AI-powered call center solution with Azure and OpenAI GPT.
Send a phone call from AI agent, in an API call. Or, directly call the bot from the configured phone number!
Insurance, IT support, customer service, and more. The bot can be customized in few seconds (really) to fit your needs.
# Ask the bot to call a phone number
data='{
"bot_company": "Contoso",
"bot_name": "Amélie",
"phone_number": "+11234567890",
"task": "Help the customer with their digital workplace. Assistant is working for the IT support department. The objective is to help the customer with their issue and gather information in the claim.",
"agent_phone_number": "+33612345678",
"claim": [
{
"name": "hardware_info",
"type": "text"
},
{
"name": "first_seen",
"type": "datetime"
},
{
"name": "building_location",
"type": "text"
}
]
}'
curl \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--url https://xxx/call \
--data $dataNote
This project is a proof of concept. It is not intended to be used in production. This demonstrates how can be combined Azure Communication Services, Azure Cognitive Services and Azure OpenAI to build an automated call center solution.
- Access the claim on a public website
- Access to customer conversation history
- Allow user to change the language of the conversation
- Assistant can send SMS to the user for futher information
- Bot can be called from a phone number
- Bot use multiple voice tones (e.g. happy, sad, neutral) to keep the conversation engaging
- Company products (= lexicon) can be understood by the bot (e.g. a name of a specific insurance product)
- Create by itself a todo list of tasks to complete the claim
- Customizable prompts
- Disengaging from a human agent when needed
- Filter out inappropriate content from the LLM, like profanity or concurrence company names
- Fine understanding of the customer request with GPT-4o and GPT 4o-mini
- Follow a specific data schema for the claim
- Has access to a documentation database (few-shot training / RAG)
- Help the user to find the information needed to complete the claim
- Jailbreak detection
- Lower AI Search cost by usign a Redis cache
- Monitoring and tracing with Application Insights
- Receive SMS during a conversation for explicit wordings
- Responses are streamed from the LLM to the user, to avoid long pauses
- Send a SMS report after the call
- Take back a conversation after a disengagement
- Call back the user when needed
- Simulate a IVR workflow
A French demo is avaialble on YouTube. Do not hesitate to watch the demo in x1.5 speed to get a quick overview of the project.
Main interactions shown in the demo:
- User calls the call center
- The bot answers and the conversation starts
- The bot stores conversation, claim and todo list in the database
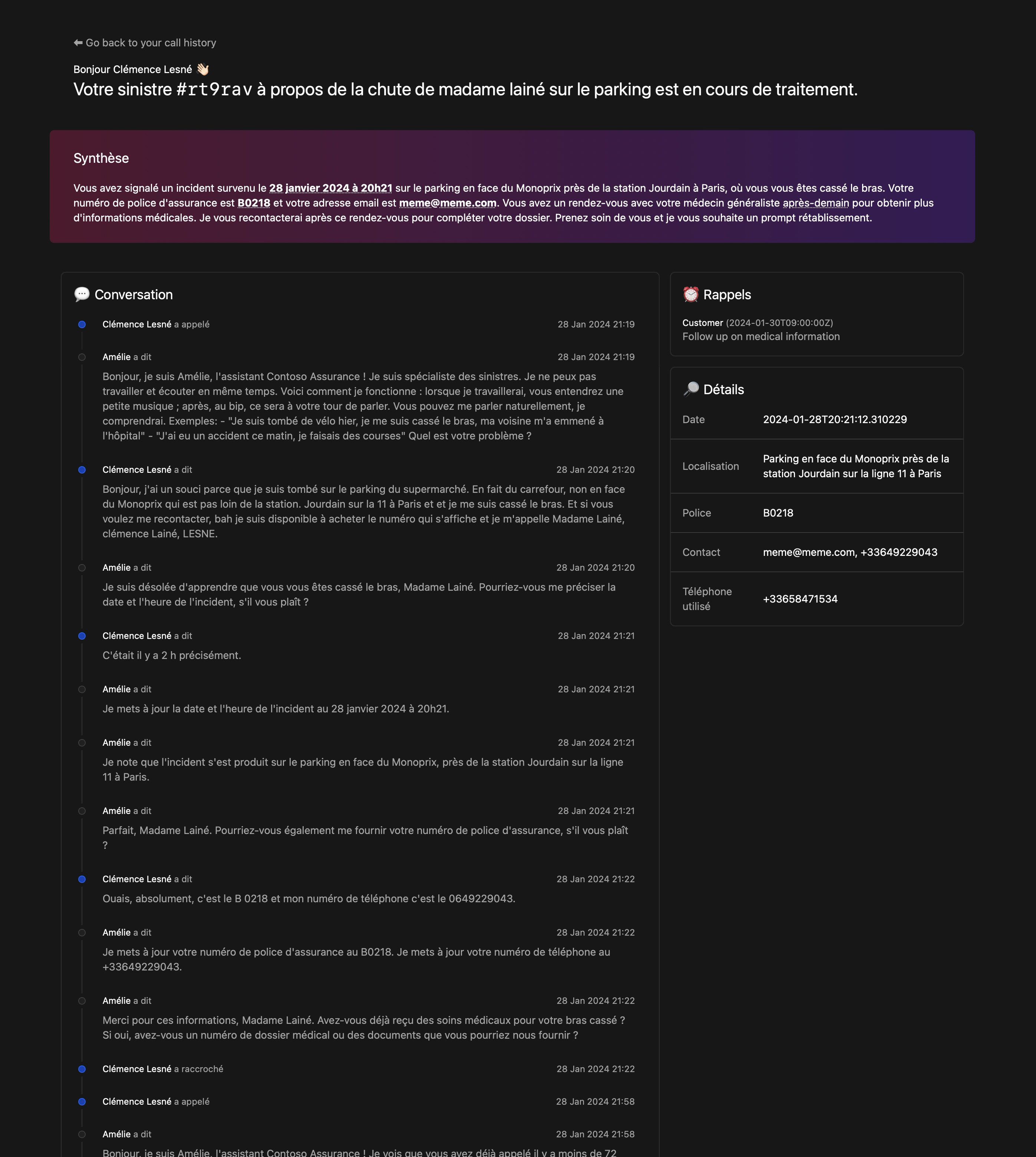
Extract of the data stored during the call:
{
"claim": {
"incident_date_time": "2024-01-11T19:33:41",
"incident_description": "The vehicle began to travel with a burning smell and the driver pulled over to the side of the freeway.",
"policy_number": "B01371946",
"policyholder_phone": "[number masked for the demo]",
"policyholder_name": "Clémence Lesne",
"vehicle_info": "Ford Fiesta 2003"
},
"reminders": [
{
"description": "Check that all the information in Clémence Lesne's file is correct and complete.",
"due_date_time": "2024-01-18T16:00:00",
"title": "Check Clémence file"
}
]
}A report is available at https://[your_domain]/report/[phone_number] (like http://localhost:8080/report/%2B133658471534). It shows the conversation history, claim data and reminders.
---
title: System diagram (C4 model)
---
graph
user(["User"])
agent(["Agent"])
app["Call Center AI"]
app -- Transfer to --> agent
app -. Send voice .-> user
user -- Call --> app
---
title: Claim AI component diagram (C4 model)
---
graph LR
agent(["Agent"])
user(["User"])
subgraph "Claim AI"
ada["Embedding\n(ADA)"]
app["App\n(Functions App)"]
communication_services["Call & SMS gateway\n(Communication Services)"]
db[("Conversations and claims\n(Cosmos DB / SQLite)")]
eventgrid["Broker\n(Event Grid)"]
gpt["LLM\n(GPT-4o)"]
queues[("Queues\n(Azure Storage)")]
redis[("Cache\n(Redis)")]
search[("RAG\n(AI Search)")]
sounds[("Sounds\n(Azure Storage)")]
sst["Speech-to-Text\n(Cognitive Services)"]
translation["Translation\n(Cognitive Services)"]
tts["Text-to-Speech\n(Cognitive Services)"]
end
app -- Respond with text --> communication_services
app -- Ask for translation --> translation
app -- Ask to transfer --> communication_services
app -- Few-shot training --> search
app -- Generate completion --> gpt
app -- Get cached data --> redis
app -- Save conversation --> db
app -- Send SMS report --> communication_services
app -. Watch .-> queues
communication_services -- Generate voice --> tts
communication_services -- Load sound --> sounds
communication_services -- Notifies --> eventgrid
communication_services -- Send SMS --> user
communication_services -- Transfer to --> agent
communication_services -- Transform voice --> sst
communication_services -. Send voice .-> user
eventgrid -- Push to --> queues
search -- Generate embeddings --> ada
user -- Call --> communication_services
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
actor Customer
participant PSTN
participant Text to Speech
participant Speech to Text
actor Human agent
participant Event Grid
participant Communication Services
participant App
participant Cosmos DB
participant OpenAI GPT
participant AI Search
App->>Event Grid: Subscribe to events
Customer->>PSTN: Initiate a call
PSTN->>Communication Services: Forward call
Communication Services->>Event Grid: New call event
Event Grid->>App: Send event to event URL (HTTP webhook)
activate App
App->>Communication Services: Accept the call and give inbound URL
deactivate App
Communication Services->>Speech to Text: Transform speech to text
Communication Services->>App: Send text to the inbound URL
activate App
alt First call
App->>Communication Services: Send static SSML text
else Callback
App->>AI Search: Gather training data
App->>OpenAI GPT: Ask for a completion
OpenAI GPT-->>App: Respond (HTTP/2 SSE)
loop Over buffer
loop Over multiple tools
alt Is this a claim data update?
App->>Cosmos DB: Update claim data
else Does the user want the human agent?
App->>Communication Services: Send static SSML text
App->>Communication Services: Transfer to a human
Communication Services->>Human agent: Call the phone number
else Should we end the call?
App->>Communication Services: Send static SSML text
App->>Communication Services: End the call
end
end
end
App->>Cosmos DB: Persist conversation
end
deactivate App
Communication Services->>PSTN: Send voice
PSTN->>Customer: Forward voice
Prefer using GitHub Codespaces for a quick start. The environment will setup automatically with all the required tools.
In macOS, with Homebrew, simply type make brew.
For other systems, make sure you have the following installed:
- Bash compatible shell, like
bashorzsh - yq
- Make,
apt install make(Ubuntu),yum install make(CentOS),brew install make(macOS) - Azure CLI
- Azure Functions Core Tools
- Twilio CLI (optional)
Then, Azure resources are needed:
- Prefer to use lowercase and no special characters other than dashes (e.g.
ccai-customer-a)
- Same name as the resource group
- Enable system managed identity
- From the Communication Services resource
- Allow inbound and outbound communication
- Enable voice (required) and SMS (optional) capabilities
Now that the prerequisites are configured (local + Azure), the deployment can be done.
File is named config.yaml:
# config.yaml
conversation:
initiate:
# Phone number the bot will transfer the call to if customer asks for a human agent
agent_phone_number: "+33612345678"
bot_company: Contoso
bot_name: Amélie
lang: {}
communication_services:
# Phone number purshased from Communication Services
phone_number: "+33612345678"
sms: {}
prompts:
llm: {}
tts: {}az loginmake deploy name=my-rg-name- Wait for the deployment to finish
- An index named
trainings - A semantic search configuration on the index named
default
make logs name=my-rg-nameTip
To use a Service Principal to authenticate to Azure, you can also add the following in a .env file:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID=xxx
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET=xxx
AZURE_TENANT_ID=xxxTip
If you already deployed the application to Azure and if it is working, you can:
- Copy the configuration from the Azure Function App to your local machine by using the content of the
CONFIG_JSONapplication setting - Then convert it to YAML format
File is named config.yaml:
# config.yaml
resources:
public_url: https://xxx.blob.core.windows.net/public
conversation:
initiate:
agent_phone_number: "+33612345678"
bot_company: Contoso
bot_name: Robert
communication_services:
access_key: xxx
call_queue_name: call-33612345678
endpoint: https://xxx.france.communication.azure.com
phone_number: "+33612345678"
post_queue_name: post-33612345678
resource_id: xxx
sms_queue_name: sms-33612345678
cognitive_service:
# Must be of type "AI services multi-service account"
endpoint: https://xxx.cognitiveservices.azure.com
llm:
fast:
mode: azure_openai
azure_openai:
api_key: xxx
context: 16385
deployment: gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
endpoint: https://xxx.openai.azure.com
model: gpt-4o-mini
streaming: true
slow:
mode: azure_openai
azure_openai:
api_key: xxx
context: 128000
deployment: gpt-4o-2024-08-06
endpoint: https://xxx.openai.azure.com
model: gpt-4o
streaming: true
ai_search:
access_key: xxx
endpoint: https://xxx.search.windows.net
index: trainings
ai_translation:
access_key: xxx
endpoint: https://xxx.cognitiveservices.azure.commake deploy-bicep deploy-post name=my-rg-name- This will deploy the Azure resources without the API server, allowing you to test the bot locally
- Wait for the deployment to finish
Copy local.example.settings.json to local.settings.json, then fill the required fields:
APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_CONNECTION_STRING, as the connection string of the Application Insights resourceAzureWebJobsStorage, as the connection string of the Azure Storage account
Important
Tunnel requires to be run in a separate terminal, because it needs to be running all the time
# Log in once
devtunnel login
# Start the tunnel
make tunnelNote
To override a specific configuration value, you can use environment variables. For example, to override the llm.fast.endpoint value, you can use the LLM__FAST__ENDPOINT variable:
LLM__FAST__ENDPOINT=https://xxx.openai.azure.comNote
Also, local.py script is available to test the application without the need of a phone call (= without Communication Services). Run the script with:
python3 -m tests.localmake dev- Code is automatically reloaded on file changes, no need to restart the server
- The API server is available at
http://localhost:8080
Training data is stored on AI Search to be retrieved by the bot, on demand.
Required index schema:
| Field Name | Type |
Retrievable | Searchable | Dimensions | Vectorizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| answer | Edm.String |
Yes | Yes | ||
| context | Edm.String |
Yes | Yes | ||
| created_at | Edm.String |
Yes | No | ||
| document_synthesis | Edm.String |
Yes | Yes | ||
| file_path | Edm.String |
Yes | No | ||
| id | Edm.String |
Yes | No | ||
| question | Edm.String |
Yes | Yes | ||
| vectors | Collection(Edm.Single) |
No | Yes | 1536 | OpenAI ADA |
Software to fill the index is included on Synthetic RAG Index repository.
The bot can be used in multiple languages. It can understand the language the user chose.
See the list of supported languages for the Text-to-Speech service.
# config.yaml
[...]
conversation:
initiate:
lang:
default_short_code: fr-FR
availables:
- pronunciations_en: ["French", "FR", "France"]
short_code: fr-FR
voice: fr-FR-DeniseNeural
- pronunciations_en: ["Chinese", "ZH", "China"]
short_code: zh-CN
voice: zh-CN-XiaoqiuNeuralIf you built and deployed an Azure Speech Custom Neural Voice (CNV), add field custom_voice_endpoint_id on the language configuration:
# config.yaml
[...]
conversation:
initiate:
lang:
default_short_code: fr-FR
availables:
- pronunciations_en: ["French", "FR", "France"]
short_code: fr-FR
voice: xxx
custom_voice_endpoint_id: xxxLevels are defined for each category of Content Safety. The higher the score, the more strict the moderation is, from 0 to 7. Moderation is applied on all bot data, including the web page and the conversation. Configure them in Azure OpenAI Content Filters.
Customization of the data schema is fully supported. You can add or remove fields as needed, depending on the requirements.
By default, the schema of composed of:
caller_email(email)caller_name(text)caller_phone(phone_number)
Values are validated to ensure the data format commit to your schema. They can be either:
datetimeemailphone_number(E164format)text
Finally, an optional description can be provided. The description must be short and meaningful, it will be passed to the LLM.
Default schema, for inbound calls, is defined in the configuration:
# config.yaml
[...]
conversation:
default_initiate:
claim:
- name: additional_notes
type: text
# description: xxx
- name: device_info
type: text
# description: xxx
- name: incident_datetime
type: datetime
# description: xxxClaim schema can be customized for each call, by adding the claim field in the POST /call API call.
The objective is a description of what the bot will do during the call. It is used to give a context to the LLM. It should be short, meaningful, and written in English.
This solution is priviledged instead of overriding the LLM prompt.
Default task, for inbound calls, is defined in the configuration:
# config.yaml
[...]
conversation:
initiate:
task: |
Help the customer with their insurance claim. Assistant requires data from the customer to fill the claim. The latest claim data will be given. Assistant role is not over until all the relevant data is gathered.Task can be customized for each call, by adding the task field in the POST /call API call.
Conversation options are documented in conversation.py. The options can all be overridden in config.yaml file:
# config.yaml
[...]
conversation:
answer_hard_timeout_sec: 180
answer_soft_timeout_sec: 30
callback_timeout_hour: 72
phone_silence_timeout_sec: 1
slow_llm_for_chat: true
voice_recognition_retry_max: 2To use a model compatible with the OpenAI completion API, you need to create an account and get the following information:
- API key
- Context window size
- Endpoint URL
- Model name
- Streaming capability
Then, add the following in the config.yaml file:
# config.yaml
[...]
llm:
fast:
mode: openai
openai:
api_key: xxx
context: 128000
endpoint: https://api.openai.com
model: gpt-4o-mini
streaming: true
slow:
mode: openai
openai:
api_key: xxx
context: 128000
endpoint: https://api.openai.com
model: gpt-4o
streaming: trueTo use Twilio for SMS, you need to create an account and get the following information:
- Account SID
- Auth Token
- Phone number
Then, add the following in the config.yaml file:
# config.yaml
[...]
sms:
mode: twilio
twilio:
account_sid: xxx
auth_token: xxx
phone_number: "+33612345678"Note that prompt examples contains {xxx} placeholders. These placeholders are replaced by the bot with the corresponding data. For example, {bot_name} is internally replaced by the bot name.
Be sure to write all the TTS prompts in English. This language is used as a pivot language for the conversation translation.
# config.yaml
[...]
prompts:
tts:
hello_tpl: |
Hello, I'm {bot_name}, from {bot_company}! I'm an IT support specialist.
Here's how I work: when I'm working, you'll hear a little music; then, at the beep, it's your turn to speak. You can speak to me naturally, I'll understand.
Examples:
- "I've got a problem with my computer, it won't turn on".
- "The external screen is flashing, I don't know why".
What's your problem?
llm:
default_system_tpl: |
Assistant is called {bot_name} and is in a call center for the company {bot_company} as an expert with 20 years of experience in IT service.
# Context
Today is {date}. Customer is calling from {phone_number}. Call center number is {bot_phone_number}.
chat_system_tpl: |
# Objective
Provide internal IT support to employees. Assistant requires data from the employee to provide IT support. The assistant's role is not over until the issue is resolved or the request is fulfilled.
# Rules
- Answers in {default_lang}, even if the customer speaks another language
- Cannot talk about any topic other than IT support
- Is polite, helpful, and professional
- Rephrase the employee's questions as statements and answer them
- Use additional context to enhance the conversation with useful details
- When the employee says a word and then spells out letters, this means that the word is written in the way the employee spelled it (e.g. "I work in Paris PARIS", "My name is John JOHN", "My email is Clemence CLEMENCE at gmail GMAIL dot com COM")
- You work for {bot_company}, not someone else
# Required employee data to be gathered by the assistant
- Department
- Description of the IT issue or request
- Employee name
- Location
# General process to follow
1. Gather information to know the employee's identity (e.g. name, department)
2. Gather details about the IT issue or request to understand the situation (e.g. description, location)
3. Provide initial troubleshooting steps or solutions
4. Gather additional information if needed (e.g. error messages, screenshots)
5. Be proactive and create reminders for follow-up or further assistance
# Support status
{claim}
# Reminders
{reminders}At the time of development, no LLM framework was available to handle all of these features: streaming capability with multi-tools, backup models on availability issue, callbacks mechanisms in the triggered tools. So, OpenAI SDK is used directly and some algorithms are implemented to handle reliability.