Depth From focus
Summary
Depth from focus/defocus is the problem of estimating the 3D surface of a scene from a set of two or more images of that scene. The images are obtained by changing the camera parameters (typically the focal setting or the image plane axial position), and taken from the same point of view [1]. In this project, I construct all in focus image by selecting and placing focused pixel at each focus/defocused images.
Build Instruction
Requirements
- opencv c++ library https://opencv.org/
- cmake https://cmake.org/
Setup Instructions
You have to sepcify opencv libary location to CMakeLists.txt. If you see CMakeLists.txt, you can find include_directories and link_directories for linking the library files to your own workstation. In my case, opencv version is 4.5.0 and installed location is located at the /usr/lcoal/Cellar/opencv/4.5.0/. But this path is varying from your own workstation, so you have to set properly for building this project.
include_directories(/usr/local/Cellar/opencv/4.5.0/include/opencv4)
link_directories(/usr/local/Cellar/opencv/4.5.0/lib/)
After setting library location, you have to make and generate project for your platform.
Image Alignment
Cause focusing a image requires movement of focal lens at the physical camera with positioning error of human, initial defocused images are mismatched each other. So, we have to set alignement of given images. So How? It is simple. First we calculate homograhy matrix of consecutive images. Let
For aligning images, you have to consider using various kinds of align methods. In this project, I use feature based method. You can find the way I use at the reference [2].
| before alignment | after alignment |
|---|---|
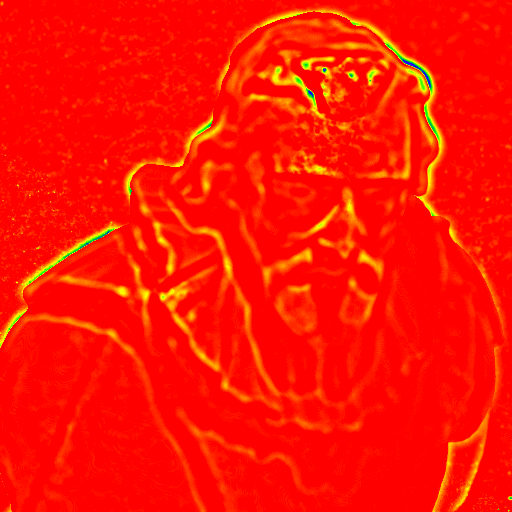 |
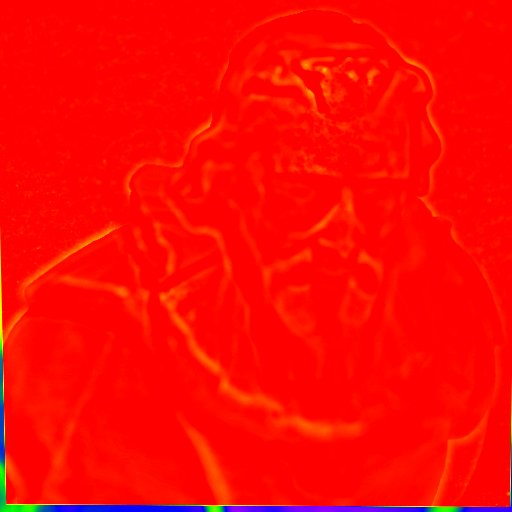 |
You can find the difference of image 1 and image 30 in above table. You can find that after the refinement the differences of image is reduced.
Initial Depth Map (Cost Volume)
Calculating Depth map
We can calculate depth map by derivative of images. Using “blurryness metric”, some of them simple and straightforward using just basic grayscale pixel intensity statistics, others more advanced and feature-based, evaluating the Local Binary Patterns of an image [3]. If the variance falls below a pre-defined threshold, then the image is considered blurry; otherwise, the image is not blurry. You can use various kind of covolution kernel for calculating color difference of each piexel (gray-scaled). The most simplestic way is first derivative (known as sobel filter). But it is not specific enough for calculating focus of images. So we use laplacian of each images for calculating more nosiy but more accurate focus measure. There are lots of variantions of laplacian kernel. Here is examples.
| Name of kernel | Equation |
|---|---|
| Laplacian | |
| Modified Laplacian | |
| Sum Of ML |
In this project, I use Laplacian as a focus Measure Method.
| Depth map of image 1 | Depth map of image 30 |
|---|---|
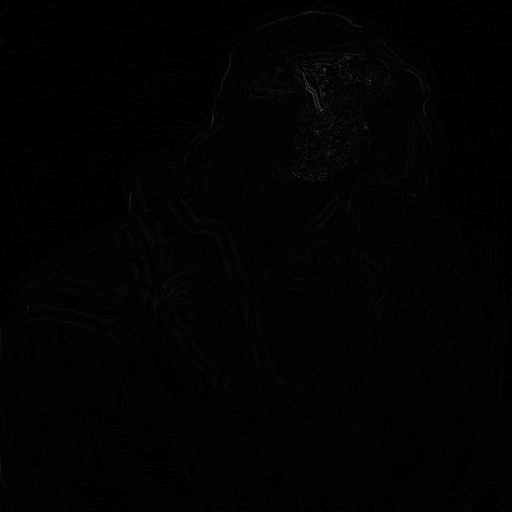 |
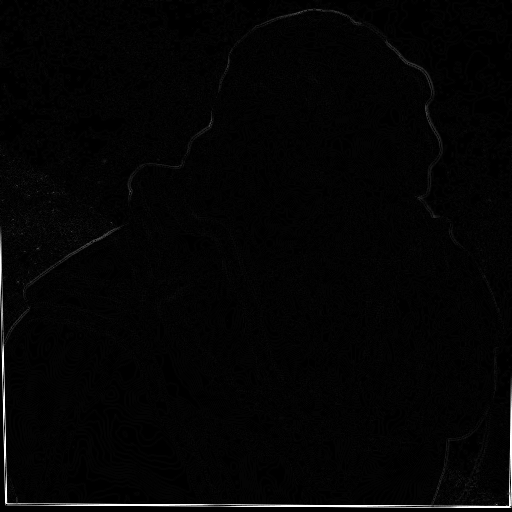 |
Calculating Cost Volume
Now calculating depth map of each images and assemble them. Then we can make cost volume. Cost volume is a terminology for "Celected data set of diaparity map" in computer vision [4]. By selecting the label of image at the highest value in the each cost volume pixels, we can get the initial depth map. But, this naive approach for calculating initial depth map has lots of noise at the depth map. So we have to reduce this noise by using graph cut and weighted median filter.
Depth Refine ment
Graph Cut
In graph theory, a cut is a partition of the vertices of a graph into two disjoint subsets [5]. I use Multi-label optimization for partitioning the image label at the cost volume. I use gco library at waterloo university [6].
Weighted Median Filter
Weighted Median (WM) filters have the robustness and edge preserving capability of the classical median filter [7]. Median filter is somple. Just takes the median of neighbor pixels and self. The only differences of weight median filter and median filter is that weighted median filter uses weighted kernel. Is is known that at the general cases, you can find more neat image by using weighted median filter than median filter [8].
| Initial depth map | Using graph cut and weighted meidan filter |
|---|---|
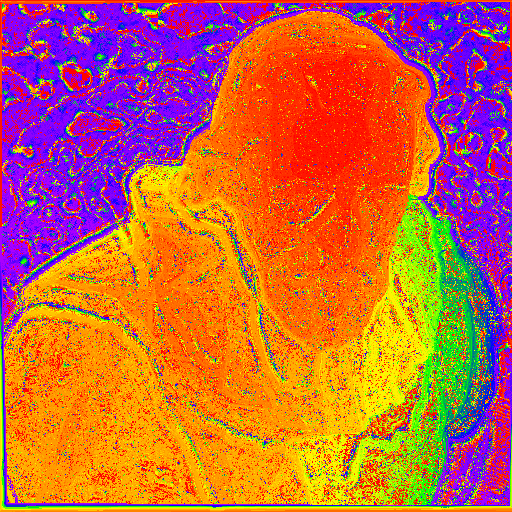 |
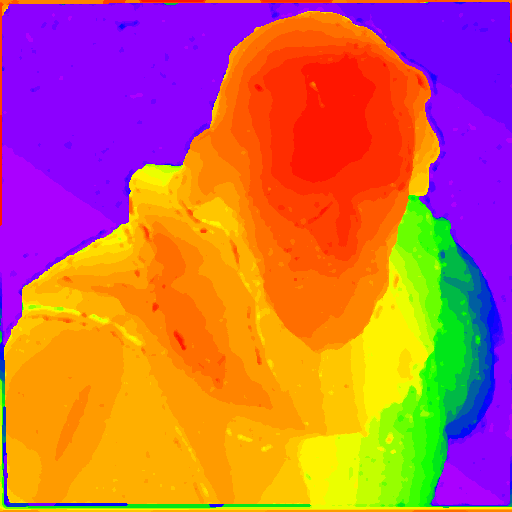 |
All in Focus
Finally, by selecting the pixel at the i'th decoused image at the depth map, we can construct final all in focus image.
References
- https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/FAVARO1/dfdtutorial.html
- https://www.learnopencv.com/image-alignment-feature-based-using-opencv-c-python/
- https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/09/07/blur-detection-with-opencv/
- http://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=dnjswns2280&logNo=222073493738&parentCategoryNo=&categoryNo=10&viewDate=&isShowPopularPosts=false&from=postView
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cut_(graph_theory)
- https://vision.cs.uwaterloo.ca/code/
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/486465
- https://dsp.stackexchange.com/questions/22412/what-is-the-advantage-of-weighted-median-filter-over-median-filter
