
This will take a long time to complete, during which it will remove all the TAP packages, repositories Tanzu Cluster Essentials, CLI and any temporary directories.
-
Delete the jump host . Export the GCP_REGION variable
GCP_REGION=<<<value>>> CLUSTER_ZONE="$GCP_REGION-a" gcloud compute instances delete tap-jump -q --zone="$CLUSTER_ZONE"