The project was the very first research project which was a part of Nano Electronics Premier League 2017. This project evaluation was counted for the marking of projects of Physics, and Fundamentals of Electronics.
The team members were as follows:
-
Aditi Singh (S1)
-
Akshaye Khanna (S2)
-
Archana Sanjay Gujar (S3)
-
Amanpreet Singh (S4)
-
Faaiz Aarzoo Shaik (S5)
-
Gaddam Sri Sai Kumar (S6)
-
Kushal Muktala (S7)
-
Ajinkya Bedekar (S8)
-
Chichghare Disha Avinash (S9)
-
Gavinson Bashan Kharmalki (S10)
-
Vineel Reddy (Buddy Mentor)
-
Satya Veer Singh (Learning Mentor)
The project number was: Project – 4
The project title was: Can Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) be used for targeted drug delivery for cancer therapies?
Our team did research on the topic and every team member was required to develop a Web Quest individually.
The link to my Web Quest: http://zunal.com/webquest.php?w=349717
This project comprises the following:
-
Presentations with individual research on the topic
-
Some lessons related to the topic
-
Excel sheet with list of all the teams
-
Webquest Design Frameworks
-
Projects assigned to every team
-
Report on Light weight Electric cars for optimum utilization of battery power using Nano-materials
-
Project template explaining the roles of every team member
-
Detailed explanation of the project
-
Project Report on Can Carbon Nano Tubes (CNT) be used for targeted drug delivery, for cancer therapy?
-
Response from the Learning Mentor (Satya Veer Singh Sir) on the basis of which the Web Quest was revised
-
Seating arrangement of all the students for the NanoElPL 2k17 Quiz
-
A timeline of the presentations which was designed in the form of league matches
Some explanations from the project co-ordinator:
For the start, critical investigation:
a. Carbon to Carbon Nano Tubes, What you understand from this?
b. What are CNTs and what are their Properties?
c. At present CNTs are used for what applications?
d. What is chemotherapy and what are its disadvantages?
e. What are physicochemical properties of CNTs?
f. What is drug delivery and how CNTs are used for drug delivery?
g. What is drug administration?
h. What is drug absorption?
i. What is drug transportation?
j. Can similar targeted drug delivery be used for dissolving clots in brain? If so how?
k. How safe these targeted drug delivery systems?
Some useful links sent to help in research purpose:
· https://www.telegraphindia.com/1160125/jsp/knowhow/story_65643.jsp
· https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3210734/
· http://www.particle-works.com/?gclid=CLyy7ImP4NICFdeGaAod0QgHVA
· https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jdd/2012/837327/
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_nanotubes_in_medicine
· http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1369702111701614
· http://www.understandingnano.com/cancer-treatment-nanotechnology.html
· http://www.understandingnano.com/nanotechnology-drug-delivery.html
· http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9783527610419.ntls0241/abstract
· http://ijpsr.com/bft-article/carbon-nanotubes-the-future-of-cancer-treatment/?view=fulltext
· https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=d52277c4-ce22-4ff1-b526-3d1537ef0496
· https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=emEua2eJp1U
· http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1984-82502013000400002
· https://www.omicsonline.org/nanomedical-platform-for-drug-delivery-2157-7439.1000122.php?aid=3266
· http://www.livestrong.com/article/71774-disadvantages-chemotherapy/
· https://beautyhealthtips.in/cancer-chemotherapy-advantages-and-disadvantages/
· http://www.healthlibrary.com/book88_chapter1038.htm
· http://chemotherapy-science.blogspot.in/p/disadvantages_2492.html
· https://canceraustralia.gov.au/affected-cancer/cancer-types/gynaecological-cancers/fallopian-tube-cancer/treatment/benefits-and-disadvantages-cancer-treatment
· https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=emEua2eJp1U
Some MCQ questions related to Nano Electronics for practice:
-
Medieval stained glass are the example of
a. Painting
b. Digital Graphics
c. Nanotecnology (Correct answer)
d. None of above
-
Method start with atoms or molecules and build up to nanostructures called
a. Bottom up approach (Correct answer)
b. Top down approach
c. None of above
-
Example for Top down method for the nano structure is
a. Lithography (Correct answer)
b. Sol gel method
c. Precipitation method
d. None of above
-
Scanning electron microscope technique can be used
a. To measure the size of the particle
b. Charge on the particle
c. Shape and size of the particle (Correct answer)
d. None of above
-
Example for 3D nano structure is
a. Nano fiber
b. Nano thin film
c. Quantum Dots (Correct answer)
d. None of above
-
A bucky ball carries
a. 50 Carbon
b. 60 Carbon (Correct answer)
c. 70 Carbon
d. None of above
-
The full name of AFM is in the area of nano technology
a. American Federation of Musicians
b. Atom free microscope
c. Atomic Force Microscope (Correct answer)
d. None of above
-
What is the size of MEMS
a. 10^-6 to 10^-4 m (Correct answer)
b. 10^-8 to 10^-4 m
c. 10^-10 to 10^-4 m
d. None of above
-
What is size of nano shell
a. 1 nm
b. 10 nm
c. 100 nm (Correct answer)
d. None of above
-
Who gave the term “Nanotechnology”
a. Richard Feynmann
b. Eric Drexler (Correct answer)
c. Sumio Tijima
d. Richard Smalley
-
"There is a plenty of room at the bottom." This was stated by
A. Issac Newton
B. Albert Einstein
C. Richard Feynman (Correct answer)
D. Eric Drexler
-
1 nanometre= _______ cm.
A. 10^(-9)
B. 10^(-8)
C. 10^(-7) (Correct answer)
D. 10^(-6)
-
The size of E.coli bacteria is ______ nm
A. 75000
B. 2000 (Correct answer)
C. 200
D. 5
-
The diameter of human hair is _______ m
A. 75000
B. 75
C. 7.5 x 10^(-5) (Correct answer)
D. 7.5 x 10^(-9)
-
The most important property of nanomaterials is
A. force
B. friction (Correct answer)
C. pressure
D. temperature
-
The diameter of a bucky ball is about ______
A. 1 Ao
B. 100 Ao
C. 1 nm (Correct answer)
D. 10 nm
-
A bucky ball is a molecule consisting of ___ carbon atoms
A. 50
B. 60
C. 75 (Correct answer)
D. 100
-
The cut-off limit of human eye to see is _____ nm
A. 10
B. 100
C. 1000
D. 10000 (Correct answer)
-
1 meter = ______ nm.
A. 10^9 (Correct answer)
B. 10^(-9)
C. 10^10
D. 10^(-10)
-
The diameter of a bucky ball is about ______
A. 1 Ao
B. 10 Ao (Correct answer)
C. 100 Ao
D. 1000 Ao
-
The diameter of hydrogen atom is ______ nm.
A. 10
B. 1
C. 0.1 (Correct answer)
D. 0.01
-
The size of a quantum dot is ______ m.
A. 5
B. 5 x 10^(-9) (Correct answer)
C. 5 x 10^(-10)
D. 5 x 10^(-11)
-
20 micron = ______ nm
A. 20 x 10^(-9)
B. 20 x 10^9
C. 200
D. 20000 (Correct answer)
-
1 mm = ______ nm
A. 10^6 (Correct answer)
B. 10^(-6)
C. 10^7
D. 10^(-7)
-
The hardest material found in nature is ______.
A. steel
B. topaz
C. diamond (Correct answer)
D. quartz
-
______ are the extentions of bucky balls.
A. Geodesic domes
B. Hexagons
C. Carbon nanotubes (Correct answer)
D. AFM and STM
-
Nanotechnology, in other words, is
A. Carbon engineering
B. Atomic engineering (Correct answer)
C. Small technology
D. Microphysics
-
The width of carbon nanotube is ______nm.
A. 1
B. 1.3 (Correct answer)
C. 1.55
D. 10
-
The diameter of fly ash particles is _____ μm
A. 5-10
B. 10-20 (Correct answer)
C. 20-30
D. 100
-
The tensile strength of a carbon nanotube is _____ times that of steel.
A. 10
B. 25
C. 100 (Correct answer)
D. 1000
-
The ratio of thermal conductivity of silver to that of a carbon nanotube is _____.
A. 100 : 1
B. 1 : 100
C. 10 : 1
D. 1 : 10 (Correct answer)
-
In a bucky ball, each carbon atom is bound to _____ adjacent carbon atoms.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3 (Correct answer)
D. 4
-
The size of red and white blood cells is in the range of _____μm.
A. 2-5 (Correct answer)
B. 5-7
C. 7-10
D. 10-15
-
10 nm = _____ m
[A] 10^-8 (Correct answer) [B] 10^-7 [C] 10^-9 [D] 10^-10
-
The size of nanoparticles is between _____ nm.
[A] 100 to 1000 [B] 0.1 to 10 [C] 1 to 100 (Correct answer) [D] 0.01 to 1
-
The diameter of hydrogen atom is...
[A] 1 [B] 10 [C] 0.1 (Correct answer) [D] 0.01
-
Carbon atoms make ____ type of bond with other carbon atoms.
[A] covalent (Correct answer) [B] ionic [C] metallic [D] hydrogen
-
Fullerene or bucky ball is made up of ____ carbon atoms.
[A] 100 [B] 20 [C] 75 [D] 60 (Correct answer)
-
The thermal conductivity of a standard SWNT along its length is ____ watt/(m.K)
[A] 3500 (Correct answer) [B] 385 [C] 35000 [D] 35
-
1 m = _____ nm.
[A] 10^-9 [B] 10^-8 [C] 10^9 (Correct answer) [D] 10^8
-
"There is plenty of room at the bottom." This was stated by _____.
[A] Eric Drexler [B] Richard Feynmann (Correct answer) [C] Harold Croto [D] Richard Smalley
-
Who coined the word 'nanotechnology'?
[A] Eric Drexler (Correct answer) [B] Richard Feynmann [C] Sumio Tijima [D] Richard Smalley
-
According to the definition by CRN, nanotechnology is...
[A] mechanical engineering [B] atomic engineering (Correct answer) [C] Newtonian mechanics [D] micro-electronics
-
Nanoscience can be studied with the help of...
[A] quantum mechanics (Correct answer) [B] Newtonian mechanics [C] macro-dynamics [D] geophysics
-
Greeks and Romans had used nanoparticles in the manufacture of...
[A] cosmetics for eyes [B] medicines [C] metal articles [D] hair-dye (Correct answer)
-
Egyptians were using ____ to prepare make-up for eyes.
[A] nanoaluminium [B] nanocopper [C] nanosteel [D] nanolead (Correct answer)
-
The sword of Tipu Sultan was made of...
[A] nanolead [B] nanoaluminium [C] Damascus steel (Correct answer) [D] Pure iron
-
_____ contains nanoparticles prepared by using biologically processed metal ores.
[A] Homeopathic medicines [B] Modern antibiotics [C] Ayurvedic 'Bhasmas' (Correct answer) [D] Modern cosmetics
-
Who was the first scientist to describe that substances having nanodimensions possess altogether different and unique properties?
[A] Richard Feynmann [B] Eric Drexler [C] Archimedes [D] Michael Faraday (Correct answer)
-
Which of the following does not apply to nanotechnology?
[A] It is a general-purpose technology. [B] It can be called Green technology. [C] Newtonian mechanics can describe it. (Correct answer) [D] It involves rearrangement of atoms.
-
The diameter of human hair is ____ nm.
[A] 50,000 (Correct answer) [B] 75,000 [C] 90,000 [D] 1,00,000
-
The diameter of human hair is ____ m.
[A] 5 x 10^-8 [B] 5 x 10^-7 [C] 5 x 10^-6 [D] 5 x 10^-5 (Correct answer)
-
The cut-off limit of human eye is ____ nm.
[A] 2,000 [B] 5,000 [C] 10,000 (Correct answer) [D] 50,000
-
The size of E.Coli bacteria is ____ nm.
[A] 2,000 (Correct answer) [B] 5,000 [C] 50 [D] 90
-
The size of RBC is ____ nm.
[A] 50 [B] 90 [C] 2,000 [D] 5,000 (Correct answer)
-
The thickness of a transistor is ____ nm.
[A] 50 [B] 90 (Correct answer) [C] 2,000 [D] 5,000
-
The size of a virus is ____ nm.
[A] 2 [B] 20 [C] 50 (Correct answer) [D] 2000
-
The diameter of a bucky ball is ____ nm.
[A] 1,000 [B] 100 [C] 10 [D] 1 (Correct answer)
-
The width of a typical DNA molecule is ____ nm.
[A] 1 [B] 2 (Correct answer) [C] 5 [D] 10
-
1 micrometer (micron) = ______ m.
[A] 10^-9 [B] 10^-8 [C] 10^-7 [D] 10^-6 (Correct answer)
-
1 micrometer (micron) = ______ nm.
[A] 1,000 (Correct answer) [B] 100 [C] 10 [D] 0.01
-
The full form of STM is...
[A] Scanning Tunneling Microscope (Correct answer) [B] Scientific Technical Microscope [C] Systematic Technical Microscope [D] Super Tensile Microscope
-
What does 'F' stand for in AFM?
[A] Fine [B] Front [C] Force (Correct answer) [D] Flux
-
Which ratio decides the efficiency of nanosubstances?
[A] Weight/volume [B] Surface area/volume (Correct answer) [C] Volume/weight [D] Pressure/volume
-
The surface area to volume ratio of a sphere with radius 1 cm is R1 and that of a sphere with radius 5 cm is R2. Then R1 = ____ R2.
[A] 3 [B] 1/3 [C] 5 (Correct answer) [D] 1/5
-
The surface area to volume ratio of a cube with side 1 unit is R1 and that of a cube with side 10 units is R2. Then R2 = ____ R1.
[A] 1/10 (Correct answer) [B] 10 [C] 1/100 [D] 100
-
The two important properties of nanosubstances are...
[A] pressure and friction [B] sticking and friction (Correct answer) [C] sticking and temperature [D] temperature and friction
-
With the help of _____, Robert F. Curl and others discovered fullerene.
[A] electron microscope [B] magnetic resonance [C] condensation technique [D] mass spectrograph (Correct answer)
-
In the structure of fullerene each carbon atom forms covalent bonds with ____ other carbon atoms.
[A] one [B] two [C] three (Correct answer) [D] four
-
Who had invented the famous 'Geodesic' dome structure?
[A] Eric Drexler [B] Buckminster Fuller (Correct answer) [C] Richard Smalley [D] Faraday
-
The largest cluster of carbon atoms in Bucky balls known till today consists of ____ carbon atoms.
[A] 60 [B] 75 [C] 180 [D] 540 (Correct answer)
-
The smallest cluster of carbon atoms in Bucky balls known till today consists of ____ carbon atoms.
[A] 75 [B] 60 [C] 20 (Correct answer) [D] 15
-
The tensile strength of an MWNT is ____ Pa.
[A] 63 x 10^6 [B] 63 x 10^7 [C] 63 x 10^8 [D] 63 x 10^9 (Correct answer)
-
The compressive strength of a nanotube _____ its tensile strength.
[A] is less than (Correct answer) [B] is greater than [C] is equal to [D] may be greater than
-
The hardness of a standard SWNT is ____ Pa.
[A] 63 x 10^6 [B] 25 x 10^6 [C] 25 x 10^9 (Correct answer) [D] 25 x 10^-9
-
The bulk modulus of a standard SWNT is ____ that of diamond.
[A] less than [B] greater than (Correct answer) [C] equal to [D] less than or equal to
-
How much current can be passed through 1 cm2 cross-section of a metal nanotube?
[A] 10^-9 A [B] 10^9 A (Correct answer) [C] 1000 A [D] 0.001 A
-
The electrical conductivity of a nanotube is ____ times that of copper.
[A] 10 [B] 100 [C] 1000 (Correct answer) [D] 1/100
-
An MWNT possesses electrical superconductivity up to temperature of...
[A] 12 K (Correct answer) [B] 12°C [C] 100 K [D] 100°
-
At room temperature, the thermal conductivity of a copper wire is ____ watt/(m.K).
[A] 3500 [B] 350 [C] 385 (Correct answer) [D] 38.5
-
In radial direction, the thermal conductivity of a nanotube is ____ watt/(m.K).
[A] 3500 [B] 385 [C] 350 [D] 0 (Correct answer)
-
The thermal stability of a nanotube is seen up to ____ K in vacuum.
[A] 100 [B] 1000 [C] 2200 [D] 3100 (Correct answer)
-
The thermal conductivity of an SWNT along length is ____ watt/(m.K).
[A] 35 [B] 350 [C] 385 [D] 3500 (Correct answer)
-
The size of a quantum dot is ____ nm.
[A] 5 (Correct answer) [B] 10 [C] 50 [D] 100
-
The wavelength of visible light is ____ nm.
[A] 40-70 [B] 400-700 (Correct answer) [C] 4000-7000 [D] 40000-70000
-
The capacity of a normal human eye to see the smallest object is ____ μm.
[A] 10000 [B] 1000 [C] 100 [D] 10 (Correct answer)
-
The width of a carbon nanotube is ____ nm.
[A] 1 [B] 1.3 (Correct answer) [C] 2.5 [D] 10
-
The thermal stability of a nanotube is seen up to ____ K in air.
[A] 100 [B] 1000 (Correct answer) [C] 2000 [D] 3100
-
Nanoparticles of which substance were found on the surface of the sword of Tipu Sultan?
[A] Gold [B] Lead [C] Carbon (Correct answer) [D] Silicon
-
Nano particles of which atom are used to control collateral damage due to explosion?
[A] Copper [B] Aluminium (Correct answer) [C] Carbon [D] Lead
-
Who prepared and explained nanotubes for the first time?
[A] Sumio Tijima (Correct answer) [B] Richard Smalley [C] Eric Drexler [D] Richard Feynmann
-
Which of the following statement/s is are true?
i.Volume to surface area ratio is very large for nanomaterials.
ii.The cut-off limit of human eye is 10-5 m.
iii.Hardness of a SWNT is about 63 x 109 Pa.
iv.Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical fullerenes.
[A] All four [B] (ii) and (iv) [C] (i), (ii) and (iv) [D] (ii), (iii) and (iv) (Correct answer)
-
Match the objects in Part A with their size in Part B.
[A] 1-a, 2-c, 3-d, 4-b [B] 1-b, 2-a, 3-c, 4-d [C] 1-a, 2-d, 3-b, 4-c (Correct answer) [D] 1-c, 2-d, 3-b, 4-a
-
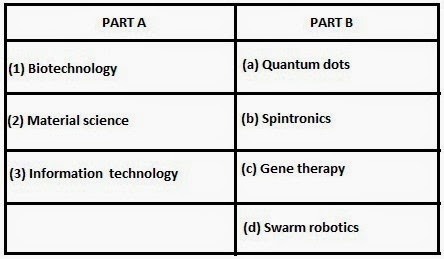
Match the items in Part A with appropriate alternative in Part B.
[A] 1-c, 2-d, 3-a [B] 1-c, 2-b, 3-a [C] 1-c, 2-a, 3-b (Correct answer) [D] 1-a, 2-b, 3-d
-
The suffix '-ene' in the name of fullerene shows the presence of _____ in the molecule.
[A] one triple bond [B] one double bond (Correct answer) [C] two single bonds [D] two triple bonds
Some Short Answer questions related to Nano Electronics for practice:
-
Who coined the word "Nanotechnology"?
ANS: K. Eric Drexler coined the word "Nanotechnology".
-
Who wrote the book "Engines of Creation"?
ANS: K. Eric Drexler wrote the book "Engines of Creation".
-
What is the meaning of the Greek word "Nano"?
ANS: "Nano" means "dwarf".
-
What is the meaning of "Technology"?
ANS: "Technology" is a process of using scientific principles and techniques to design new materials, devices, and systems for prosperity, comforts, betterment and enhancement of human life.
-
What is Atomic Engineering?
ANS: Atomic Engineering is the science involving manufacture of products with different properties by rearrangement of atoms.
-
Define: Nanotechnology.
ANS: Nanotechnology is atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule building of structures that will be helpful in manufacturing new devices and systems.
-
How much is 1 micron in meter?
ANS: 1 micron is equal to 10^-6 meter.
-
What is the size of an integrated circuit transistor?
ANS: The size of an integrated circuit transistor is 90 nm.
-
What is the size of a virus?
ANS: A virus is 50 nm in size.
-
Mention the width of a DNA molecule.
ANS: A DNA molecule has width of about 2 nm.
-
What is the diameter of the hydrogen atom?
ANS: The diameter of the hydrogen atom is 0.1 nm.
-
What is the full form of MEMS?
ANS: "MicroElectro Mechanical Systems" is the full form of MEMS
-
What is the size of red blood cells?
ANS: The size of red blood cells is 5000 nm.
-
What is the size of a quantum dot?
ANS: The size of a quantum dot is 5 nm.
-
Who invented STM(Scanning Tunneling Microscope)?
ANS: Gern Binnig and Heinrich Rohre of IBM Research Lab invented STM in 1981.
-
What can be considered as a loose atom or molecule floating in space?
ANS: Anything smaller than a nanometer can be considered as a loose atom or molecule floating in space.
-
What made it possible to study atoms and their manipulation in developing new structures?
ANS: The invention of Scanning Tunneling Microscope(STM) made it possible to study atoms and their manipulation in developing new structures.
-
What is the full form of AFM?
ANS: The full form of AFM is Atomic Force Microscope.
-
Which two types of fundamental molecules find wide applications in nanotechnology?
ANS: Bucky balls and carbon nanotubes are two types of fundamental molecules that find wide applications in nanotechnology.
-
Why does nanotechnology play by different rules?
ANS: Nanotechnology plays by different rules because of larger surface area relative to the volume of nanomaterials.
-
Who discovered Buckminsterfullerene(bucky ball)?
ANS: Robert F. Curl,Jr.; Harold W. Croto; and Richard E. Smalley discovered the buckminsterfullerene in 1985.
-
What does a bucky ball comprise of?
ANS: A bucky ball comprises of 60 carbon atoms in the architectural configuration of a soccer ball(sphere).
-
Who designed the famous geodesic dome?
ANS: American architect Buckminster Fuller designed the famous geodesic dome.
-
What are carbon nanotubes? OR What are fullerenes?
ANS: Carbon nanotubes are long tubular structures formed by joining bucky balls without their ends closing so that spheres are not formed.
-
Who conceptualised carbon nanotubes?
ANS: Richard Smalley conceptualised carbon nanotubes.
-
What is a bucky tube?
ANS: A bucky tube is a carbon nanotube derived from bucky balls.
-
Mention the types of carbon nanotubes.
ANS: The types of carbon nanotubes are: (1) Single Walled Nano Tube (SWNT) and (2) Multi Walled Nano Tube (MWNT)
-
List out the areas of nanoscience.
ANS: The areas of nanoscience are: (1) nanotubes (2) nanofabrication (3) nanomaterials (4) nanocomposites
-
Who photographed nanotubes for the first time?
ANS: Sumio Tijima of NEC Laboratory photographed nanotubes for the first time.
-
Why do carbon nanotubes have very high tensile strength?
ANS: Carbon nanotubes have very high tensile strength due to carbon-carbon bonds and the fact that each carbon tube is a very large molecule.
-
How do carbon nanotubes conduct heat ? OR Why do carbon nanotubes have high thermal conductivity?
ANS: Carbon nanotubes have high thermal conductivity because they conduct heat by vibrations of covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
-
How is nanotechnology useful in destroying tumours of cancer?
ANS: A nanoshell of 100nm diameter floating through the body will be able to get attached only to cancerous cells which upon excitation by a laser beam will dissipate heat and destroy the tumour.
-
How can the melting point of materials be tuned using nanotechnology?
ANS: The melting point of materials can be tuned by controlling their particle size in the range of nanoscale.
-
How can collateral damage be minimized during explosion using nanotechnology?
ANS: The collateral damage during explosion can be minimized by varying the size of nanoparticles in munitions.
-
What is the use of nanocrystals?
ANS: Nanocrystals can be used to transform electricity into light without excessive loss of energy due to heating.
-
Which fields of science will be affected by the progress of nanotechnology?
ANS: The fields like nanotubes, nanofabrication, nanomaterials and nanocomposites will be affected by the progress of nanotechnology.
-
Mention two phenomena which are dominant and important at nanoscales(as compared to larger dimensions).
ANS: Sticking and friction are dominant and important at nanoscales.
-
How can the mapping of DNA of a newly born baby be useful?
ANS: The mapping of DNA of a newly born baby can help obtain information about future potential problems, enabling to curtail diseases at an early stage.
-
Mention the range of wavelength of visible light in nanometer.
ANS: The range of wavelength of visible light is 400 to 700 nm.
-
Who outlined the "Vision and Prospects of Atomic Engineering'?
ANS: Richard Feynman.
-
What is the diameter of human hair?
ANS: The diameter of human hair is 75000 nm.
-
What is the full form of GPS?
ANS: The full form of GPS is Global Positioning System.
-
What is the size of MEMS?
ANS: The size of MEMS is 10^-6 to 10^-4 m.
-
What is the size of a nanoshell?
ANS: The size of a nanoshell is 100 nm.
-
What are magnetic properties of nanomaterials?
ANS: Non-magnetic materials become magnetic when the cluster size reduces to 80 atoms. Bulk magnetic moment increases with decreases in coordination number Ferro magnetic materials exhibit superparamagnetism at nanograin sizes. Paramagnetic materials exhibit ferromagnetism at nano grain size.
-
How nanomaterials change mechanical properties?
ANS: Higher hardness and mechanical strength (2-7 times) when grain size reduces from 1 μm to 10 nm. Higher moduli of elasticity (30%-40%). Very high ductility and super plastic behavior at low temperatures.
-
What are luminescence properties of nanomaterials?
ANS: Greater luminescence efficiency in nano semiconductor materials.
-
Mention two techniques for synthesis of nano phase materials.
ANS: Mechanical; Inert gas condensation; alloying; Sol-gel technique; Electro-depostion; Laser synthesis; Spraying.
-
Mention two forms of nanomaterials used in nanoelectronics.
ANS: Nanodots, nanorods, Carbon nanotubes and Fullerenes.
-
What is shape memory effect?
ANS: Certain metallic alloys like alloy of gold (Au) and Cadmium (Cd) exhibit a plastic nature, when cooled to a lower temperature. The return to their original dimensional configuration (metallic) during heating at high temperature. This effect is called Shape Memory Effect (SME). How nanomaterials are used in nanomagnets?
-
How nanomaterials used in super capacitors?
ANS: Capacitor value depends on area of plates, insulating material and distance between plates. Insulating materials using nanomaterials increase the capacitance value.
-
What is wave packet? if so how?
ANS: Deviations from Ohm’s law is due to: Wave mechanical theory.
-
Can nanomaterial deviate Ohm’s law?
ANS: This transistor is made up of Carbon tubes.
-
Indian Scientists developed tiniest transistors in 2005 which was reported in Silicon India. What they used to make these transistors?
-
How nanowires are used in high density memories?
-
How super capacitors are used in renewable energy?
-
How resistance size can be reduced using nanomaterials?
-
What are metallic glasses?
ANS: Metallic glasses are the newly developed engineering materials which shares the properties of both metals and glasses. They are glasses having metallic properties.
-
What are the advantages of using metallic glasses as transformer core material?
ANS: Metallic glasses are ferromagnetic. They possess low magnetic losses, high permeability and saturation magnetization with low coactivity. They also have extreme mechanical hardness and excellent initial permeability. These properties make them useful as transformer core materials. Moreover power transformers made of metallic glasses are smaller in size and efficient in their performance.