 Read the paper here.
This project was originally developed as part of the course EDAN70 Project in Language Technology
at Lund University.
Read the paper here.
This project was originally developed as part of the course EDAN70 Project in Language Technology
at Lund University.
In this paper we outline an attempt to build a system for Trilingual Entity Discovery and Linking (TEDL) based on a paper by Yang et al. (2017). Entity Discovery and Linking is the problem of finding and identifying names of people, organizations, locations and so on (i.e. entities) in arbitrary unstructured bodies of text.
The solution to this problem can be divided into two distinct parts: Mention Detection (MD) – the process of detecting and capturing sequences of words as references to an entity, and Entity Linking (EL) – the linking of a detected entity in the text to an existing entity. This latter step requires disambiguating the detected entity from a list of possible candidates of existing entities based on some set of heuristics.
Our model for detecting entity mentions is based on a deep neural network consisting of two Bidirectional Long ShortTerm Memory (BiLSTM) layers. The entity linking is accomplished by creating a mapping from words to Wikipedia articles and generating a list of candidates from that mapping for each detected entity.
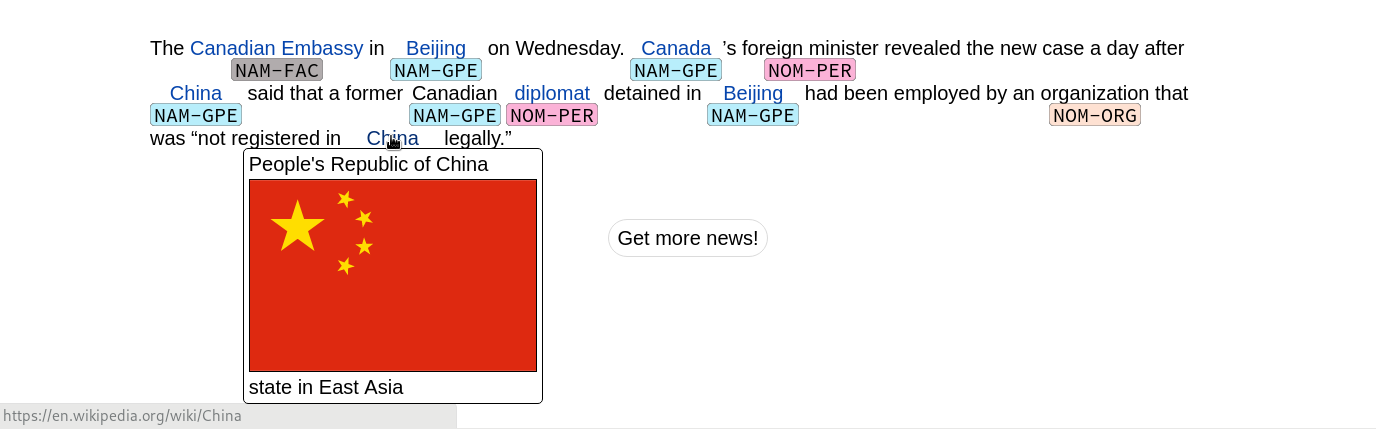
We also describe a graphical interface for demonstrating our system where news articles are fetched and annotated with entity classifications and Wikipedia links.
We evaluate the system using neleval (Nothman et al., 2014) on data from the Text Analysis Conference (TAC) 2017 and achieve F1 scores of 0.692 in strong typed mention match and 0.494 in strong typed all match.
Finally, as this is a work in progress, we discuss some planned improvements for the future of this project.