We recommend to use Docker to create a virtual system to study this tutorial.
If you are using Windows, you can follow the official installation guide Install Docker Desktop on Windows
If you are using MacOS, you can follow the official installation guide Install Docker Desktop on Mac
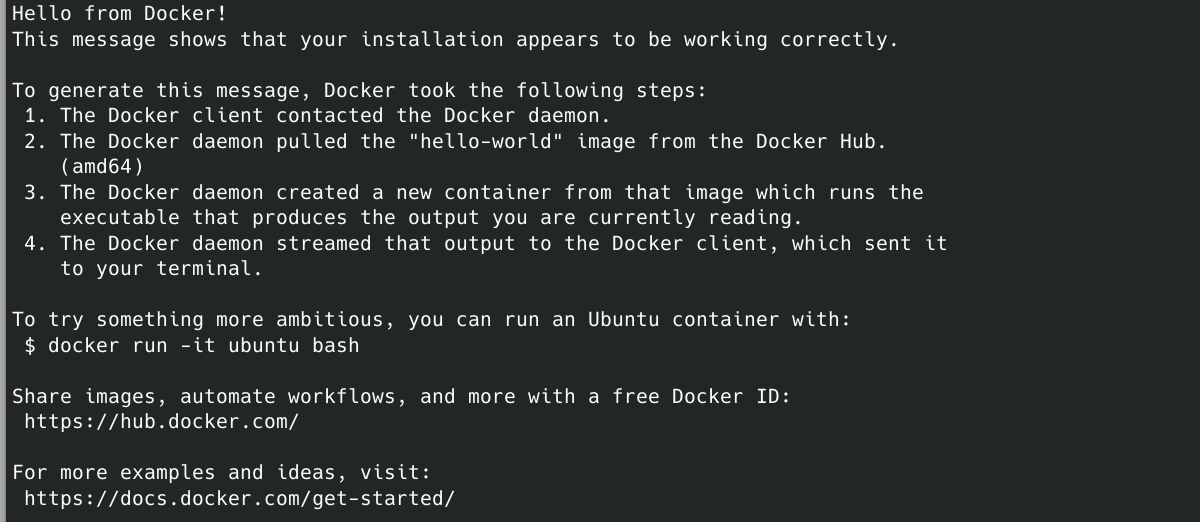
To confirm if you successly install Docker, run docker run hello-world
You may also want to check this page to get started with docker.
Then let's create an Ubuntu container named EPETutorial for this tutorial.
# run the line below if you are using Linux/MacOS
# whoami will tell your username
docker run -p 8899:8888 --name EPETutorial -v /home/$(whoami)/EPETutorial:/root -it ubuntu /bin/bashor if you are running windows, please substitue the <USERNAME> below with your username on your machine.
docker run -p 8899:8888 --name EPETutorial -v C:\Users\<USERNAME>\EPETutorial:/root -it ubuntu /bin/bash
What we did by this command:
- mount a folder under your home directory called
EPETutorialto your docker container path/root/. This is done by-v /home/$(whoami)/EPETutorial:/root- specify the name
EPETutorialto the container. done by--name EPETutorial- publish a container's port(s) 8888 to the host port 8899. done by
-p 8899:8888Check more info bydocker run --help
You'll see your shell prompt change to something like root@15105b7f505b:~#, and this means you are in the Ubuntu container.
Then we will install the requird packages
apt update && apt upgrade -y # update the package list
apt install git python3 python3-pip python3-dev tree -y # install git and python pip3 install jupyter scipy numpy matplotlib # install the python related modules Then clone this repo via commands:
cd ~ # this will navigate to the home directory, this is /root
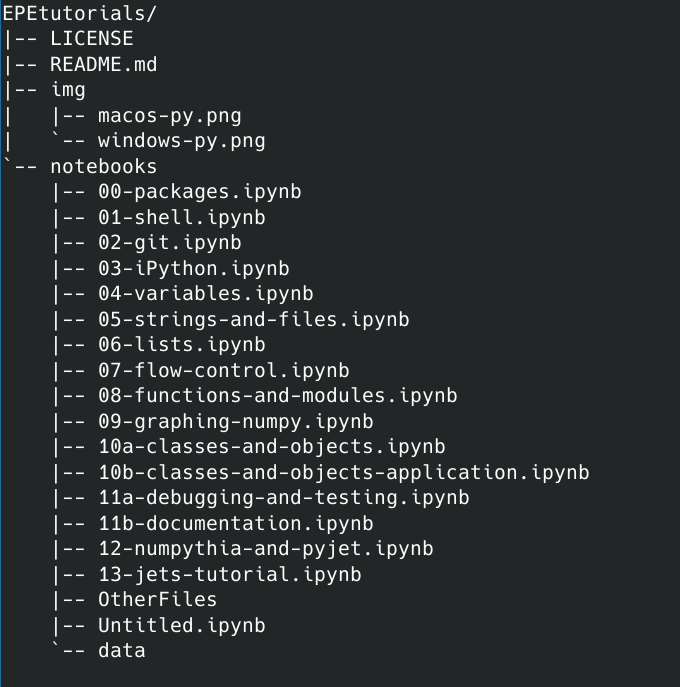
git clone https://github.com/uwepe-analysis/EPEtutorials To confirm you successfully clone this repository, try
tree -L 2 EPEtutorials
Now we are ready for the first chapter exercise for shell. For the other chapters,
In the Ubunutu container, run
jupyter notebook --ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8888 --no-browser --allow-root
You'll see a message like this
Copy/paste this URL into your browser when you connect for the first time,
to login with a token:
http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=d6e80acaf08e09853dc72f6b0f022b8225f94f
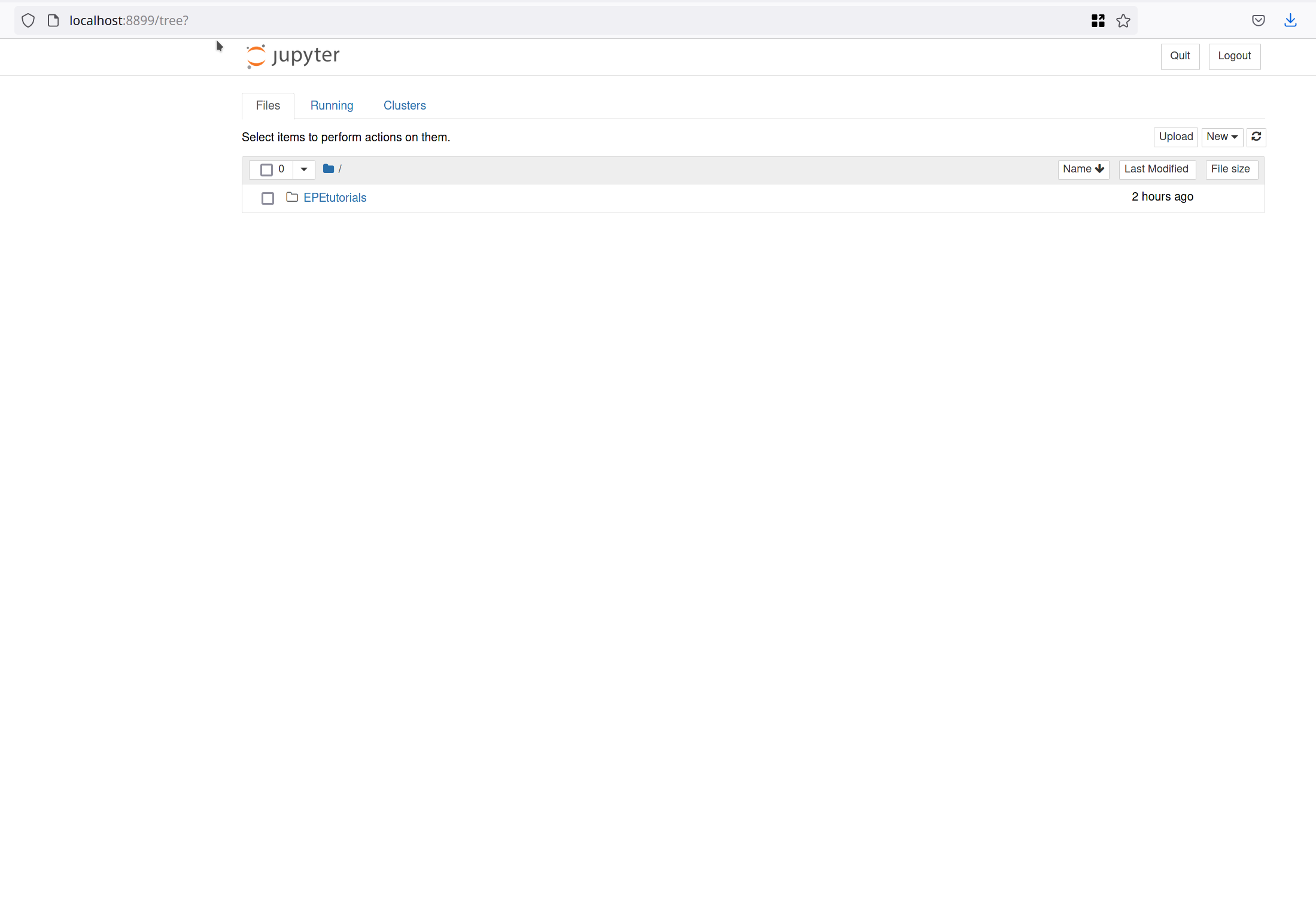
Then open your browser and navigate to this link:
localhost:8899
if it is the first time you connect to the jupyter-notebook, you are asked to input a token. Just copy and paste the token on your machine, and log in.
Finally, if your browser shows this, the env is ready to go.
To leave the Unbuntu container enviorment, type exit or use key shortcut <Control>+C, this will quit the container and stop all the activities. To detach the work, use the shortcut <Control>+P, <Control>+Q .
To attach the session, make sure the container is not stopped (you can docker start <Container-Name>), then docker attach EPEtutorial.
You can use docker ps -a to check the status of all containers.
Depends on which operating system(OS) you are using, different ways are recommended here to install Python.
First, we install python3 and then use pip3, a package manager for Python, to install Jupyter notebook and other scientific packages. And our tutorials are designed in the format of Jupyter notebook and can be run easily.
-
Download Python 3.9 from https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-391/ and install it. Be sure to check the box that says to add Python 3.9 to your path.
-
Run
PowerShellfrom the Start menu. Search for it, and just pressEnterto run it. -
In your
PowerShell(Terminal) program, runpython. You run things in Terminal by just typing the name and pressing Enter. If you type python and it does not run, then you have to reinstall Python and make sure you check the box for “Add python to the PATH.” It’s very small so look carefully.
What you should see:
Homebrew is recommended here. It calls itself The missing package manager for macOS and is an essential tool for any developer.
Open a terminal, run
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"You'll be asked to install Command Line Tools for Xcode if you have it installed.
After installation of Homebrew,
brew install python3Open a terminal, and it could be called GNOME Terminal, Konsole, or xterm.
sudo apt update
sudo apt -y upgrade
sudo apt install python python3-pip python-dev With Python installed, wu run pip3 to install other packages.
pip3 install jupyterlab scipy numpy matplotlib
To install git, go to this website and download the installer for your operating system. If you do not already have a bash shell installed, make sure to also choose that option for install as git is a terminal application.
On Windows, make sure you configure the terminal emulator to use Windows' default console window. This will make it easier for you to access your computer's files and it is a lot nicer to look at.
brew install gitsudo apt install git -yAnaconda is a Python distribution that makes it easy to install Python plus a number of its most often used 3rd party libraries in a flexible way on a Windows or Linux machine.
To install anaconda, first go to this website, and download the installer for Python 3. Once downloaded, follow the install wizard. The default settings are usually good choices. Make sure to choose Anaconda's python kernel as default, as it makes using the different frameworks and plugins much easier.
On Windows, make sure to select the option "Add Anaconda to my PATH environment variable". There will be red text saying it is not recommended, but you will not be able to access the Anaconda package from your bash terminal with out this option checked.
If you already have pip and Python 3 installed, you can run pip3 install anaconda in bash to get Anaconda.
Once you have successfully installed git, python and jupyterlab, create a github account and sign in. You can download the repository by clicking on the green "Clone or Download" button and copy the link next to "Clone with HTTPS". Open up git bash, and type git clone [The web address here]. This will download the repository to your local machine at your home directory. Then, open jupyter notebook either by the Anaconda Navigator or by going to git bash and typing jupyter notebook (or jupyterlab), then your browser will be open.
Note: as for the notebooks, you are encouraged to do Chapter 12 and the Chapter 13 is optional.
-
Type every line of the codes in your jupyter notebook and run it(Shift + Enter), do not just copy and paste
-
Do exercise