MetalOS is homebrew operating system for x86-64. It is 64-bit only and has only been tested in Hyper-V Gen2.
- Open solution file in VS and build all or open VS 2022 Native x64 command promot and run
.\scripts\build_solution.cmd - Run
.\scripts\build_vhd.cmdto build.\out\MetalOS.vhdx - Create a new VM in
Hyper-V Manager, Gen2, reference the buildvhdx, disable secure boot. - Turn on Com ports:
Get-VMComPort -VMName MetalOS
Set-VMComPort -VMName MetalOS -Path \\.\pipe\metalos_com1 -Number 1
Set-VMComPort -VMName MetalOS -Path \\.\pipe\metalos_com2 -Number 2
Get-VMComPort -VMName MetalOS
- If theres a weird access error fix
icaclsin.\scripts\build_vhd.cmd
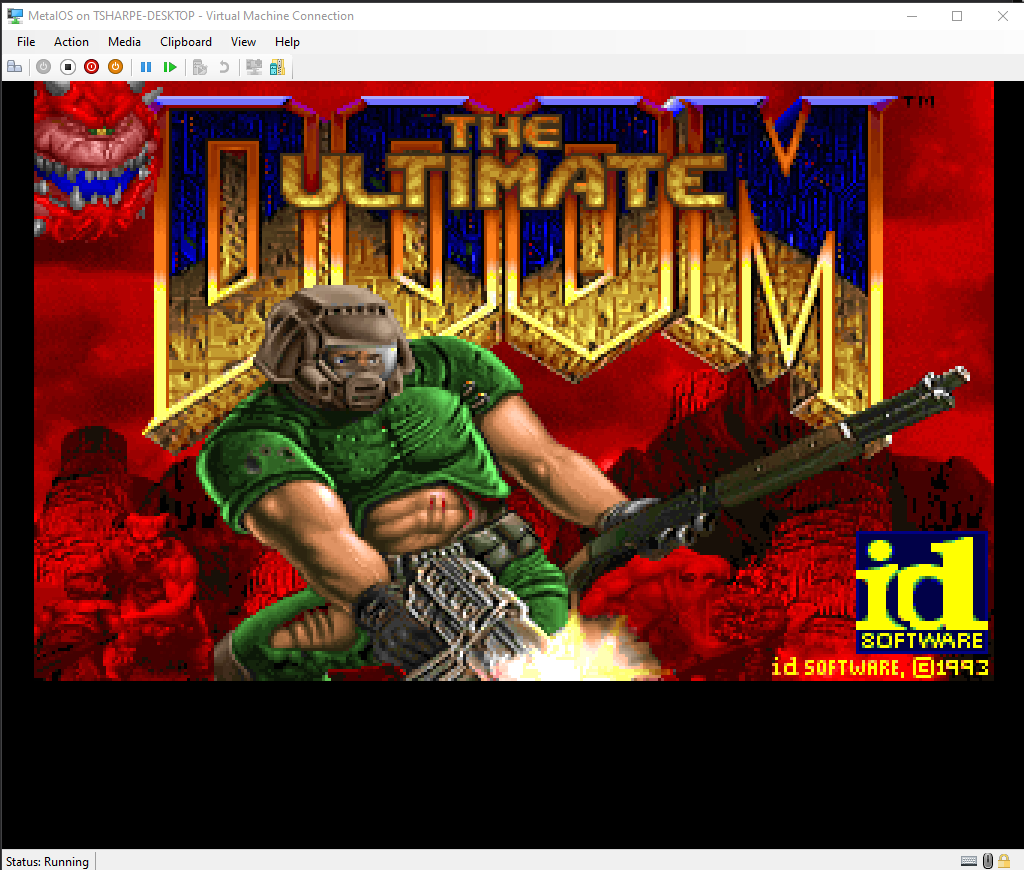
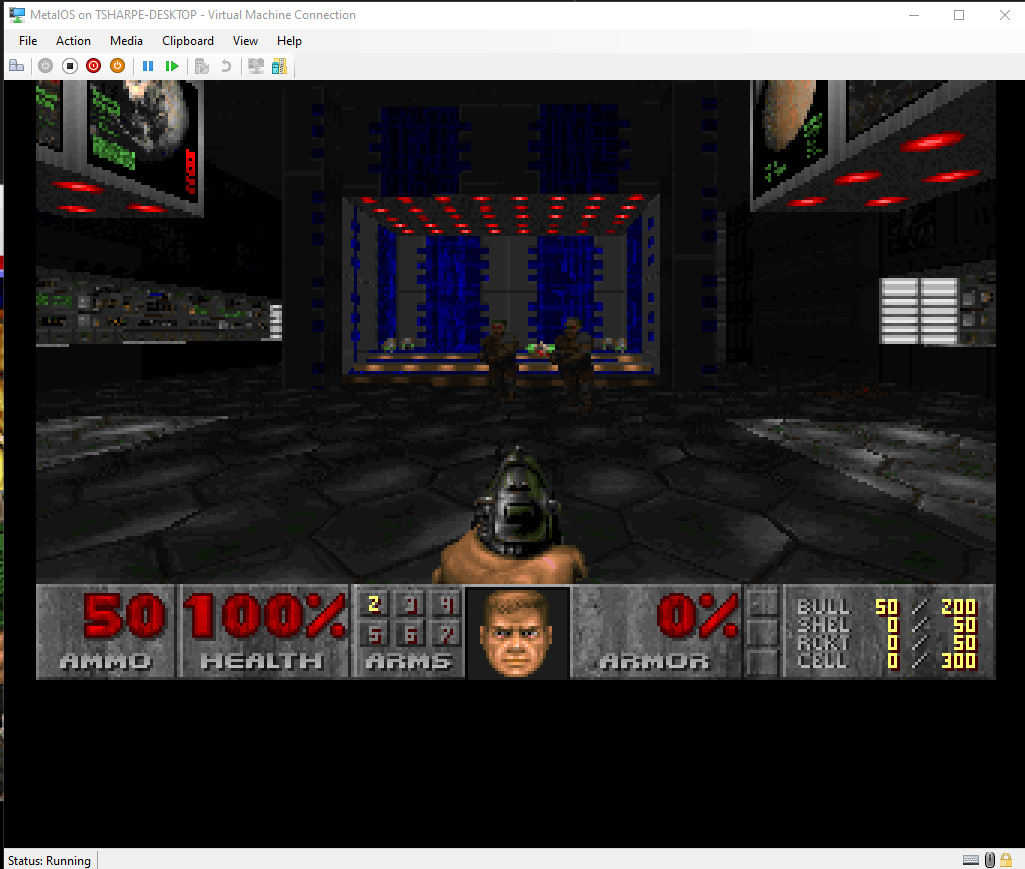
- Run DOOM!
- 48-bit canonical virtual address space (not identity paging)
- Low half used for Usermode
- High half used for Kernel mode
- Ring 0 (Kernel) and Ring 3 (User)
- Modern systemcall interface (syscall instruction)
- 32-bit compatibility
- Additional architectures
- Support for bios
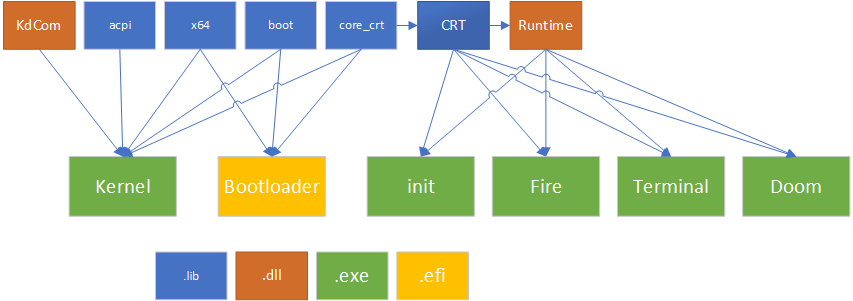
| Project | Type | File | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetalOS.Kernel | Exe | moskrnl.exe | Monolithic kernel |
| MetalOS.Boot | EFI App | BOOTX64.efi | EFI Bootloader |
| MetalOS.Apps.Doom | Exe | doom.exe | Doom ported for MetalOS |
| MetalOS.OS.Fire | Exe | fire.exe | Doom fire implemented as standalone app |
| MetalOS.OS.Runtime | DLL | mosrt.dll | MetalOS Runtime library |
MetalOS is a monolithic kernel that uses a custom UEFI bootloader:
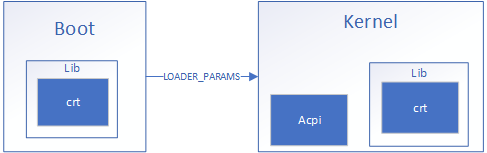
Note: All executable formats (Kernel, Doom, Runtime, and even Boot) are Microsoft PE files. Boot contains a loader for the Kernel, the Kernel contains a loader for the usermode process (as well as the Runtime) and the Runtime contains a loader for subsequent DLLs the usermode process may desire.
The main purpose of Boot is to load the Kernel, however it must also:
- Detect Graphics Device from UEFI (using Graphics Output Protocol)
- Allocate Page Table Pool for Kernel
- Allocate Page Frame Number Database for Kernel's PhysicalMemoryManager
- Allocate and load Kernel's PDB into physical memory (to allow for bugcheck stack walks)
See also: Loader Params
Monolithic preemptive kernel.
Quick Notes:
- UEFI Runtime is mapped into Kernel address space, allowing runtime services to be called
- Each process has at least one thread
- Each user thread also contains a kernel thread for when executing Kernel code (interrupt handler, systemcall)
Usermode interface is provided by MetalOS.h, a required Init static library, and a single runtime dll.
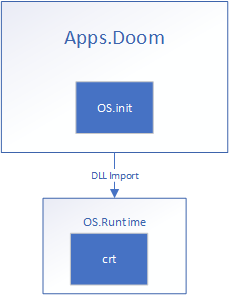
This dll contains the MetalOS native interface as well as the expected CRT interfaces (stdio, stdlib, string, ctype).
The init library provides two exports for use by the kernel:
- InitProcess
- InitThread
These are the starting entry points for the first thread in a process and subsequent threads, respectively. InitProcess is responsible for finishing to load the process (and dependencies), executing main, and calling ExitProcess once main returns. InitThread retrieves its entry point and calls ExitThread on its return. Init depende on Runtime which means every process running has Runtime loaded as well.
Native Interface Subset:
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Environment | GetSystemInfo |
| GetProcessInfo | |
| Process/Thread | Sleep |
| ExitProcess | |
| ExitThread | |
| File/IO | CreateFile |
| ReadFile | |
| UI | AllocWindow |
| PaintWindow | |
| MoveWindow | |
| GetWindowRect | |
| GetMessage | |
| PeekMessage | |
| GetScreenRect |
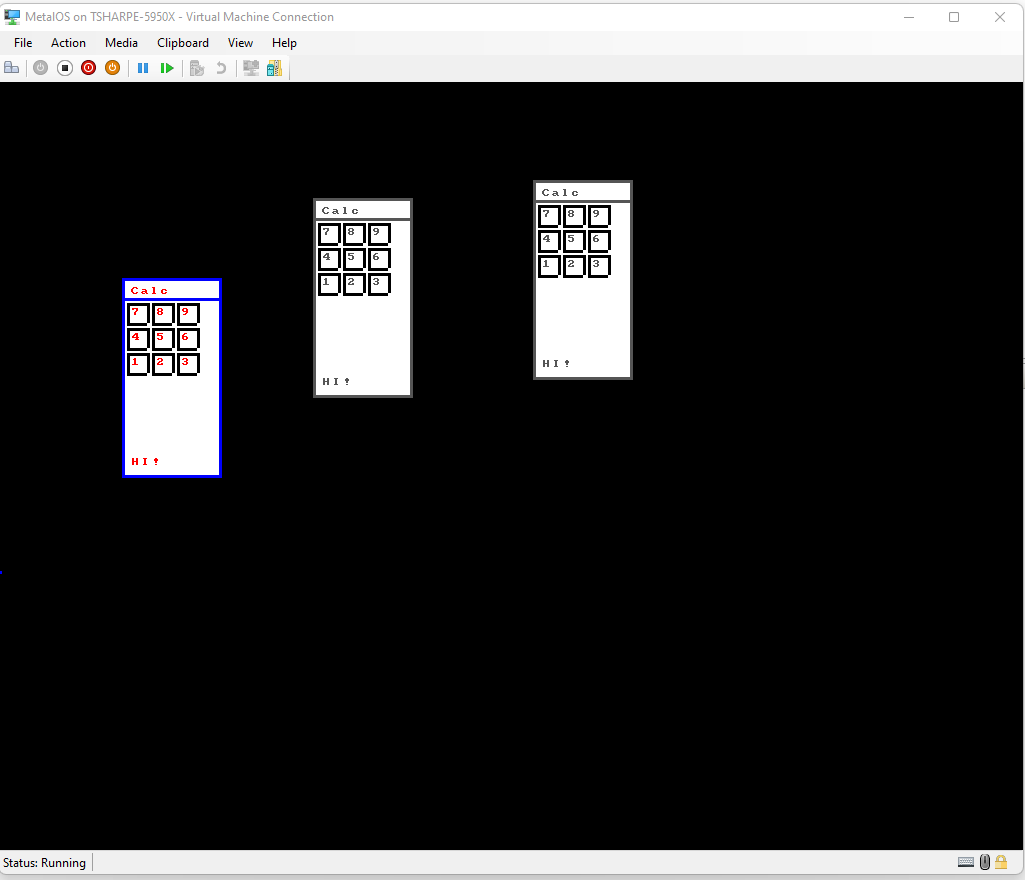
Windowing system is implemented in kernel mode, handles composing windows to frame buffer and handling input events. Currently supports
- Tracking which window has focus
- Click and drag moving of windows
-
Kernel Call Stack (virtual unwind + PDB support) for Assertions/Bugchecks
IP: 0xffff8000010122c6 Function: ?Bugcheck@Kernel@@QEAAXPEBD00@Z Line: 395
IP: 0xffff800001017b3c Function: ?SetScreenBuffer@Kernel@@QEAA?AW4SystemCallResult@@PEAX@Z Line: 173
IP: 0xffff800001015383 Function: ?Syscall@Kernel@@QEAA_KPEAUSystemcallFrame@@@Z Line: 899
IP: 0xffff80000102e87f Function: SYSTEMCALL_HANDLER Line: 56
IP: 0xffff800001039c9c Function: x64_SYSTEMCALL Line: 50 -
Kernel debugging using WinDbg
- ACPCIA
- Virtual Stack Unwinder from coreclr
- kvprintf
Gen2 Hyper-V was chosen early into development for its 64-bit UEFI environment (versus the real mode bios booting of Gen1). Gen1 VMs use emulated legacy hardware which allows it to run most operating systems without any modification. However, Gen2 VMs use all synthetic hardware, which requires using the VMBus for access, an entirely undocumented protocol (Guests are required to be aware of Hyper-Vs existence). Drivers used in MetalOS relied heavily on looking at linux driver source (drivers that were written by Microsoft).
- VMBus
- Keyboard
- Mouse (Basics)
- Video Adapter
- SCSI
- Network
 May need to set sympath force kernel symbol:
May need to set sympath force kernel symbol:
.reload /f /i moskrnl.exe=0xffff800001000000