- OOP and Design Patterns Course Assignment
- /PaintApp: Github Respository Link
Team Members:
| Name | ID |
|---|---|
| Ahmed Youssef Sobhy Elgoerany | 21010217 |
| Ahmed Mustafa Elmorsy Amer | 21010189 |
| Ali Hassan Ali Mohamed | 21010837 |
| Moustafa Esam El-Sayed Amer | 21011364 |
The Paint Application is a feature-rich drawing and painting tool designed for creative expression and design. Developed with VueJS for the frontend and Spring Boot for the backend, the application leverages RESTful APIs to facilitate communication between the two layers.
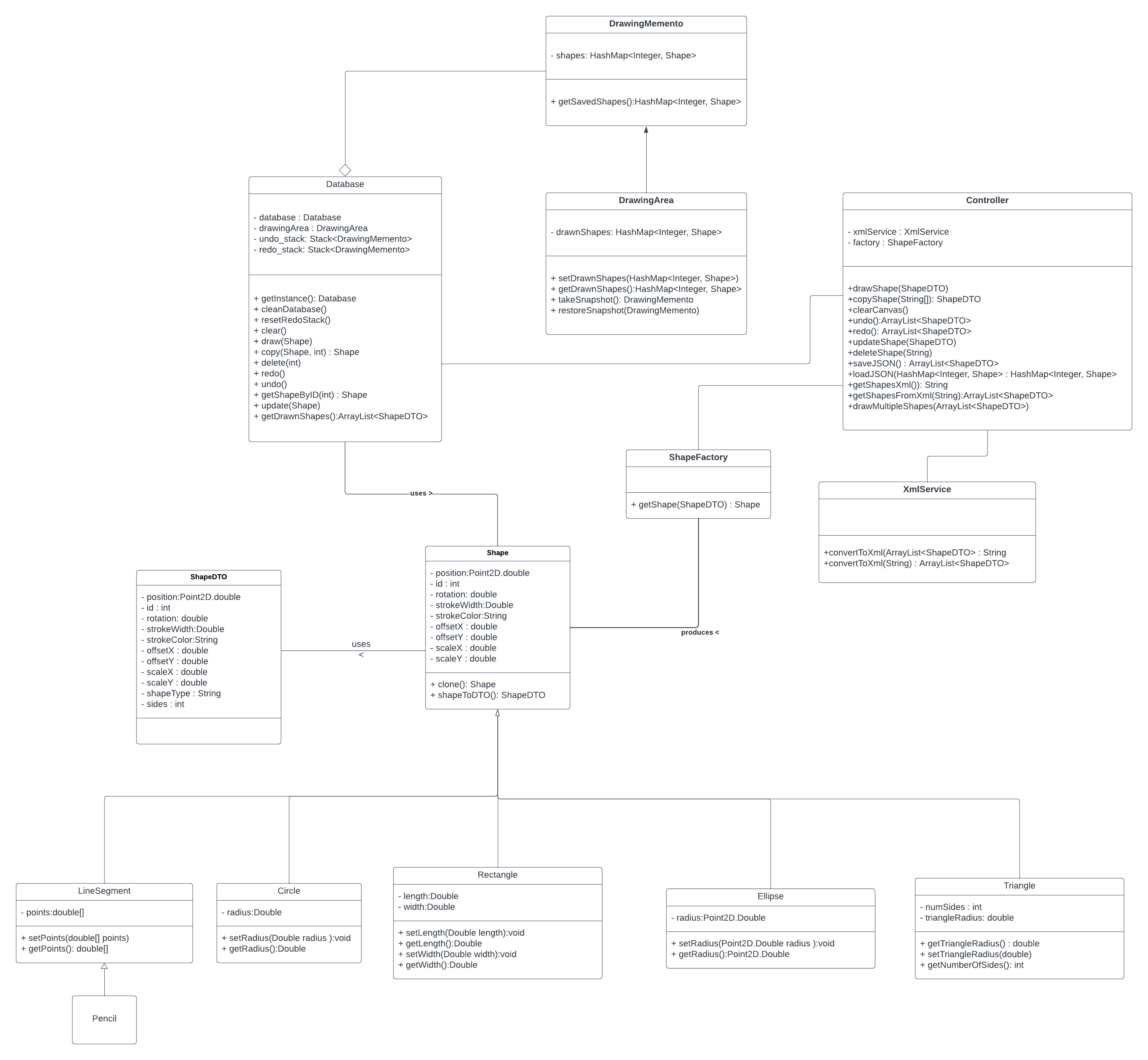
The object-oriented model encapsulates various geometric shapes, fostering a hierarchy that includes Line Segment, Circle, Ellipse, Triangle, Rectangle, and Square. The model's robustness is underpinned by the effective application of inheritance and polymorphism.
The UML class diagram visually represents the structure of the object-oriented model, meticulously detailing the classes, attributes, and methods. Inheritance relationships and polymorphism are prominently featured, showcasing the elegance of the design.
The GUI of the application boasts an extensive array of functionalities for users:
Main Features
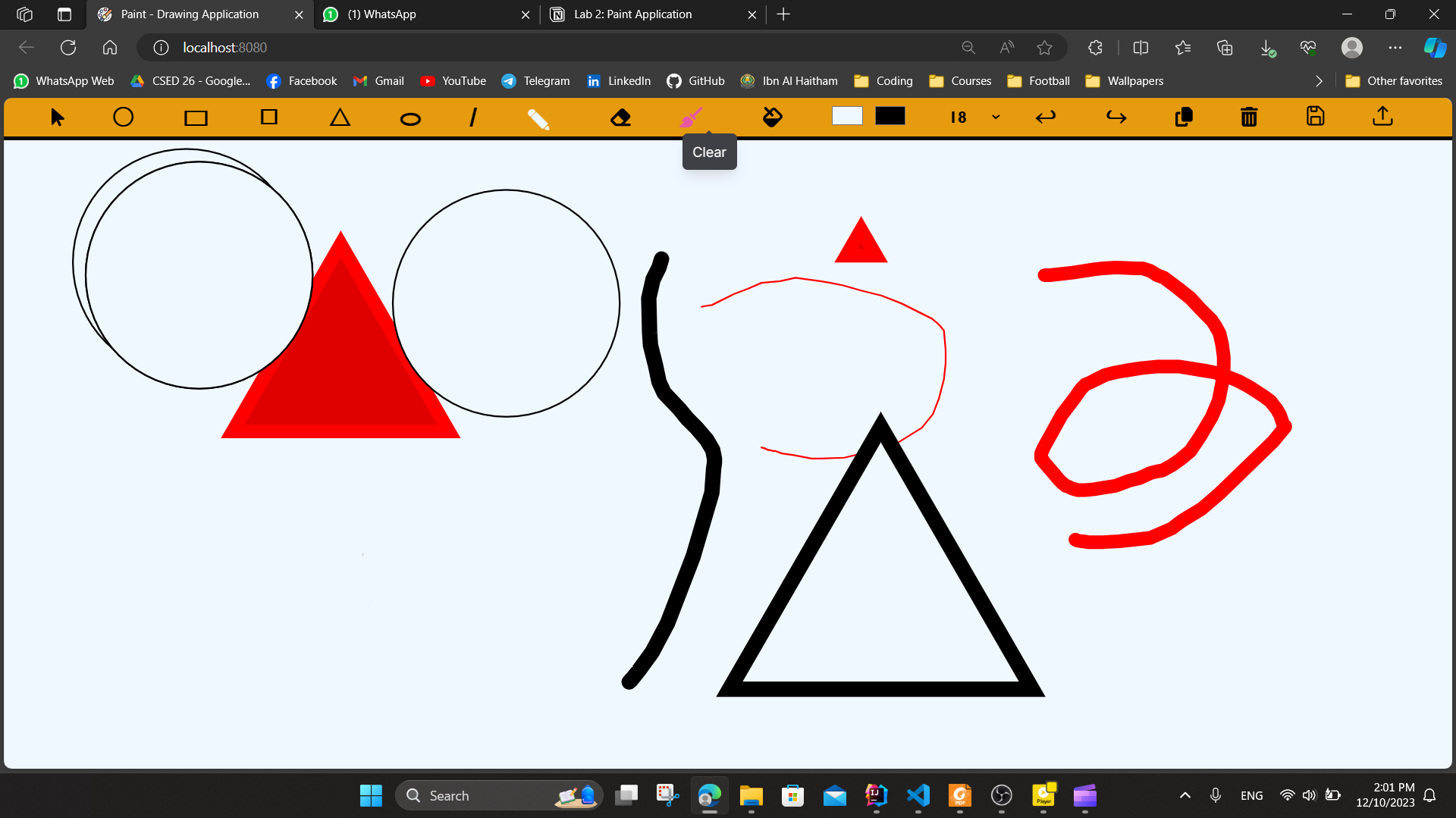
- Drawing Shapes: For example, Triangle, Square, Rectangle, Line Segment, Ellipse, and Circle (by mouse dragging).
- Resizing and rotation of the selected object.
- Select: Selecting the element gives you the ability to resize, move, copy, or delete the shape.
- Move: Moving the selected object without the need to click on the select button.
- Delete: Delete the selected object without the need to click on the select button.
- Copy: Copy the selected object without the need to click on the select button.
- Colour Picker for Fill and Stroke: Colorizing the shapes while drawing.
- Undo: The user can undo their last actions as many times as they want.
- Redo: The user can redo as many times as they want.
- Save options: Save as JSON and XML files. This also saves your drawing history, meaning that after you load the saved file, you can undo as many times as you want.
- Load options: Load previously saved JSON and XML drawing files.
Extra Features
- Free-hand drawing: Drawing with a pencil in a freeform way with the desired size of the pencil.
- Eraser: Erasing in a freeform way with the desired size of the eraser.
- Auto-save: Your unsaved work won’t be lost as long as the backend server is up and running. You can refresh as many times as you want.
- Hovering on shapes changes their color and adds a shadow to focus on them, helping people concentrate on the shape. It also assists color-blind people.
- Multiple stroke widths options to select while drawing.
- Clear the canvas: This action clears the drawing area. It can also be undone if done by mistake.
- Fill the shape: An option to fill the selected (previously drawn) shape with the desired color from the color picker.
- There is an endpoint
/cleanthat can be accessed to clean the database (mostly for developers). - Keyboard Functionality: CTRL+Z to undo & CTRL+Y to redo.
The GUI is designed with a focus on user-friendliness. Functionality is easily accessible through the interface, providing a seamless user experience.
- Shape Factory Design Pattern
- The Shape Factory Design Pattern dynamically generates various geometric shapes, offering a flexible and extensible approach to shape creation.
- Prototype Design Pattern
- Efficient copying of shapes is achieved through the application of the Prototype Design Pattern, simplifying the creation of new shapes based on existing ones.
- Memento Design Pattern
- The Memento Design Pattern manages the undo and redo functionality, capturing and storing snapshots of the canvas state in stacks for easy restoration.
- Singleton Design Pattern
- The Singleton Design Pattern ensures a single, centralized database instance, managing the current drawn shapes, undo stack, and redo stack. This design choice optimizes resource utilization and prevents unnecessary duplication.
- RESTful API Endpoints:
/draw(POST): Accepts a JSON request containing shape data, creates a new shape using a factory, and stores it in the database./copy(POST): Accepts an array of strings containing shape IDs for copying, retrieves the specified shape from the database, clones it, and stores the copy in the database./clear(GET): Clears the entire canvas by removing all shapes from the database and putting an empty snapshot in the undo stack./undo(POST): Undoes the last action by reverting the state of the database to the previous state./redo(POST): Redoes the last undone action by reverting the state of the database to the next state./update(POST): Accepts shape data, creates a new shape using a factory, and updates the corresponding shape in the database./delete(POST): Accepts the ID of a shape to be deleted and removes it from the database./saveJSON(POST): Retrieves all shapes from the database and returns their data in JSON format./saveXML(GET): Retrieves all shapes from the database and returns their data in XML format./loadXML(POST): Accepts XML data, cleans the database, parses the XML to obtain shape data, and draws the shapes on the canvas.**/loadJSON(POST)**: Accepts JSON data, cleans the database, parses the JSON to obtain shape data, and draws the shapes on the canvas./clean(GET): Cleans the database by removing all shapes from the database.
- Shape Management:
- Shapes are represented using a
Shapeclass, and their data is transferred between the client and server usingShapeDTO(Data Transfer Object). - Shapes are created and manipulated using a
ShapeFactoryclass. - The
Databaseclass is responsible for storing and managing the drawn shapes.
- Shapes are represented using a
- XML Serialization and Deserialization:
- The
XmlServiceclass is used to convert a list of shape DTOs to XML format (getShapesXml) and vice versa (getShapesFromXml).- Service Annotation:
- The
@Serviceannotation indicates that this class is a service component and is eligible for Spring's auto-detection and wiring.
- The
- XML Conversion Methods:
convertToXmlMethod:- Takes an
ArrayList<ShapeDTO>as input. - Uses the
XmlMapperfrom the Jackson library to convert the list ofShapeDTOobjects to an XML string. - Throws
JsonProcessingExceptionif an error occurs during the XML conversion.
- Takes an
convertXmlToShapesMethod:- Takes an XML string as input.
- Uses the
XmlMapperto convert the XML string back into anArrayList<ShapeDTO>using theTypeReferenceclass. - Throws
IOExceptionif an error occurs during the XML deserialization.
- Service Annotation:
- The
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS):
- CORS is enabled to allow requests from a specific frontend origin (
http://localhost:8080).
- CORS is enabled to allow requests from a specific frontend origin (
- This Java class
Databaseserves as a repository for managing the state of drawn shapes in a collaborative drawing application. Let's break down some of its functionalities:- Singleton Design Pattern:
- The class follows the Singleton pattern, ensuring that only one instance of the
Databaseis created, providing a global point of access to its functionality.
- The class follows the Singleton pattern, ensuring that only one instance of the
- DTO Conversion:
getDrawnShapesDTOsconverts the drawn shapes into a list ofShapeDTOobjects for transmission to the frontend.
- Singleton Design Pattern:
- The
ShapeFactoryclass acts uses Factory Design Pattern for creating instances of different shapes, promoting flexibility and encapsulation by centralizing the creation logic based on the type of shape specified in theShapeDTOdata. DrawingAreaclass serves as a container for managing the state of drawn shapes in your application. The Memento pattern is employed to capture and restore the state, allowing for actions like undo and redo in a drawing context.DrawingAreaas Originator:- The
DrawingAreaclass encapsulates the state of drawn shapes. - It provides a
takeSnapshotmethod to create a Memento (snapshot) of its current state.
- The
DrawingMementoas Memento:- This inner class represents a snapshot of the
DrawingArea's state. - It stores a copy of the
drawnShapesstate when created.
- This inner class represents a snapshot of the
undo_stackandredo_stackas Caretaker:- The stacks manage the different states of the
DrawingArea(Originator). - The
undoandredooperations involve popping Mementos from one stack and pushing them onto the other.
- The stacks manage the different states of the
The Paint Application harmoniously combines a well-designed object-oriented model with advanced drawing and painting features. The backend design patterns enhance the application's flexibility, maintainability, and overall user experience. With its intuitive interface and comprehensive functionality set, the application stands as a powerful tool for creative expression.
-
Ensure Java and Node.js are installed on your system.
-
Make sure that you install Font Awesome icons:
-
Clone the GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/ahmedyoussefg/PaintApp.git
- Open the backend project in your preferred IDE.
- Run the Spring Boot application to start the backend server.
-
Navigate to the front-end project directory and run the following commands:
npm install npm run serve
-
Access the application in your web browser at the localhost URL.
-
Video of usage: htps://drive.google.com/file/d/1OV6NC1OX2X-jKH9di-1vPVWT8v8maIWC/view?usp=drive_link