This repository is currently undergoing active development. Functionality may be in flux
The OpenShift Container Platform ecosystem contains mechanisms for securely managing container images. This includes but is not limited to image signing and image scanning.
A set of Ansible tools is available to aid in the automation and configuration of the target environment.
Image signing is a way to apply a digital signature to a container image. This guide describes how an automated process can be created an implemented within OpenShift. The goal is to produce an environment that allows for only the execution of signed images from trusted sources (Red Hat Container Catalog [RHCC]) along with assets that are created within an organization or group.
Image scanning is a process for inspecting the composition of a container image for vulnerabilities or threats. While there are a number of tools on the market today, this guide will describe how image scanning can be utilized to verify the content of images prior to their deployment into a production environment.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a concept representing computer systems through programming constructs instead of of physical hardware. When used in combination with automation tools, such as Ansible, it provides the ability to repeatably apply components in a rapid manner.
Two architectures will be presented in order to highlight the concepts of image signing and image scanning:
- Automated image scanning leveraging the controller pattern. Images that are built on the OpenShift platform are automatically scanned as they are pushed to the integrated Docker registry.
- Inclusion of image signing and image scanning as part of a Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
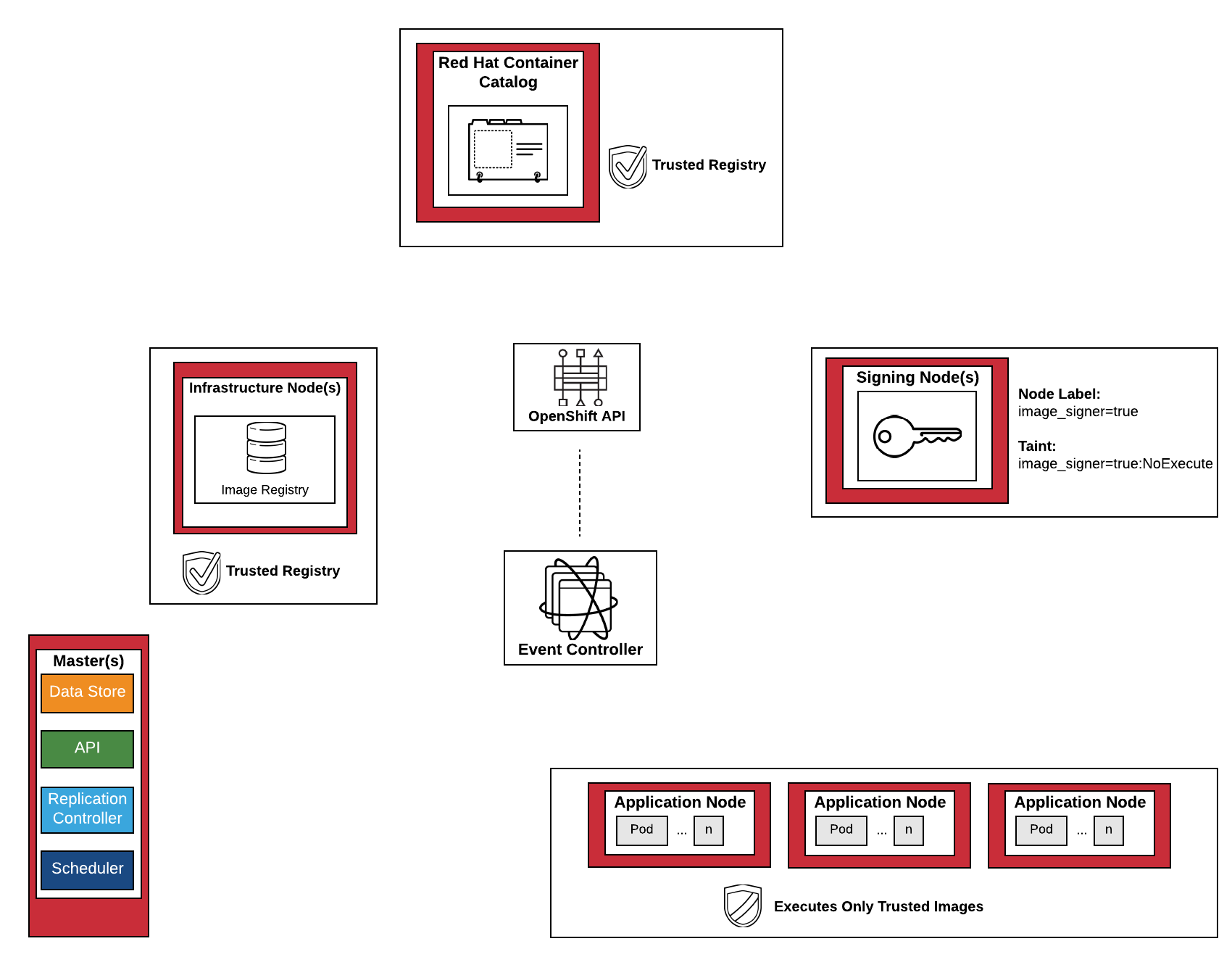
Both architectures utilize a typical OpenShift environment by specifying dedicated nodes for performing image management actions. The key difference between image management nodes and the rest of the nodes in the environment is relaxing the image requirement policies to allow for signing actions to occur on these nodes.
Two ways to ensure only image management workloads are scheduled onto these dedicated nodes is through Node Selectors placed on image management resources and tainting image management nodes. Image management resources are configured with tolerations to allow execution on the tainted nodes.
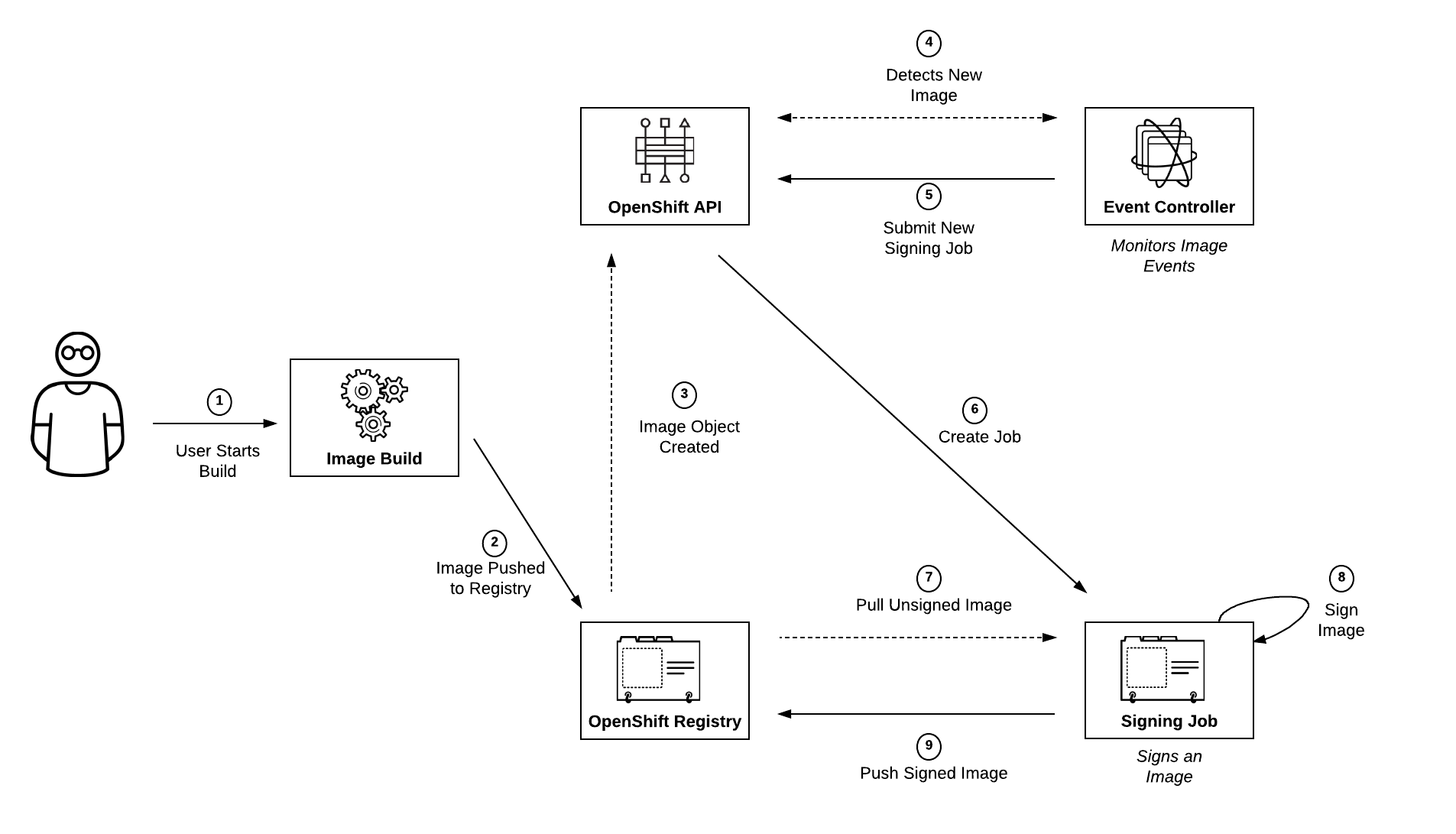
Deployment of a controller which monitors the OpenShift API at a cluster level. When an image is pushed to the integrated Docker registry, a process is initiated to sign the image with a previously configured assets configured within the environment. Images will be forbidden from executing within the environment until it has undergone a signing action either from the event controller process or have originated from a trusted container registry (Red Hat Container Catalog).
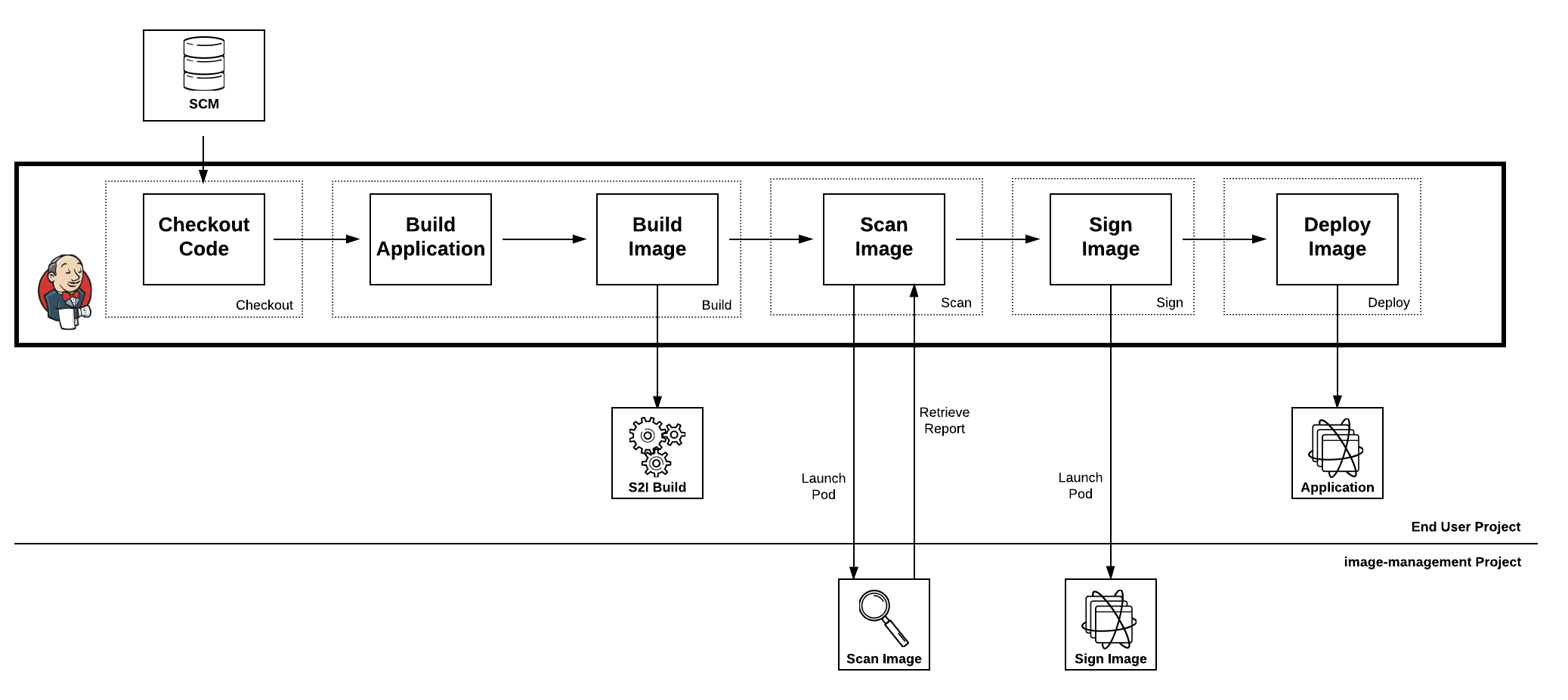
Implementation of image scanning and image signing as part of a Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) process using the Jenkins pipeline as code concept. Source code is retrieved from a source code management tool which is then compiled and packaged into an artifact. The artifact is packaged into a Docker image through the execution of the Source-To-Image build process. Once complete, the resulting image is scanned for vulnerabilities. The end user is provided the ability to review the results of the scan and decide whether to continue or abort the pipeline. If approved, the image is signed using the tools previously configured in the environment and then is ultimately deployed.
A set of Ansible playbooks and roles is available to automate the configuration of an OpenShift environment for the tooling provided by here. The following are actions which are performed in the automation tooling:
- Creation of GPG keys
- Configuration of OpenShift host machines to enable signature verification along with trusted sources
- Deployment of OpenShift cluster resources to host image signing resources
- Building a base image containing tooling to perform image signing and image scanning tasks
- Deployment of the image signing event controller if the controller pattern is chosen
- Deployment of the assets to support
The inventory file is broken down into 3 (three) host groups:
- gpg - Machine responsible for creating GPG keys
- image_managers - OpenShift nodes responsible for signing images
- masters - OpenShift masters. At least one host is required in order to execute actions using the OpenShift API
- nodes - All OpenShift nodes
The OpenShift environment can be configured by executing the image-signing-scanning-setup.yml playbook in the ansible/playbooks folder.
By default, the Image Scanning and Signing Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery Pipeline architecture is deployed. To instead deploy the Automated Scanning using the Controller Pattern architecture, set the deploy_eventcontroller=false inventory variable.
When ready, execute the following command from within the playbooks directory to initiate the setup:
ansible-playbook -i hosts image-signing-scanning-setup.yml
Once the playbook completes, the OpenShift environment will be configured to handle image scanning, signing and execution.