GO-a-GO annotates functional terms that are overrepresented in a given set of gene pairs. The enrichment of Gene Ontology terms is calculated from a permutation test for overrepresentation of gene pairs that are associated with a common term.
You can install the development version of GO-a-GO from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("ajank/GOaGO")Let us run GO-a-GO on a set of gene pairs associated with human GM12878-specific chromatin loops. We can inspect a few rows of the dataset:
library(GOaGO)
#>
tail(genePairsGM12878Specific)
#> Key: <loopID>
#> loopID chrom1 start1 end1 centroid1 distance_to_TSS1 geneID1 chrom2
#> <int> <char> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <char>
#> 1: 9384 chrX 55740000 55750000 55745000 0 10325 chrX
#> 2: 9390 chrX 57610000 57620000 57615000 0 158586 chrX
#> 3: 9418 chrX 73830000 73835000 73832500 0 51132 chrX
#> 4: 9423 chrX 77160000 77170000 77162500 0 538 chrX
#> 5: 9434 chrX 80060000 80070000 80065000 0 254065 chrX
#> 6: 9434 chrX 80060000 80070000 80065000 0 254065 chrX
#> start2 end2 centroid2 distance_to_TSS2 geneID2 loop_distance pairID
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1: 56750000 56760000 56755000 4016 442454 1010000 806
#> 2: 57940000 57950000 57940000 2933 7789 325000 807
#> 3: 74140000 74145000 74142500 286 340533 310000 808
#> 4: 77350000 77360000 77357500 0 5230 195000 809
#> 5: 80450000 80460000 80455000 0 6451 390000 810
#> 6: 80450000 80460000 80455000 0 79366 390000 811The column names ending with 1 and 2 refer to the first and second
loop anchors, respectively. The essential columns are: geneID1 and
geneID2 (gene identifiers from a database of choice), pairID
(identifier of a gene pair), and loopID (identifier of a chromatin
loop). As some loop anchors overlapped Transcription Start Sites of
multiple genes, the dataset contains all gene combinations for these
loops.
When running GO-a-GO, we should specify that gene identifiers are from
the ENTREZ database, and use the Bioconductor org.Hs.eg.db package as
the source of Gene Ontology annotations for human genes, taking all
three subontologies (Biological Process, Molecular Function, and
Cellular Component). We will run 10,000 permutations, and use the
default p-value cutoff of 0.05 with Benjamini-Hochberg correction:
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
# set the number of CPU threads to use
library(BiocParallel)
options(MulticoreParam=MulticoreParam(workers=2))
goago <- GOaGO(genePairsGM12878Specific, keyType = "ENTREZID",
OrgDb = org.Hs.eg.db, ont = "ALL", numPermutations = 10000L)The overrepresented GO terms are as follows:
print(goago@result)
#> ONTOLOGY ID Description Count Ratio
#> 1 BP GO:0034728 nucleosome organization 8 0.009864365
#> 2 BP GO:0006334 nucleosome assembly 8 0.009864365
#> 3 BP GO:0065004 protein-DNA complex assembly 8 0.009864365
#> 4 CC GO:0000786 nucleosome 16 0.019728730
#> 5 MF GO:0030527 structural constituent of chromatin 16 0.019728730
#> 6 MF GO:0046982 protein heterodimerization activity 16 0.019728730
#> 7 BP GO:0007608 sensory perception of smell 5 0.006165228
#> 8 MF GO:0023023 MHC protein complex binding 4 0.004932182
#> BgRatio pvalue p.adjust qvalue
#> 1 0.0008122072 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 2 0.0006606658 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 3 0.0012011097 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 4 0.0007096178 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 5 0.0006099877 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 6 0.0013130703 0e+00 0.000000 0.00000000
#> 7 0.0005589396 2e-04 0.022925 0.01918421
#> 8 0.0003787916 2e-04 0.022925 0.01918421Note that some of the p-values have the value of zero, which means that for all the randomizations fewer gene pairs were associated with a given term than in the input dataset.
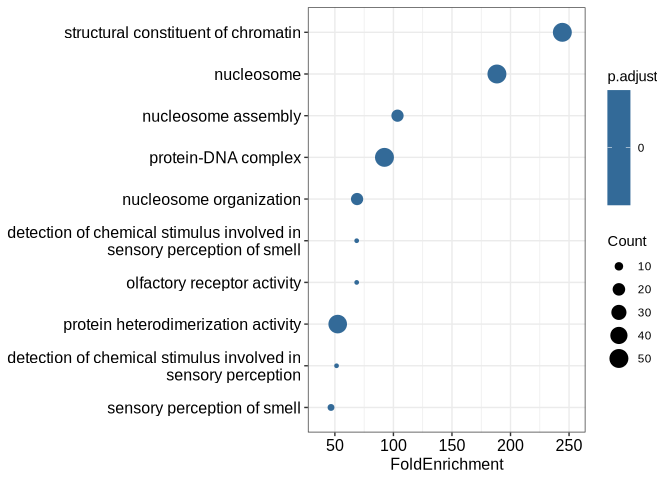
We can plot the overrepresented GO terms as a dotplot. The x-axis shows
the log2 fold change of the fraction of gene pairs sharing
the given term; Ratio is the fraction in the input gene pairs, while
BgRatio is the fraction in permuted ones. Color indicates the adjusted
p-value:
DotPlot(goago)Note that by default only the terms associated with at least 5 gene
pairs are shown; you can change this by setting minTermPairs to any
other value.
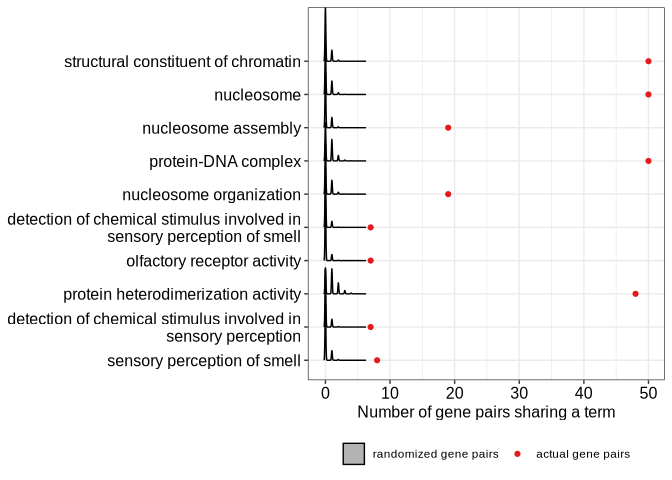
We can also see the sampling distributions of numbers of gene pairs sharing each GO term, obtained for the randomized gene pairs. From these distributions, empirical p-values were calculated:
RidgePlot(goago)
#> Picking joint bandwidth of 0.115