Train transformer language models with reinforcement learning.
I don't feel like updating the entire readme at the moment, just know that you can replace trl.gpt2 with trl.bloom, replace any other instance of "GPT2" with "Bloom," and any demo code should work. The py files aren't built from the demo notebooks so if you were planning on using that functionality, sorry. Also you can do
!pip install git+https://github.com/aicrumb to install this thing. I'm possibly looking towards releasing a Colab notebook that finetunes Bloom-560m for prompt generation with Stable Diffusion (depending on certain factors mostly outside of my control).
With trl you can train transformer language models with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). The library is built on top of the transformer library by 🤗 Hugging Face. Therefore, pre-trained language models can be directly loaded via transformers. At this point only decoder architectures such as GTP2 are implemented.
Highlights:
- PPOTrainer: A PPO trainer for language models that just needs (query, response, reward) triplets to optimise the language model.
- GPT2 model with a value head: A transformer model with an additional scalar output for each token which can be used as a value function in reinforcement learning.
- Example: Train GPT2 to generate positive movie reviews with a BERT sentiment classifier.
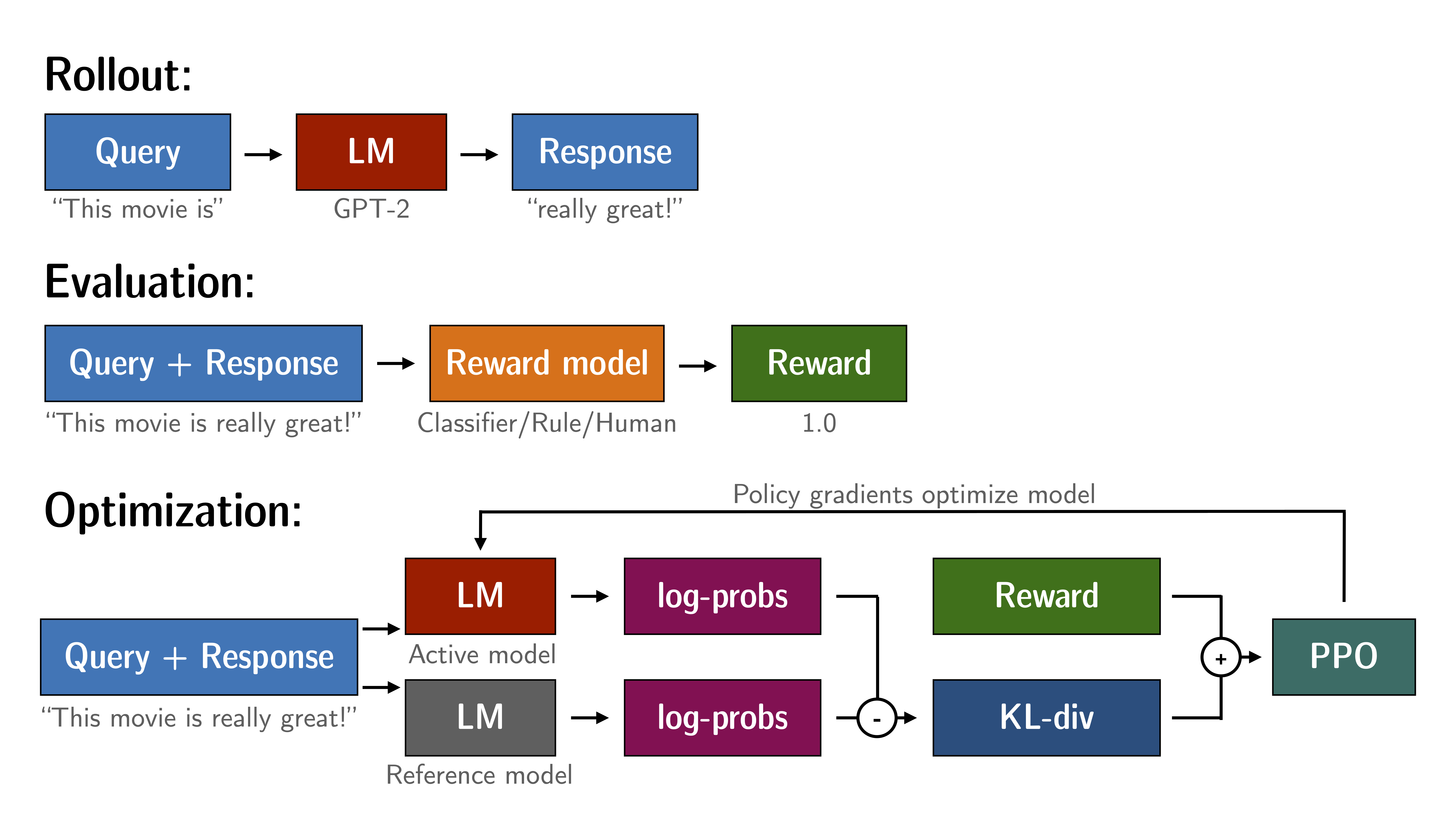
Fine-tuning a language model via PPO consists of roughly three steps:
- Rollout: The language model generates a response or continuation based on query which could be the start of a sentence.
- Evaluation: The query and response are evaluated with a function, model, human feedback or some combination of them. The important thing is that this process should yield a scalar value for each query/response pair.
- Optimization: This is the most complex part. In the optimisation step the query/response pairs are used to calculate the log-probabilities of the tokens in the sequences. This is done with the model that is trained and and a reference model, which is usually the pre-trained model before fine-tuning. The KL-divergence between the two outputs is used as an additional reward signal to make sure the generated responses don't deviate to far from the reference language model. The active language model is then trained with PPO.
This process is illustrated in the sketch below:
Install the library with pip:
pip install trlIf you want to run the examples in the repository a few additional libraries are required. Clone the repository and install it with pip:
git clone https://github.com/lvwerra/trl.git
cd tlr/
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you run Jupyter notebooks you might need to run the following:
jupyter nbextension enable --py --sys-prefix widgetsnbextensionFor Jupyterlab additionally this command:
jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-managerThis is a basic example on how to use the library. Based on a query the language model creates a response which is then evaluated. The evaluation could be a human in the loop or another model's output.
# imports
import torch
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer
from trl.gpt2 import GPT2HeadWithValueModel, respond_to_batch
from trl.ppo import PPOTrainer
# get models
gpt2_model = GPT2HeadWithValueModel.from_pretrained('gpt2')
gpt2_model_ref = GPT2HeadWithValueModel.from_pretrained('gpt2')
gpt2_tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
# initialize trainer
ppo_config = {'batch_size': 1, 'forward_batch_size': 1}
ppo_trainer = PPOTrainer(gpt2_model, gpt2_model_ref, gpt2_tokenizer, **ppo_config)
# encode a query
query_txt = "This morning I went to the "
query_tensor = gpt2_tokenizer.encode(query_txt, return_tensors="pt")
# get model response
response_tensor = respond_to_batch(gpt2_model, query_tensor)
response_txt = gpt2_tokenizer.decode(response_tensor[0,:])
# define a reward for response
# (this could be any reward such as human feedback or output from another model)
reward = [torch.tensor(1.0)]
# train model with ppo
train_stats = ppo_trainer.step([query_tensor[0]], [response_tensor[0]], reward)
For a detailed example check out the notebook 04-gpt2-sentiment-ppo-training.ipynb, where GPT2 is fine-tuned to generate positive movie reviews. An few examples from the language models before and after optimisation are given below:
This library is built with nbdev and as such all the library code as well as examples are in Jupyter notebooks. The following list gives an overview:
index.ipynb: Generates the README and the overview page.00-core.ipynb: Contains the utility functions used throughout the library and examples.01-gpt2-with-value-head.ipynb: Implementation of atransformercompatible GPT2 model with an additional value head as well as a function to generate sequences.02-ppo.ipynb: Implementation of the PPOTrainer used to train language models.03-bert-imdb-training.ipynb: Training of DistilBERT to classify sentiment on the IMDB dataset.04-gpt2-sentiment-ppo-training.ipynb: Fine-tune GPT2 with the BERT sentiment classifier to produce positive movie reviews.
Currently using trl==0.0.3:
05-gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb: Fine-tune GPT2 with the BERT sentiment classifier to produce movie reviews with controlled sentiment.
The PPO implementation largely follows the structure introduced in the paper "Fine-Tuning Language Models from Human Preferences" by D. Ziegler et al. [paper, code].
The language models utilize the transformers library by 🤗 Hugging Face.