Features • Development • Usage • License • Contribution
- Written in Kotlin
- No boilerplate code
- Easy initialization
- Supports Lottie, Gifs, Images and more
- Written for Jetpack Compose
- Add the JitPack repository to your project's build.gradle file
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
- Add the dependency in your app's build.gradle file
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.akshaaatt:Dialogs-Android:2.0.0'
}
- Prerequisite: Latest version of the Android Studio and SDKs on your pc.
- Clone this repository.
- Use the
gradlew buildcommand to build the project directly or use the IDE to run the project to your phone or the emulator.
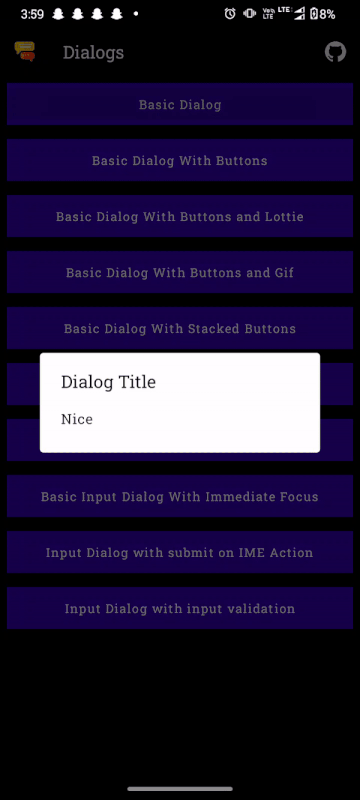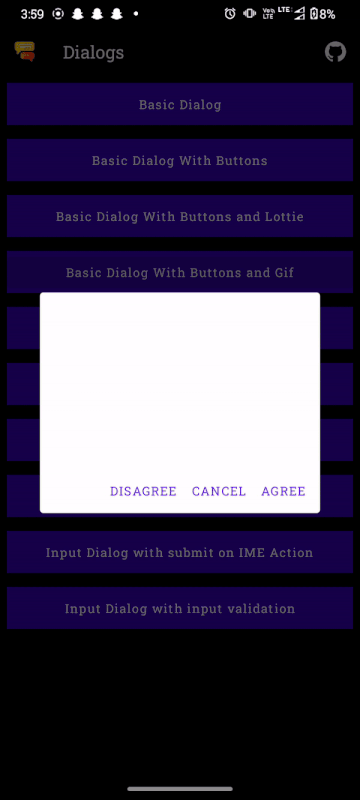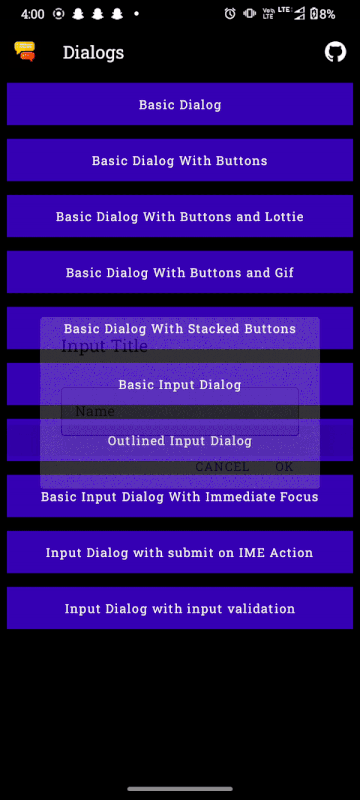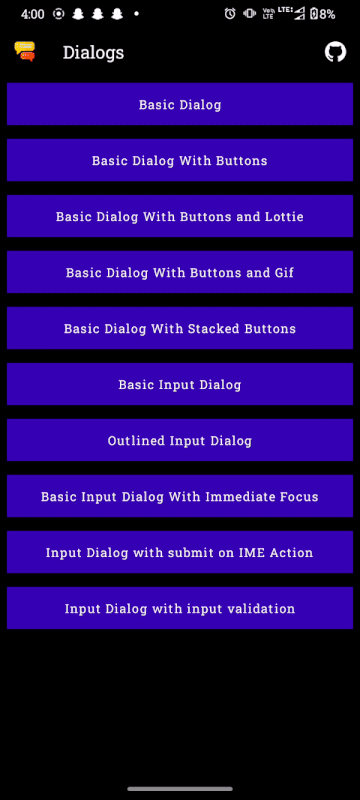
val dialogState = rememberMaterialDialogState()
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState) {
title(text = "Use Location Services?")
message(res = R.string.location_dialog_message)
}
/* This should be called in an onClick or an Effect */
dialog.show()The dialog is shown when the dialog.show() is called. The hard coded strings for all the components in the example above can be replaced with a string resource id.
Buttons can be added to the dialog by adding the buttons parameter:
MaterialDialog(
dialogState = dialogState,
buttons = {
positiveButton("Ok")
negativeButton("Cancel")
}
) {
...
}If the text of the buttons is too long to fit in one row the buttons will be automatically stacked on top on one another.
Input Dialogs
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState, buttons = { ... }) {
...
input(label = "Name", placeholder = "Jon Smith") { inputString ->
/* Do something */
}
...
}In the code snippet above creates the dialog seen in the image (without the title). Once an input is entered and the user presses the positive button, the dialog will callback with the string the user inputted. The input function also has other parameters which can be found in the comment above the input function implementation. You can also change the style of the dialog by making use of the textFieldStyle parameter. For example, the following code can be used for an outlined text field:
input(label = "Name", placeholder = "Jon Smith", textFieldStyle = TextFieldStyle.Outlined) { inputString ->
/* Do something */
}List Dialogs
Below is an example of a plain list dialog:
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState) {
...
listItems(listOf("Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3"), onClick { index, item ->
//Do Something
})
...
}If you would like to use a custom list item layout you can use the following code:
data class TextIcon(text: String, icon: ImageAsset)
val items = listOf(
TextIcon("Item 1", imageFromResource(R.drawable.item_one))
TextIcon("Item 2", imageFromResource(R.drawable.item_two))
TextIcon("Item 3", imageFromResource(R.drawable.item_three))
)
...
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState) {
...
listItems(items, onClick { index, item ->
//Do Something
}) {
Row {
Box(Modifier.preferedSize(40.dp)) {
Image(it.icon)
}
Text(it.text, modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 12.dp))
}
}
...
}Single Choice List
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState, buttons = { ... }) {
listItemsSingleChoice(
list = listOf("Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3"),
disabledIndices = listOf(1),
initialSelection = 2
) {
//Do Something
}
}As seen in the code snippet above you can pass in a list of indices of items which should be disabled (ie. cannot be selected) and the item index which should selected to start with. By default, if no initial selection is given it will default to the first item.
Multiple Choice List
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState, buttons = { ... }) {
listItemsSingleChoice(
list = listOf("Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3"),
disabledIndices = listOf(1),
initialSelection = listOf(1)
) {
//Do Something
}
}As seen in the code snippet above you can select which items will be disabled (ie. cannot be selected) and also a list of item indicies which should be initially selected.
Custom View
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState, buttons = { ... }) {
customView {
//Define your view here
}
}The custom view provides a box with the appropriate material design padding's assigned to it so that your content. If you don't want the padding you can just put your composable anywhere in the dialog.build scope and it will be displayed as normal.
Theming
The background colour of the dialog can be changed by using the backgroundColor parameter of the build function:
MaterialDialog(dialogState = dialogState, buttons = { ... }, backgroundColor = Color.Red) {
title(text = "Use Location Services?")
message(res = R.string.location_dialog_message)
}The shape of the dialog is defaulted to the MaterialTheme.shapes.medium property but can also be set using the shape parameter in MaterialDialog .
This Project is licensed under the GPL version 3 or later.
You are most welcome to contribute to this project!