This is the three-dimensional electromagnetic field analysis program for arbitrary objects irradiated by arbitrary beams. This is the extension of "bem3_emf_b1" using iterative solution. This program can analyze multiple scattering between objects with less memory than "bem3_emf_b1". Intel Math Kernel Library and libpng are required. Gmsh is used for create a mesh data of object. The electromagnetic field analysis program "multi_fbeam" is used for analyze incident field.
-
type 'make' command to compile.
The executable d3b2_create_matrix, d3b2_bv_solver, example1.out, example2.out, example3.out, example4.out are created. The executable d3b2_create_matrix is the solver of boundary integral equations, it outputs coefficient matrices and its inverse matrices. The executable d3b2_bv_solver is the sovler for boundary value, it analyzes multiple scattering using iterative solution when defined multiple objects. The example1.out is the executable of source code example1.c, it shows a simplest example using "bem3_emf_b2". The example2.out is the execubable of source code example2.c, it shows a example of electromagnetic field intensity analysis. The example3.out is the executable of source code example3.c, it shows a example of outputting the instantaneous value of electromagnetic field as an image. The example4.out is the executable of source code example4.c, it shows a example of far-field intensity analysis. -
type './d3b2_create_matrix' with arguments of medium datafile name, mesh datafile name, output object datafile name, rotation and translation settings (optional).
For example, './d3b2_create_matrix medium_data.txt cone_m1.msh cone_m1_md_x00.obj',
'./d3b2_create_matrix medium_data.txt cone_m1.msh cone_m1_md_xpi.obj 1 0 0 3.14159265 0 0 0'.
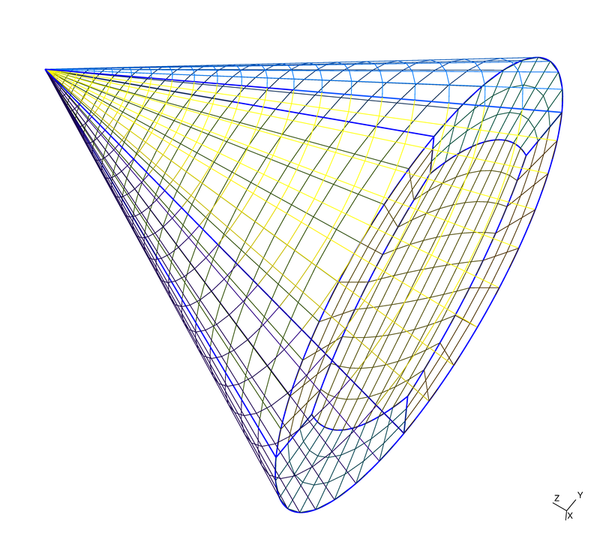
In the second case, the rotation axis is x-axis, the rotation angle is 3.14159265 (Rodrigues' rotation formula is used), the translation vector is zero-vector. The medium_data.txt is the sample of medium datafile, one medium is defined in it. The domain numbers are assigned to the medium from 1 in order. The cone_m1.msh is the sample of mesh datafile, it is a cone object. It was created by Gmsh geometry file cone_m1.geo in the mesh_sample folder. The cone_m1_image.png is the visualization result of the cone_m1.msh (using Gmsh). The ipw.txt is the sample of incident field datafile, a plane-wave is defined in it. Please refer to the "multi_fbeam" for detail. The d3b2_create_matrix outputs object datafile, coefficient matrices and its inverse matrices (binary file with the .cmat file extention) with the specified datafile name. -
type './d3b2_bv_solver' with arguments of object setting datafile name, output datafile name.
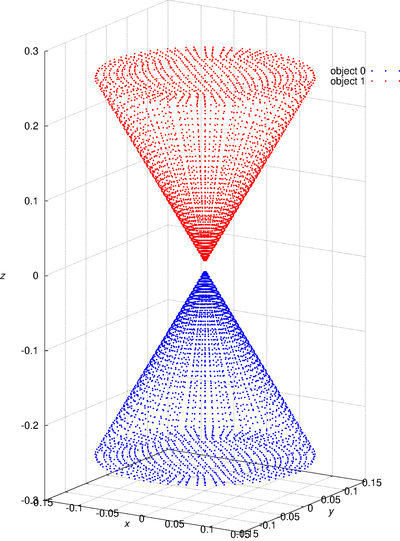
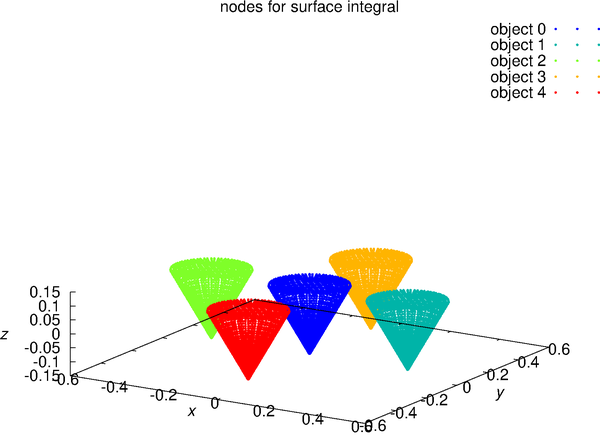
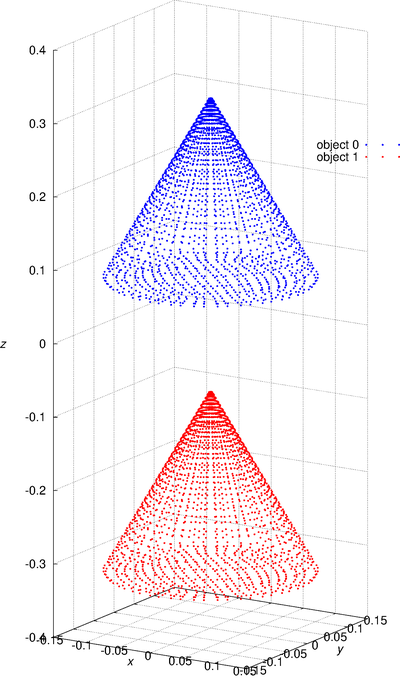
For example, './d3b2_bv_solver object_settings.txt ex.dat'. The object_settings.txt is the sample of object setting datafile, two cone objects defined in it. The objects are set by using the output object datafile name and an additional translation vector. The setting of reset_flag_of_incident_field in object setting datafile can reset the incident field. It can change the incident field, except the wavelength and refractive index. As a simple representation of the analysis model, the nodes used for the surface integral are output as point cloud data. In this case, the file "ex.particles" is output, and the visualization result is "ex_particle.png". The image was created using gnuplot script "gscript_particles.plt" and converted eps to png by using ImageMagick. -
type './example1.out' with an argument of datafile name output by d3b2_bv_solver.
For example, './example1.out ex.dat'. This executable calculates electromagnetic field, radiation force and torque. -
type './example2.out' with an arguemnt of datafile name output by d3b2_bv_solver.
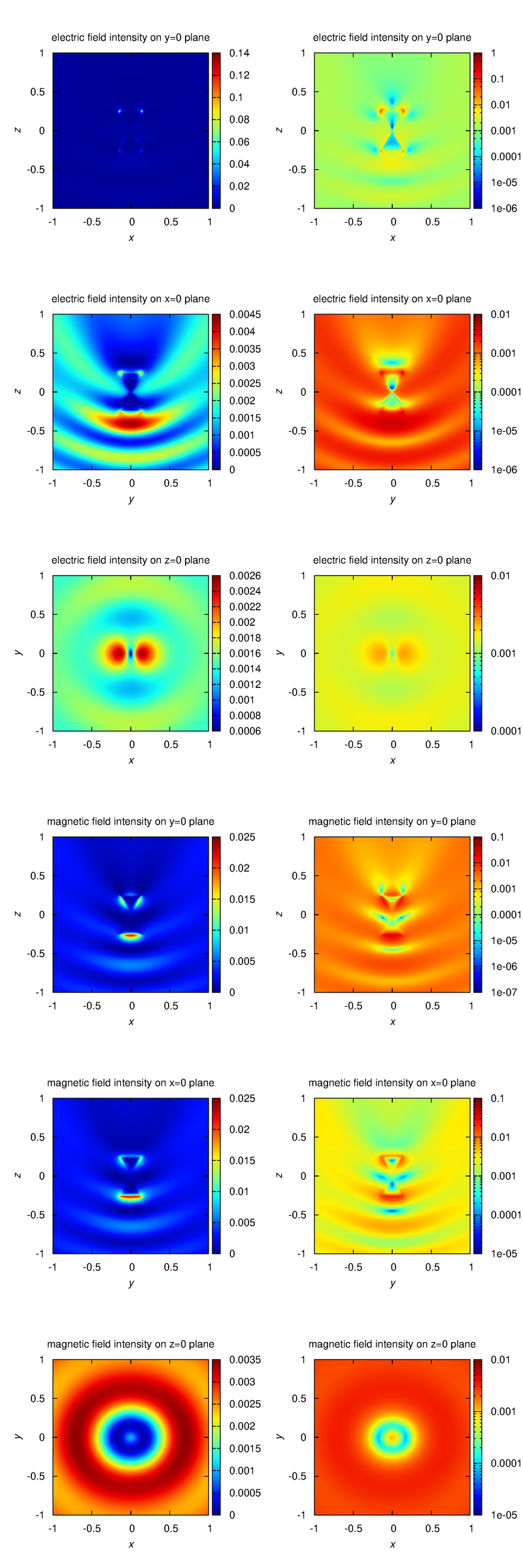
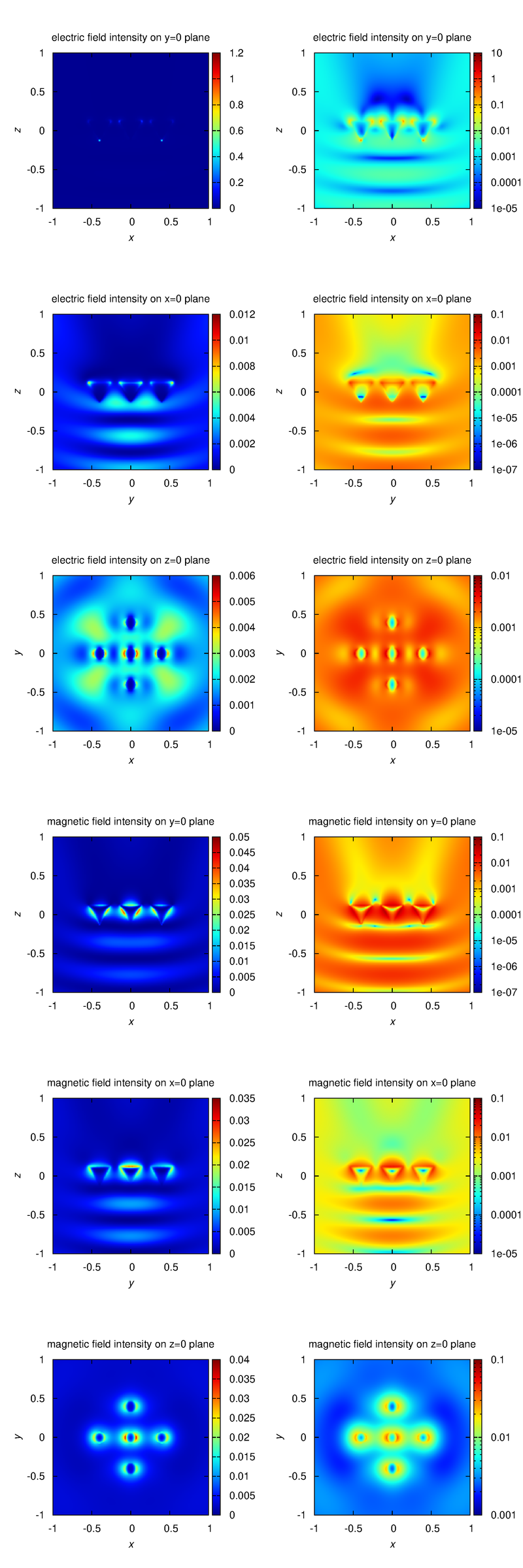
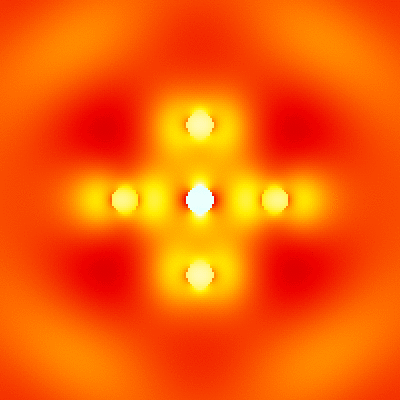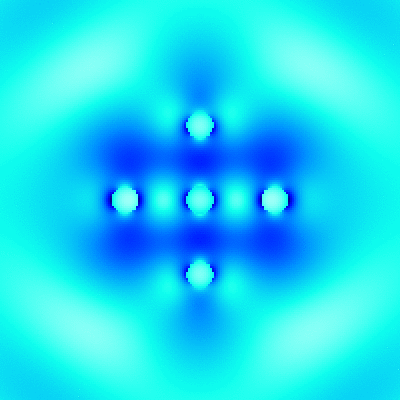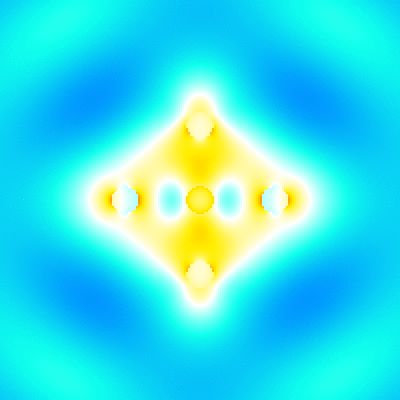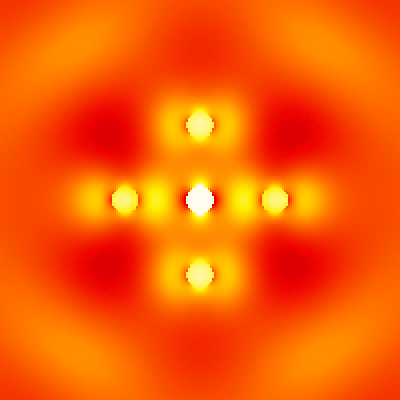
For example, './example2.out ex.dat'. This executable calculates electromagnetic field intensity distributions, outputs them to text files. The I_example2_logcb.png is the visualization result of intensity distributions, created by Gnuplot script gscript_example2_logcb.plt (using ImageMagick to convert eps to png). -
type './example3.out' with an argument of datafile name output by d3b2_bv_solver.
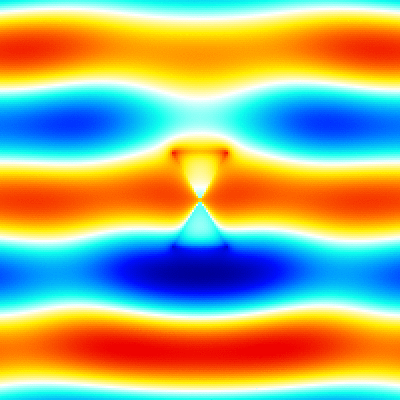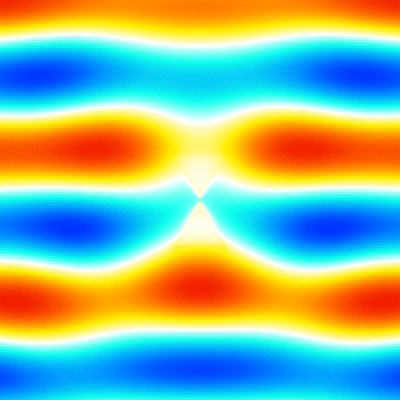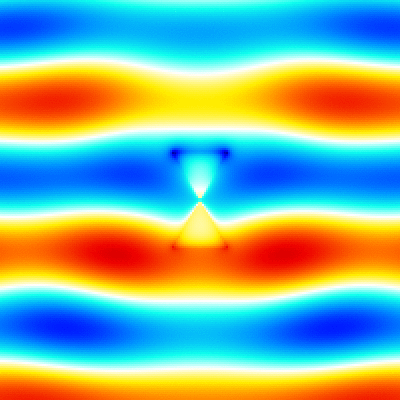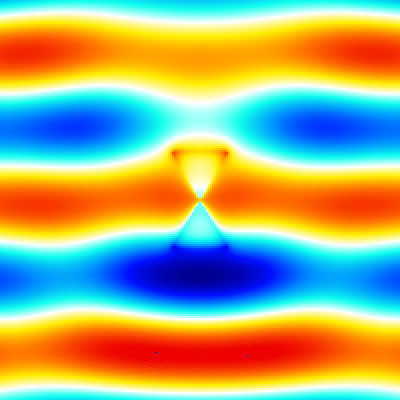
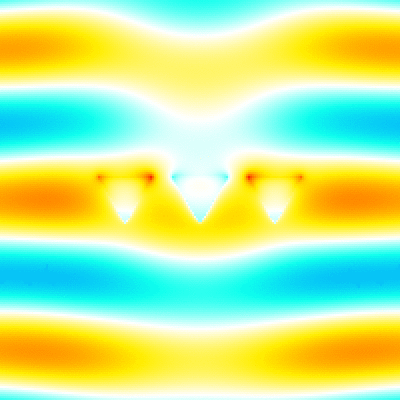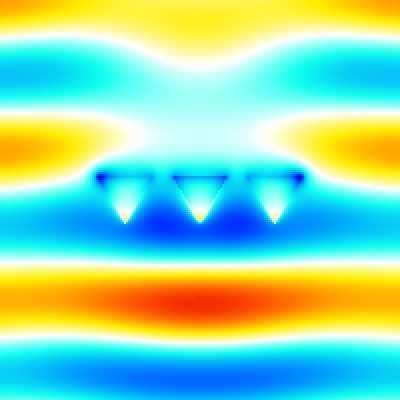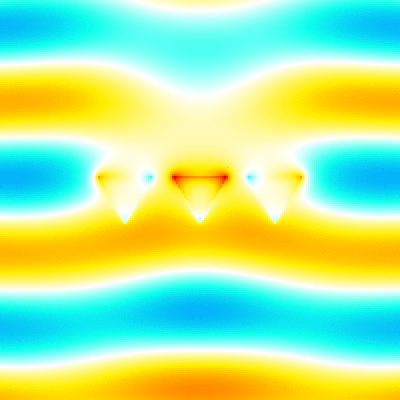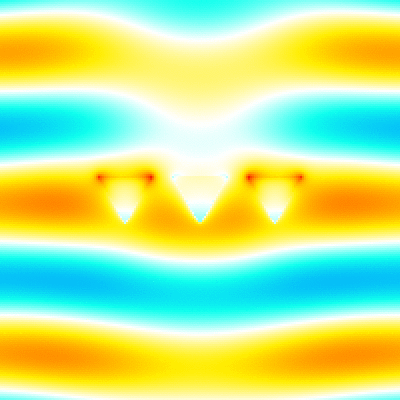
For example, './example3.out ex.dat'. This executable calculates instantaneous value of the electromagnetic fields, outputs them to png image files. The image files are output to the folder which has a name adding "images" to the datafile name specified in the argument (file-extension is excluded). Each image file has a name that indicates the cross section, field component, and number of time steps (ex. xz_Ex_014.png). The color bar is output as color_bar.png in the same folder. The range of color bar in each cross section is output to the info.txt file (ex. xy_info.txt for z=0 plane). The xz_Ex.gif, yz_Ex.gif and xy_Ex.gif are animated gifs that concatenate the png files created by using the shell script gif_animation.sh. -
type './example4.out' with an argument of datafile name output by d3b2_bv_solver.
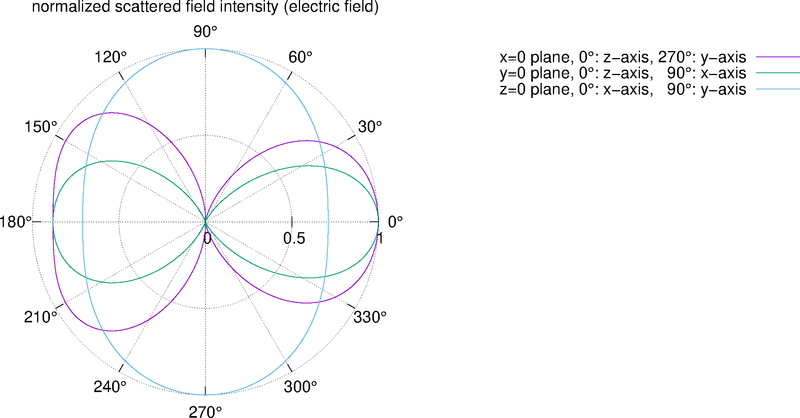
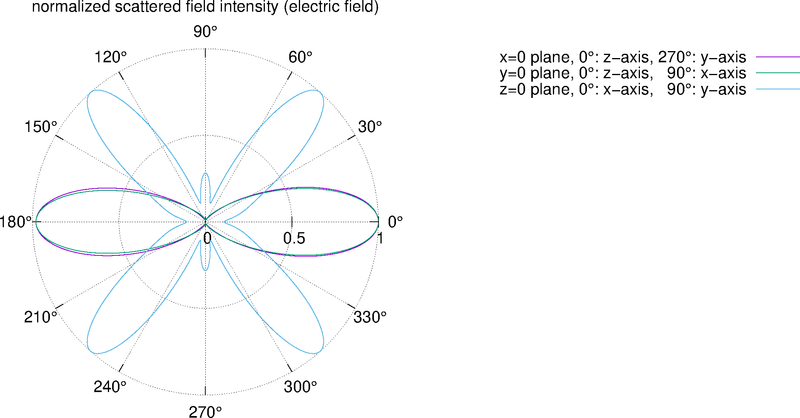
For example, './example4.out ex.dat'. This executable calculates far-field intensity distributions and outputs them to text files. The I_example4.png is the visualization result of electric field intensity distributions, created by gnuplot script gscript_example4.plt.
Please see d3b2_src/bem3_emf_b2.h for detail of functions. The main parts of the code are parallelized by using OpenMP. The number of threads is controlled by the environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS.
This is the analysis result of plane wave scattering by the five cone objects. The object datafile is the same as the above example.
The verification results are in the folder verification1 and verification2. The results in the folder verification1 are the analysis results of two cone objects using two different method. The one uses the iterative solution and the other uses the combined object (in the folder combined_object). The results in the folder verification2 are the analysis results of three sphere objects. The results using the code "emf_mie_ms" is in the folder emf_mie_ms_result.
This code can use quadrangular ( bi-linear ) and triangular ( linear triangular ) elements. I recommend using quadrangular element for reduce required memory. The samples of mesh data are in the folder mesh_sample. The file with extension .geo is the Gmsh geometry file. The file with extension .msh is the mesh datafile created by using Gmsh geometry file. These mesh files are created by the command 'gmsh -2 -tol 1.0e-15 -format msh2 xxxx.geo' in command line ( xxxx.geo is a geometry file). The domain number (Physical Surface) 99 is assigned to the open region in Gmsh geometry file, because Gmsh can't use the number 0 (assigned to open region in the code). Please refer to the manual of Gmsh for detail of geometry file.
This program use the own defined system of units (OSU), optimized for optics.
The system of units is defined as ( speed of light in vacuum ),
( permeability of vacuum ).
For the conversion from OSU to MKSA system of units, the unit of length in OSU is defined as
[m] in MKSA, the unit of power in OSU is defined as
[W] in MKSA. The conversions of base unit are follows.
,
,
,
,
,
.
Please see com_src/osu_mksa.h and com_src/osu_mksa.c for detail of conversions.
- Intel Math Kernel Library MKL
- The official PNG reference library libpng
- Three-dimensional mesh generator Gmsh
- The command-line driven graphing utility gnuplot
- The utilities for manipulating images ImageMagick
- The electromagnetic field analysis program multi_fbeam
- The electromagnetic field analysis program bem3_emf_b1
- The electromagnetic field analysis program emf_mie_ms