The GitHub Actions for pushing to GitHub repository local changes authorizing using GitHub token.
With ease:
- update new code placed in the repository, e.g. by running a linter on it,
- track changes in script results using Git as archive,
- publish page using GitHub-Pages,
- mirror changes to a separate repository.
To ensure your GitHub Actions workflows function correctly, it's important to configure the GITHUB_TOKEN with the appropriate access rights for each repository.
Follow these steps to set up the necessary permissions:
- Navigate to your repository on GitHub.
- Click on
Settingslocated in the repository toolbar. - In the left sidebar, click on
Actions. - Under the
Actionssettings, find and click onGeneral. - Scroll down to the
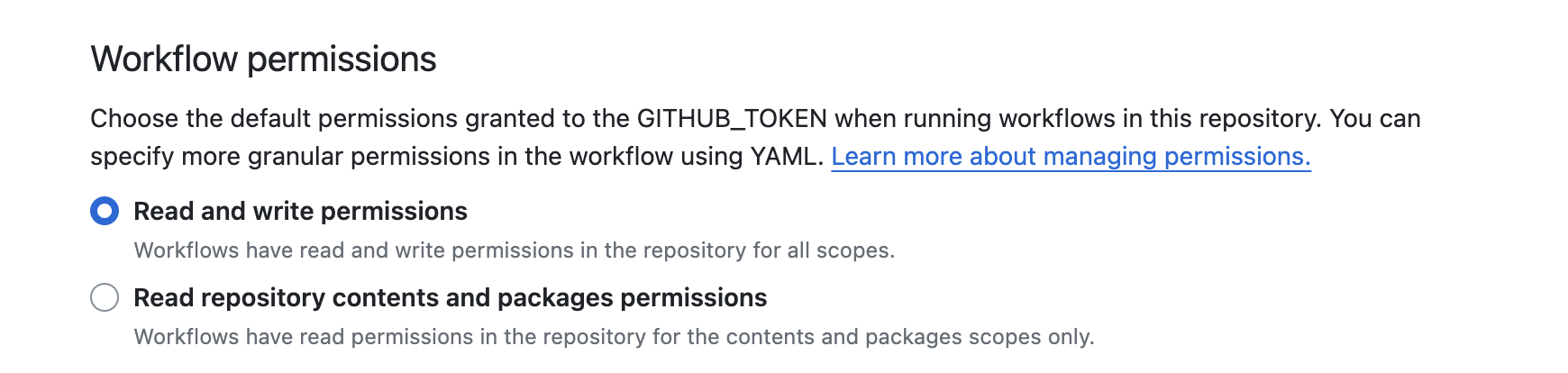
Workflow permissionssection. - You will see the default permission setting for the
GITHUB_TOKEN. Click on the option forRead and write permissions. - With this setting, your workflow will have the ability to read the contents of the repository and push back changes, which is required for using this GitHub Action.
Make sure to save your changes before exiting the settings page.
Note
Granting Read and write permissions allows workflows to modify your repository, which can include adding or updating files and code. Always ensure that you trust the workflows you enable with these permissions.
The GITHUB_TOKEN permissions can also be configured globally for all jobs in a workflow or individually for each job. This example demonstrates how to set the necessary permissions for the contents and pull-requests scopes on a job level:
jobs:
job1:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions: # Job-level permissions configuration starts here
contents: write # 'write' access to repository contents
pull-requests: write # 'write' access to pull requests
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4To apply permissions globally, which will affect all jobs within the workflow, you would define the permissions key at the root level of the workflow file, like so:
permissions: # Global permissions configuration starts here
contents: read # 'read' access to repository contents
pull-requests: write # 'write' access to pull requests
jobs:
job1:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4Adjust the permission levels and scopes according to your workflow's requirements. For further details on each permission level, consult the GitHub documentation.
An example workflow to authenticate with GitHub Platform and to push the changes to a specified reference, e.g. an already available branch:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
persist-credentials: false # otherwise, the token used is the GITHUB_TOKEN, instead of your personal access token.
fetch-depth: 0 # otherwise, there would be errors pushing refs to the destination repository.
- name: Create local changes
run: |
...
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
branch: ${{ github.ref }}An example workflow to use the branch parameter to push the changes to a specified branch e.g. a Pull Request branch:
name: Example
on: [pull_request, pull_request_target]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
branch: ${{ github.head_ref }}An example workflow to use the force-with-lease parameter to force push to a repository:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
force_with_lease: trueAn example workflow to use a GitHub App Token together with the default token inside the checkout action. You can find more information on the topic here:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
persist-credentials: false
- name: Generate Githup App Token
id: generate_token
uses: tibdex/github-app-token@v1
with:
app_id: ${{ secrets.APP_ID }}
installation_id: ${{ secrets.INSTALLATION_ID }}
private_key: ${{ secrets.APP_PRIVATE_KEY }}
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "test@test.com"
git config --local user.name "Test"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ env.TOKEN }}An example workflow to use the non default token push to another repository. Be aware that the force-with-lease flag is in such a case not possible:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
token: ${{ secrets.PAT_TOKEN }}
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "test@test.com"
git config --local user.name "Test"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.PAT_TOKEN }}
repository: Test/test
force: trueAn example workflow to update/ overwrite an existing tag:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git tag -d $GITHUB_REF_NAME
git tag $GITHUB_REF_NAME
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
force: true
tags: trueAn example workflow to authenticate with GitHub Platform via Deploy Keys or in general SSH:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ssh-key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
persist-credentials: true
- name: Create local changes
run: |
...
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
ssh: true
branch: ${{ github.ref }}An example workflow to push to a protected branch inside your repository. Be aware that it is necessary to use a personal access token and use it inside the actions/checkout action. It may be a good idea to specify the force-with-lease flag in case of sync and push errors. If you want to generate an adequate personal access token, you can follow these instructions:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
fetch-depth: 0
token: ${{ secrets.PAT_TOKEN }}
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "test@test.com"
git config --local user.name "Test"
git commit -a -m "Add changes"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.PAT_TOKEN }}
repository: Test/test
force_with_lease: true| name | value | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| github_token | string | ${{ github.token }} |
GITHUB_TOKEN or a repo scoped Personal Access Token. |
| ssh | boolean | false | Determines if ssh/ Deploy Keys is used. |
| branch | string | (default) | Destination branch to push changes. Can be passed in using ${{ github.ref }}. |
| force | boolean | false | Determines if force push is used. |
| force_with_lease | boolean | false | Determines if force-with-lease push is used. Please specify the corresponding branch inside ref section of the checkout action e.g. ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}. |
| atomic | boolean | true | Determines if atomic push is used. |
| push_to_submodules | string | 'on-demand' | Determines if --recurse-submodules= is used. The value defines the used strategy. |
| tags | boolean | false | Determines if --tags is used. |
| directory | string | '.' | Directory to change to before pushing. |
| repository | string | '' | Repository name. Default or empty repository name represents current github repository. If you want to push to other repository, you should make a personal access token and use it as the github_token input. |
If you see the following error inside the output of the job, and you want to update an existing Tag:
To https://github.com/Test/test_repository
! [rejected] 0.0.9 -> 0.0.9 (stale info)
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://github.com/Test/test_repository'
Please use the force instead the force_with_lease parameter. The update of the tag is with the --force-with-lease parameter not possible.
The Dockerfile and associated scripts and documentation in this project are released under the MIT License.
GitHub are registered trademarks of GitHub, Inc. GitHub name used in this project are for identification purposes only. The project is not associated in any way with GitHub Inc. and is not an official solution of GitHub Inc. It was made available in order to facilitate the use of the site GitHub.