kubewatch is a Kubernetes watcher that currently publishes notification to Slack. Run it in your k8s cluster, and you will get event notifications in a slack channel.
Create a new Bot: https://my.slack.com/services/new/bot
Edit the Bot to customize its name, icon and retrieve the API token (it starts with xoxb-).
Invite the Bot into your channel by typing: /join @name_of_your_bot in the Slack message area.
When you have helm installed in your cluster, use the following setup:
helm install kubewatch stable/kubewatch --set='rbac.create=true,slack.channel=#YOUR_CHANNEL,slack.token=xoxb-YOUR_TOKEN,resourcesToWatch.pod=true,resourcesToWatch.daemonset=true'You may also provide a values file instead:
rbac:
create: true
resourcesToWatch:
daemonset:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
deployment:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
pod:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: true
replicaset:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
replicationcontroller:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
services:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
secret:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
configmap:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
slack:
channel: '#YOUR_CHANNEL'
token: 'xoxb-YOUR_TOKEN'And use that:
$ helm upgrade --install kubewatch stable/kubewatch --values=values-file.ymlIn order to run kubewatch in a Kubernetes cluster quickly, the easiest way is for you to create a ConfigMap to hold kubewatch configuration. It contains the SLACK bot API token and channel to use.
An example is provided at kubewatch-configmap.yaml, do not forget to update your own slack channel and token parameters. Alternatively, you could use secrets.
Create k8s configmap:
$ kubectl create -f kubewatch-configmap.yamlCreate the Pod directly, or create your own deployment:
$ kubectl create -f kubewatch.yamlA kubewatch container will be created along with kubectl sidecar container in order to reach the API server.
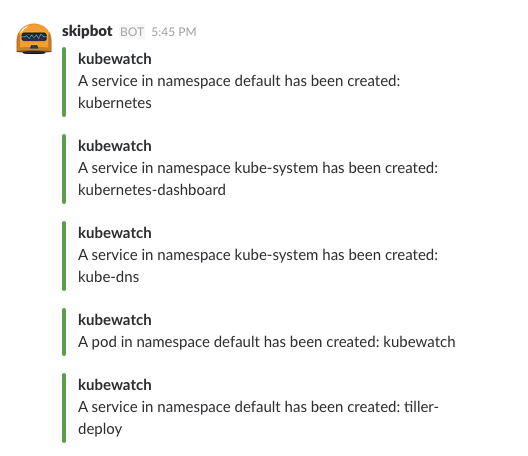
Once the Pod is running, you will start seeing Kubernetes events in your configured Slack channel. Here is a screenshot:
To modify what notifications you get, update the kubewatch ConfigMap and turn on and off (true/false) resources:
resource:
deployment:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
replicationcontroller:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
replicaset:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: true
daemonset:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
services:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
pod:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
secret:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
configmap:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
ingress:
watch: true
events:
create: true
update: true
delete: false
Kubernetes Engine clusters running versions 1.6 or higher introduced Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). We can create ServiceAccount for it to work with RBAC.
$ kubectl create -f kubewatch-service-account.yamlIf you do not have permission to create it, you need to become a admin first. For example, in GKE you would run:
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=REPLACE_EMAIL_HERE
Edit kubewatch.yaml, and create a new field under spec with serviceAccountName: kubewatch, you can achieve this by running:
$ sed -i '/spec:/a\ \ serviceAccountName: kubewatch' kubewatch.yamlThen just create pod as usual with:
$ kubectl create -f kubewatch.yaml- you need go v1.5 or later.
- if your working copy is not in your
GOPATH, you need to set it accordingly.
$ go build -o kubewatch main.goYou can also use the Makefile directly:
$ make build$ make docker-image
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
kubewatch latest 919896d3cd90 3 minutes ago 27.9MB$ go get -u github.com/bitnami-labs/kubewatchKubewatch supports config command for configuration. Config file will be saved at $HOME/.kubewatch.yaml
$ kubewatch config slack --channel <slack_channel> --token <slack_token>$ kubewatch config flock --url <flock_webhook_url>// rc, po and svc will be watched
$ kubewatch config resource --rc --po --svc
// only svc will be watched
$ kubewatch config resource --svcYou have an altenative choice to set your SLACK token, channel via environment variables:
$ export KW_SLACK_TOKEN='XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX'
$ export KW_SLACK_CHANNEL='#channel_name'You have an altenative choice to set your FLOCK URL
$ export KW_FLOCK_URL='https://api.flock.com/hooks/sendMessage/XXXXXXXX'$ kubewatch