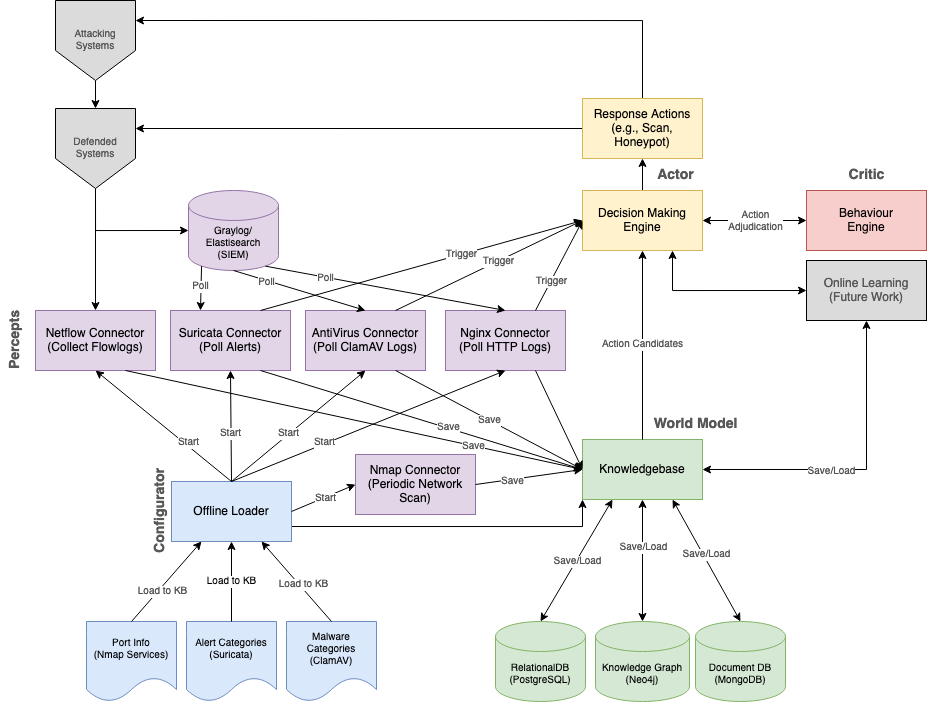
This project will build on the ideas of the AICA framework as outlined in Theron et al. This project will work towards a fully-functional agent with increasingly advanced capabilities that can be used in both research and production contexts. The following diagram depicts the high-level structure of the agent:
- Ensure
gitis installed, use package manager (apt, yum, brew, etc) if needed. - Install Docker; instructions are avaiable here.
- Install micromamba from https://mamba.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation/micromamba-installation.html, and let it update your PATH. You may need to relog after this step.
- Ensure
makeis installed, for example in Ubuntu this is part of thebuild-essentialspackage you can install with apt. - Clone this repo, and open in IDE of your choice (ensure .gitignore is updated as necessary)
- Copy
manager/.env.sampletomanager/.envand make any necessary changes. Notably, all of the "" passwords should be set to something unique. The GRAYLOG_ROOT_PASSWORD_SHA2 value should be generated likeecho 'SOMEPASSWORD' | sha256sum, or an equivalent generate of SHA256 hashes. Make sure this is done before you runmake startfor the first time. If these are changed, amake rebuild_purgeormake stop_purge; make startwill be required. - Set the MODE variable like
export MODE=emu(for Bash, other shells may vary). - You can now run
make depsto build your development environment, thenmake buildto build the Docker containers, andmake startto launch AICA. See more below.
- Install git from https://git-scm.com/download/win; use Unix-style line endings.
- Install Docker from https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop; a reboot will be required.
- Add Docker to System Path (instructions):
C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin - Install micromamba from https://mamba.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation/micromamba-installation.html, and let it update your PATH. You may need to relog after this step.
- Install Make from https://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/make.htm; yes this is from 2006
- Add Make to System Path:
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin - Clone this repo, and open in IDE of your choice (ensure .gitignore is updated as necessary)
- Copy
manager/.env.sampletomanager/.envand make any necessary changes - In Powershell, set the MODE variable like:
$env:MODE = 'emu' - You can now run
make depsto build your development environment,make buildto build the Docker containers, andmake startto launch AICA. See more below.
It is important to ensure your main branch is up-to-date before each working session, and you should commit your changes incrementally and often to ensure minimal divergence and chance of merge conflicts. Changes should be "intact" functionally (i.e., don't submit partially-completed work) and keep the main repository in a working state. This means you should think about functionality in the smallest possible chunks to keep your contributed work up to date.
You can bootstrap your environment with make init, which will create a conda environment for building and testing.
Changes must be pushed to a branch and PR'ed to main. Before pushing your changes, you should first locally execute a make test and ensure it completes successfully. If it does not, either fix the issues or propose exclusions to the relevant test areas (will be subject to peer review).
Once you have a passing build, you should commit your changes to a branch with a commit message that will be meaningful to any reviewers of your code explaining (at a high level) what you changed and why. You can then push the branch and make a PR.
This code should be run via the Makefile. You will need to specify whether you want to start this in emulation mode or virtualized mode with the MODE environment variable (i.e., MODE should be either emu or virt). If using "virt" mode, which is intended for live usage capturing from a real network outside the Docker environment, you much copy the docker-compose-local-overrides.yaml.example file to docker-compose-local-overrides.yaml and modify as appropriate.
When starting from scratch, run the following: make build && make start. Subsequently, use make stop and make start (or make restart) to stop/start the containers and make build to build them again (make rebuild is a handy alias for stop/build/start). You can use make clean to clean up all container- and code-related files.
Once you have started the agent, you can use the various make <system>-shell commands (e.g., make attacker-shell) to open shells on various containers. You might wish, for example, to start a shell on the attacker and nmap the target host.
You can view logs from the Dockerized containers with make logs. This will show all containers, so you might wish to pipe this to grep/egrep to include/exclude containers by name as desired. For example: make logs | egrep ^(manager\b|manager_graphdb).
You can monitor the agent through several interfaces:
- http://localhost:8000: Primary front-end. Django app as defined in
manager/aica_django/. - http://localhost:7474: Neo4j web interface
- http://localhost:5555: Celery Flower instance, where you can monitor task execution
The AICA agent is built as a Django project, and so the normal Django conventions are followed in the manager/ directory. Tests should be added to manager/aica_django/tests and use Django testing conventions. Other top-level directories contain files for other containers in the emulated environment. They should contain at least a Dockerfile and any files needed to be copied into the built container.
Makefileis the primary entry point for this code. It should include test entrypoints as well as entrypoints..dockerignoretells Docker what not to copy into container contextsenvironment.ymlcontains Conda environment specification for build/test..gitignoretells git which files to never check into the repository..yamllintconfigures the YAML lint that runs at build/test timedocker-compose.ymlis the YAML file instructing docker-compose how to create the necessary containers and networks for the agent. The additionaldocker-compose-emu.ymlanddocker-compose-virt.ymlhave addition definitions intended for those modes only and are additionally invoked in theMakefilebased on the MODE environmental variable.
The primary maintainer for this project is @bblakely-anl, a cybersecurity and machine learning researcher at Argonne National Laboratory.