Ionicitude
AngularJS module for using the Wikitude cordova plugin in an Ionic project.
Table of content
- Introduction
- Installing the Cordova Wikitude plugin
- Installing Ionicitude
- Initialization
- Checking Device's Features
- Execute code only when ready
- Launching an AR World
- Interaction between the Ionic app and the AR View
- API Definition
- Demo Application
- Contribution and Issues
- License
Introduction
This bower package is designed for Ionic developers that wants to use the cordova Wikitude plugin to add Augmented Reality (AR) in their app. It provides an Angular Service, named Ionicitude, with a simple API to interact with the cordova plugin, wether it be setting it, launching it or handling the AR Views' requests (more about that later).
Disclaimer
Please note that this project is not developped in association with or related to neither the Ionic team nor the Wikitude team.
What is the cordova Wikitude plugin?
It's a plugin that allows users to experience Augmented Realtity on their device through an hybrid Cordova (or Ionic in our case) app. This AR experience can rely on user's location (think Ingress) or on images recognition and tracking, or both. The possibilities are quite impressive and I encourage you to take a look at the official Demo app to grasp the extent of what can be accomplish with the plugin.
An AR Experience is, in the end, nothing more than a bunch of HTML/CSS/JS files. This set of files is called ARchitect World by the Wikitude staff.
Since it's quite a pain to type, I'll call them AR World throughout the rest of this README.
Important note
Installing the Cordova Wikitude plugin
Since Ionicitude is a service that uses the cordova Wikitude plugin, you'll need to first install the plugin on your project. Do it with the following command (that can take a while: it's a heavy plugin):
ionic plugin add https://github.com/Wikitude/wikitude-cordova-plugin.git
Wikitude Licence Key
To use the Wikitude plugin, you have to have a valid licence key. You can obtain one by registering on the Wikitude site (top-right of the screen), logging in, and accessing the licence key management page. Here, you can download a free trial licence key for the Wikitude SDK.
Note that the free trial let's you use all the plugin functionnality (geo and 2dtracking) without any time limit, but put a splash screen before every AR World launch and a big "Trial" watermark all over your screen. This is apparently not the case with a paid licence key.
The downloaded file is juste a plain text file containing your licence key.
Copy it, go to the WikitudePlugin.js file (located in your app structure at plugins/com.wikitude.phonegap.WikitudePlugin/www/WikitudePlugin.js) and paste it as the value to this._sdkKey on line 11.
Note : If you already installed any platform to your project, you'll need to install them again for the plugin modification to propagate (see next point for android platform).
Android platform version ^5.0.0
If you want your Ionic app to build correctly for android, with the cordova Wikitude plugin installed, it's absolutely imperative that you add the android platform with at least its 5.0.0 version. Otherwise your build will fail.
You didn't add any platform ?
That's cool. But, when you do, don't forget to do it with:
ionic platform add android@5.0.0
You already added your platform(s) ?
Hey, no prob'. You can check your installed android platform version with...
ionic platform
...and if it's lower than 5.0.0, you can update it:
ionic platform update android@5.0.0
How to check it worked
When it's done, you can check that everything's OK by typing this command (and crossing your fingers):
ionic build android
If you see an easing BUILD SUCCESSFULL at the end of the process, congrats! Your app is building.
Known Android bugs
Please, be advised that I've been confronted, when using the Wikitude plugin, to some awkwards bugs on Android devices regarding the back button handling from within an AR View, and the user location tracking lifecycle. If you encouter them or any other bugs related to the Wikitude plugin, please go on the Github Wikitude repo or on the Wikitude Developer Forum (you'll need to register).
Having mostly developped with Ionic on Android, I don't know if these bugs also impact iOS builds. From the few tests that I've done, it's apparently not the case.
Installing Ionicitude
OK
1a. With ionic add
Using any command ligne tool, go to your app's root directory and type:
ionic add tazaf/ionicitude
or
bower install --save-dev tazaf/ionicitude
After some download, Ionicitude will be installed on your project. The files will be locate in www/lib/ionicitude.
You will then need to add the following line in your app's index.html, after the calls to ionic.bundle.js and cordova.js :
<script src="lib/ionicitude/dist/ionicitude.min.js"></script>Or, if you want the humanly readable version :
<script src="lib/ionicitude/dist/ionicitude.js"></script>1b. Manually
You can simply download the latest version of this project on your computer and place it wherever you like in your project. Then, locate either the ionicitude.min.js file or the ionicitude.js file, both being in the dist folder of the downloaded project, and copy them in your own project, wherever you like.
You will then need to include the file in your app's index.html, after the calls to ionic.bundle.js and cordova.js :
<script src="path/to/the/file/ionicitude.min.js"></script>Or, if you copied the humanly readable version :
<script src="path/to/the/file/ionicitude.js"></script>Note: you'll obviously need to replace path/to/the/file with the actual path to the file.
2. Registering the dependency
Whatever installing method you choose, you'll finally have to register the module in your app's dependencies:
// In app.js or wherever you created your app's module
angular.module('app', ['ionic', 'IonicitudeModule', /* other dependencies */]);Initialization
Before it can be used, the Ionicitude service needs to be initialized. This means loading the Wikitude plugin and setting up some default Ionicitude behavior. You can do this by calling this method:
Ionicitude.init();Please, see API Definition > init() for the complete details about this method, or continue reading to see some of them in their context.
I suggest that you call this function in the app.run() block that every Ionic app normally has, specificaly in the $ionicPlatform.ready() block.
// Should be in the app.js under a slightly different aspect.
angular
.module('app')
.run(run);
function run($ionicPlatform, Ionicitude) {
$ionicPlatform.ready(function () {
// Some Ionic code about StatusBar and stuff...
Ionicitude.init();
});
}Ionicitude.init() is a promise that returns the Ionicitude service as the resolved value. If anything goes wrong while initializing, the error is passed as the rejected value.
Checking Device's Features
We already saw that an AR World can be geo-based or image-recognition-based, or both. The device that wants to launch such AR World must support whatever features it requires, and the Wikitude plugin must know wether or not the device supports said features.
This can be done with this method:
Ionicitude.checkDevice();Please, see API Definition > checkDevice() for the complete details about this method, or continue reading to see some of them in their context.
Note: By default, checkDevice() is called by Ionicitude.init(). If you want init() to skip this checking part, you can pass an object as the method's argument, with at least the property doDeviceCheck set to false
Ionicitude.init({
doDeviceCheck: false // This will tell init() to skip the call to checkDevice()
// Any other init param
});Be advised that if you do skip the call to checkDevice() in the init part, you will have to call the method yourself at one point. Preferably before you try to launch any AR World
As for now, there's only two features that an AR World can require:
'geo'- This feature is needed by an AR World when it wants to use the user's location and manipulates geodata in a general way.'2d_tracking- This feature is needed by an AR World when it wants to use image recognition and/or image tracking.
Initially, checkDevice() checks if the device supports both of these features, but if your app will ever use only one of them, you can tell that to Ionicitude when initializing the service by passing an object argument to Ionicitude.init() with at least a reqFeatures array property:
// Your app only needs geolocation features ? Do...
Ionicitude.init({
reqFeatures: ['geo']
});
// Your app only need image tracking and/or recognition ? Do...
Ionicitude.init({
reqFeatures: ['2d_tracking']
});reqFeatures that doesn't reference a valid Wikitude feature will not cause the check to fail. It will just be ignored.
The result of the check will be stored and available through the Ionicitude.deviceSupportsFeatures property, as a Boolean.
checkDevice() returns you a promise, for you to react to any of the outcome:
Ionicitude.checkDevice()
.then(function(success) {
// What do you want to do if the device supports eveything?
})
.catch(function(error) {
// What do you want to do if the device doesn't support at least one of the feature?
});Execute code only when ready
Please note that Ionicitude.init() has some asynchronous behavior (especially while checking the device). This means that some of your code using Ionicitude could be executed before the initialization process is finished, resulting in potential error (see issue #3).
To ensure that the code using the module is executed only when Ionicitude has done initializing, you can use this method:
Ionicitude.ready();Please, see API Definition > ready() for the complete details about this method.
The syntax is exactly like the $ionicPlatform.ready() function, provided by Ionic. You encapsulate the code you want to execute inside an anonymous function, passed as the argument to the Ionicitude.ready() method. Say you want to launch an AR World (more on that on the next point), you would write something like this:
// This could be in a controller for example.
Ionicitude.ready(function () {
Ionicitude
.launchAR('myAR')
.then(function (success) {
// ...
}
.catch(function (error) }
// ...
}
});This will ensure that the launch is done only when Ionicitude's initialization is fully completed.
Some Ionicitude's method can be safely called even if the module is not initialized, so using the ready() method is not mandatory for every use case. Nonetheless, it's a good practice to always encapsulate any call the module inside this method, to be extra sure.
Launching an AR World
What's an AR World
The most simplistic AR World possible is just an HTML file (generally index.html), that loads up all the Wikitude logic. See this Gist for a blank minimal index.html file to use in your new AR Worlds.
More advanced AR Worlds contains an HTML file, one or several JS files (with your custom code or third party libraries), maybe some CSS, perhaps some image-tracking related files (specific to Wikitude, see their documentation for more information) or whatever file is useful for this particular AR World..
Expected files organization
In order to correctly launch your AR Worlds, Ionicitude expects three things:
- You have a folder named
wikitude-worldsin your app'swwwfolder (optionnal, see below) - Each of your AR World is contained in a single folder (named as you like) inside
wikitude-worlds - Each AR World folder contains at least an HTML file named
index.html
If you want to use another name than wikitude-worlds for your AR Worlds' root folder (point #1), you can do that by passing an object argument with at least a worldsRootFolder property when calling Ionicitude.init():
Ionicitude.init({
worldsRootFolder: 'my-personal-ar-worlds-folder-with-a-much-better-name'
});You must still follow rules #2 et #3. Otherwise, your world will not load correctly and you won't know why, because Wikitude does not throw an error if you try to load a file that doesn't exist
In the end, your files organization should look like this:
[your app root directory]/
...
www/
...
wikitude-worlds/ **Or whatever name you set**
world-foo/
index.html
... some other files or folders ...
world-bar/
index.html
... some other files or folders ...
Actually launching an AR World
To launch an AR, simply call the Ionicitude.launchAR(), and pass it the name of the folder containing the AR World's files that you want to launch. Say you want to launch the world-foo AR World, you would call the method like that:
Ionicitude.launchAR('world-foo');Please, see API Definition > launchAR() for the complete details about this method.
This will take the index.html file inside the world-foo folder, and launch an AR View with it.
launchAR() returns a promise, for you to react to any outcome:
Ionicitude.launchAR()
.then(function(success) {
// What to do when the launch is successfull
})
.catch(function(error) {
// What to do when the launch has failed
});checkDevice() test, Ionicitude.launchAR() will throw an UnsupportedFeatureError.
Interaction between the Ionic app and the AR View
Important explanations ahead!
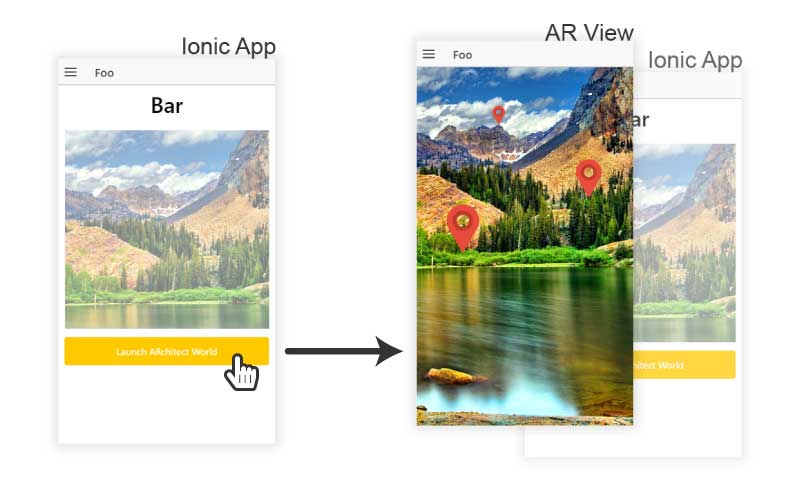
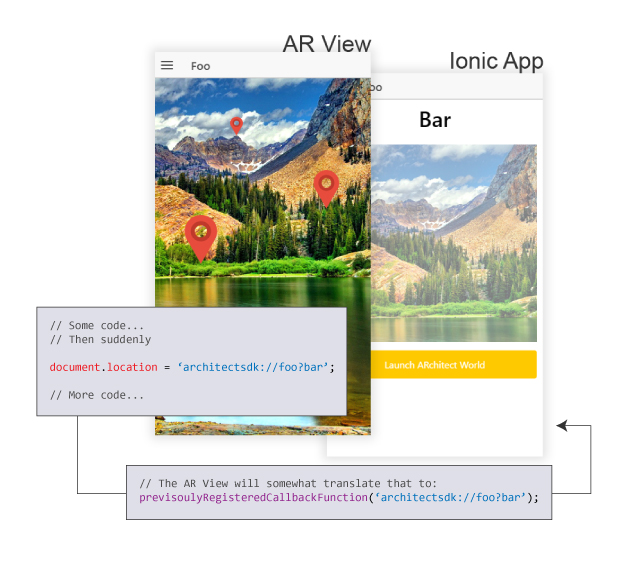
It's very important to understand that when the Wikitude plugin launches an AR View, it does not so in the context of your Ionic App. It creates a completely new, independant, agnostic WebView, that comes over your Ionic App WebView (check the following diagram). This means that all your data, scopes, services, controllers or whatever your app is using are complete strangers for the AR View.
To overcome this, the Wikitude staff added some callback mechanism for the two WebViews to communicate, much like a basic client/server architecture, the AR View being the client, and your app being the server.
From: AR View, To: Ionic App
Remember when I said earlier that an AR World is ultimately juste HTML/CSS/JS files? Well, whenever one of your AR World's JS file execute a document.location statement that starts with architectsdk://, like this one...
// Somewhere in an AR World'JS file
document.location = 'architectsdk://foo?bar';... that's the signal for the AR View that it needs to call a previsouly registered callback function on the Ionic App (more on that later), and pass it the URL (the value of document.location) as a String argument.
This previsouly registered callback function is then responsible of analyzing, interpreting and executing whatever it's asked to do by the URL.
Thankfully, Ionicitude provides you with it's own callback handling mechanism, so you wouldn't have to worry about that. But you can still set up your own mechanism, if you want. Please, see Ionicitude Callback Handling Mechanism for more details.
From: Ionic App, To: AR View
If you want your Ionic App to trigger some behavior inside the AR View (in reaction to an AR View document.location call, for example), you can use Ionicitude.callJavaScript() (mind the capital 'S') to do so.
Please, see API Definition > callJavaScript() for details about this method.
For now, this method is just a wrapper around the Wikitude's callJavaScript function.
This method works kinda like eval(). You pass it a javascript statement as a String argument, and it will try to execute this statement on the context of the AR View.
// Somewhere in your Ionic code
Ionicitude.callJavascript('getQuestion(42)');This will call the getQuestion() function, passing it 42 as it's only argument.
Note that getQuestion() must be defined in the AR World's JS, not on your Ionic App's JS.
This callJavaScript() method is designed to be called only when an AR View is currently active. If you try to call Ionicitude.callJavaScript() without having any active AR View, nothing will happen.
Ionicitude Callback Handling Mechanism (CHM)
Ionicitude comes with it's own Callback Handling Mechanism (CHM) to deal with document.location calls. It is enabled by default when calling Ionicitude.init(), but you can use your own if you like. You'd just have to pass an object with at least a customCallback property as an argument to the Ionicitude.init() function. The value of customCallback must be a function that takes one argument, the URL:
Ionicitude.init({
// Using your custom CHM over Ionicitude's one.
customCallback: function(arViewUrl) {
// Do whatever handling you want to do with every document.location call's URL received from an AR View
}
});If you do use your personnal CHM, you can skip the rest of this section.
document.location URL format
To properly function, Ionicitude's CHM needs that every URL passed as a value to document.location in an AR World's JS follows a particular format.
- The URL needs to start with
architectsdk://, as this is a requirement from the Wikitude plugin (you could store that somewhere in a variable to avoid rewriting it everytime). - The following characters must be the name of the Action that the AR View want the Ionic App to execute, or, in other words, the name of the function that will be called by the Ionic App.
- If this function needs argument(s)...
- the name of the Action in point #2 must be followed by the
?character. - the remaining characters must form a valid JSON Object declaration. Each of this object property being one of the needed arguments.
- the name of the Action in point #2 must be followed by the
Valids AR View's URL
All the following document.location's URLs will be correctly interpreted and executed by the CHM:
"architectsdk://foo"will call thefooAction with no argument"architectsdk://foo?{"bar":"baz"}"will call thefooAction with{bar: "baz"}as its argument"architectsdk://foo?{"bar": 1, "baz": {"fooBar": 123}}"will call thefooAction with{bar: 1, baz: {fooBar: 123}}as its argument
Invalids AR View's URL
All the following URLs will fail, throwing a SyntaxError:
foo- URL does not start witharchitectsdk://architectsdk://foo()- the parenthesis must not be presentarchitectsdk://foo{"bar": "baz"}- the?character is missing between the Action's name and the JSON Object argumentarchitectsdk://foo?bar- the characters following the?must form a valid JSON Object.
CHM Actions Mapping
Obviously, the Action name that you pass in the document.location's URL must match an existing function, somewhere. By default, Ionicitude's CHM will try and execute this function from it's own Action library. But because Ionicitude is (sadly) not omniscient, it can not already contain everything that your AR View could call. In fact, its kinda empty in the beginning.
Registering Actions
You'll have to register an Action to Ionicitude's library before calling it from inside an AR View. Do this by calling Ionicitude.addAction() and passing it either a name and an anonymous function as a callback, or just a named function. Anything else will throw a TypeError.
Please, see API Definition > addAction() for details about this method.
This is OK:
// Give a string name and an anonymous function.
Ionicitude.addAction('foo', function() {
// Some code describing what the 'foo' Action does.
});// Declare the function and then give it to the method.
function foo() {
// Some code describing what the 'foo' Action does.
}
Ionicitude.addAction(foo);// Give a named function directly to the method.
Ionicitude.addAction(function foo() {
// Some code describing what the 'foo' Action does.
});This is NOT OK:
// Don't pass only an anonymous function.
Ionicitude.addAction(function() {
// Some code describing what the Action does.
});Be sure to register the Action BEFORE your AR View calls it.
To register multiple Actions one after another, you can simply chain your calls to Ionicitude.addAction():
// As you can see, the method you chose to use doesn't matter
function foo() { /* Some code */ }
Ionicitude
.addAction(foo)
.addAction('bar', function() { ... })
.addAction(function baz() { ... });
// Ionicitude's Action library now contains three Actions
// — 'foo', 'bar' and 'baz' —
// that can be called with a 'document.location' statement.Action's arguments
When called by a document.location statement, a registered Action's callback will receive two arguments:
service: The Ionicitude service, if you need to call any method from its APIparam: An object containing, as its properties, your callback's arguments, when provided by thedocument.locationstatement (seedocument.locationURL format)
Full example
To wrap up all this Action business, here is a example.
Let's say that your document.location statement looks like this:
// In your AR View's JS
document.location = 'architectsdk://foo?{"bar":"Some argument value", "baz": 125.252}'Then, your param argument's value will translate to...
// You don't have to write this anywhere, it's just a clearer way to look at the data
{
bar: "Some argument value",
baz: 125.252
}... and your foo Action should be registered like this...
// Somwhere in your Ionic App's JS, but after calling Ionicitude.init()
Ionicitude.addAction(function foo(service, param) {
// You can access your param properties
console.log(param.bar); // Will print : "Some argument value", in the console of the Ionic WebView
console.log(param.baz); // Will print : 125.252, in the console of the Ionic WebView
// You can also access the Ionicitude service API
service.close(); // Or any other API's function
});If your Action only needs the param argument without the service one, its callback still must accept the two arguments in the right order : function foo(service, param) { ... }.
But if your Action needs only to interact with the service, its callback could accept one argument : function foo(service) { ... }.
API Definition
addAction()
Adds an Action to the Ionicitude Action Library that can then be triggered by an AR View, with a document.location statement. You can add an action by either passing a name and an anonymous callback, or just a named callback.
When called, the callback will be passed to arguments: service, the Ionicitude Service for you to call any of its method, and param, the object passed in the document.location URL. Declare your callback argument depending on its needs.
The Ionicitude Service is returned so that you can chain calls to addAction().
Arguments
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| nameOrFunction | STRING/FUNCTION |
If STRING, the name of the Action to add. If named FUNCTION, the Action to add under the same name. |
| callback | FUNCTION |
[Optionnal] If nameOrFunction is of type STRING, an anonymous function to add as the Action. |
Returns
OBJECT- The Ionicitude Service
Throws
TypeErrorwhennameOrFunctionis neither aSTRINGnor aFUNCTIONnameOrFunctionis aSTRINGandcallbackis not present ornullnameOrFunctionis aSTRINGandcallbackis not aFUNCTIONnameOrFunctionis an anonymousFUNCTION
SyntaxErrorwhen- The name of the Action to add has already been used for a previsouly registered Action
Usage
Ionicitude
.addAction('foo', function(service) {
// This Action is named 'foo' and can access the Ionicitude Service API
}
.addAction('bar', function(service, param) {
// This Action is named 'bar' and can access both
// the Ionicitude Service API (even if it doesn't need to)
// and as any 'param' it needs
}
.addAction('baz', function() {
// This Action is named 'baz' and doesn't need neither the Ionicitude Service nor any 'param'.
};callJavaScript()
This is a just a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's callJavaScript function. See Official Doc for more information.
Allows you to executre a JavaScript statement from the Ionic App into the context of the currently active AR View.
Arguments
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| js | STRING |
A litteral javascript statement to execute in the context of the currently active AR View. |
Usage
// Will prompt an alert in the AR View
Ionicitude.callJavaScript('alert(\'Hello\')');captureScreen()
This is a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's captureScreen function but it implements promises instead of callbacks. See Official Doc for more information.
Allows you to take a screenshot of the currently active AR View.
Arguments
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| withUI | BOOLEAN |
Indicates wether or not the AR View UI should be part of the screenshot. |
| fileNameOrPath | STRING/NULL |
If it's a file name or a file path, the screenshot will be saved in the application bundle. If NULL, the screenshot will be saved in the device photo gallery. |
Returns
PROMISE- A promise of a screenshot.
Usage
Ionicitude.captureScreen(true) // Screenshot will contain AR View UI and will be saved in the photo gallery.
.then(function(success) {
// React to a successfully captured screen
}
.catch(function(error) {
// React to a failed captured screen
};checkDevice()
This method is called by the Ionicitude.init() method. You can force-skip this call by passing and argument to Ionicitude.init() (see API Definition > init() for details). You should then manually call this method before launching an AR World.
Checks if the device supports the features needed by your app.
The result of the check will be available through the Ionicitude.deviceSupportsFeatures property.
By default, the needed features against which the device is check are geo and 2d_tracking. You can change that by passing an argument to Ionicitude.init() (see API Definition > init() for information).
Returns
PROMISE- A promise of a check result.
Usage
Ionicitude.checkDevice()
.then(function(success) {
// React to a device supporting all the requested features
}
.catch(function(error) {
// React to a device not supporting at least one of the requested features
};close()
This is a just a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's close function. See Official Doc for more information.
Close the currently active AR View, and returns to the Ionic App last view.
Usage
Ionicitude.close();hide()
This is a just a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's hide function. See Official Doc for more information.
Allows you to hide the currently active AR View, in order to show it again at a later time using Ionicitude.show() (see API Definition > show() for details).
Usage
Ionicitude.hide();init()
Must be called prior to any other Ionicitude's API call.
Initializes the Ionicitude Service, then returns it for you to chain methods calls, if necessary.
This initialization first loads up the Wikitude plugin, then sets up the Ionicitude's CHM (see Ionicitude Callback Handling Mechanism for more information) and, finally, calls Ionicitude.checkDevice() (see API Definition > checkDevice() for more information).
Note that this method is designed to be called one time, and one time only. If you call it a second time, you'll break the space-time continuum nothing will happen.
Arguments
You can change the method's default behavior or modify some of the service's settings by passing an object as the method's argument. This object can have the following properties, that are all optionnal:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| customCallback | FUNCTION |
Default to Ionicitude CHM. A function that will be used to handle and react to any document.location call executed from an AR View's JS code. This function must take one argument, which will be the value of the document.location statement. |
| doDeviceCheck | BOOLEAN |
Default TRUE. Pass FALSE to skip the checkDevice() method call. If you do, you'll need to manually call the method later on. |
| reqFeatures | ARRAY |
Default ['geo', '2d_tracking']. An array of strings indicating which features are required by your app. Can be 'geo', '2d_tracking' or both. Anything else will be ignored. |
| worldLoadConfig | OBJECT |
Default {camera_position: 'back'}. An object of additionnal settings for the AR Views. For now only one setting is available, camera_position, that can be either front (to use the device front camera) or back (to use the device back camera). |
| worldsRootFolder | STRING |
Default "wikitude-worlds". A string that references a folder's name in your app in which your AR Worlds' folders are stored (see Expected File Organization for more information). |
Returns
OBJECT- The Ionicitude Service.
Usage
// Full default usage
Ionicitude.init();
// With custom behavior and/or settings
Ionicitude.init({
customCallback: function(URL) { /* Handle the URL yourself */ },
doDeviceCheck: false, // Will skip the call to checkDevice()
reqFEatures: ["geo"], // checkDevice() will only check the geolocalization feature
worldLoadConfig: {camera_position: 'front'}, // The front camera will be used by the AR Views.
worldsRootFolder: "my_custom_world_folder"
});launchAR()
Launch an AR World with the Wikitude plugin, and returns a promise. This creates a new AR View and switches the app's focus to it.
Argument
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| world_ref | STRING |
The name of the folder that contains the files for the AR World to launch. This folder must exist in a folder named "wikitude-worlds" in your app's www directory. If you want to change the name of this folder (or event it's path), you can by passing an argument to Ionicitude.init() (see API Definition > init() for details). |
Returns
PROMISE- A promise of a launched AR World.
Throws
UnsupportedFeatureErrorwhen:- Trying to launch an AR World that requires features not supported by the device (see Checking Device's Features)
Usage
Ionicitude.launchAR("my_world_folder_name")
.then(function(success) {
// React to a successfull AR World launching
})
.catch(function(error) {
// React to a failed AR World launching
});ready()
Encapsulate your code that is using the Ionicitude service in this method. That will ensure that this code is executed only when or if the module has finished initializing.
Argument
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| code | FUNCTION |
An anonymous function that contains the code to execute only when Ionicitude is fully initialized. |
Usage
Ionicitude.ready(function () {
Ionicitude.launchAR("myAR")
.then(function(success) {
// ...
})
.catch(function(error) {
// ...
});
});show()
This is a just a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's show function. See Official Doc for more information.
Allows you to show a previously hidden AR View.
Usage
Ionicitude.show();setLocation()
This is a just a wrapper around the Wikitude plugin's setLocation function. See Official Doc for more information.
Use this function to inject a user's location into the currently active AR View.
It's not clear in the Wikitude documentation wether this method should be used for testing purpose (since they use the world "simulated" in the arguments description) or for production purpose. Anyway... since Wikitude automatically tracks the device location on a geolocalization-based AR World, you shouldn't need to call this method.
Arguments
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| latitude | NUMBER |
The latitude (in decimal degree) of the location to inject. |
| longitude | NUMBER |
The longitude (in decimal degree) of the location to inject. |
| altitude | NUMBER |
The altitude (in meters) of the location to inject. |
| accuracy | NUMBER |
The accuracy (in meters) of the location's data. |
Usage
Ionicitude.setLocation(31.2543139, -24.258480555555554, -10000, 20000):Demo Application
An demo application that uses Ionicitude in an Ionic app can be found here.
Contribution and Issues
Any contribution or enhancement to this Ionicitude Demo App are welcomed and will be appreciated.
If you experience bugs or strange behaviors will testing this app, please do not hesitate to raise an issue about it.
In both case, please, use the GitHub tools of this repository (merge request and issues) rather than sending a personnal email. This way, it will be easier to manage and keep track of what's happening. Thanks !
License
This package is licensed under the MIT Licence. See LICENCE.txt or read the following text:
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2016-Present Mathias Oberson
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.