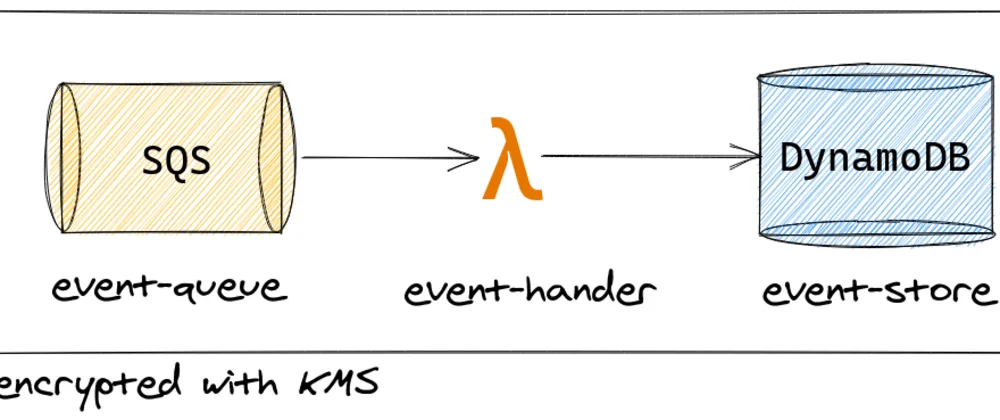
dynamodb-as-eventstore
Using DynamoDB as EventStore with SQS and Lambda.
Article at https://learnings.aleixmorgadas.dev/p/dynamodb-as-eventstore
Setup local environment
I assume you have:
- Terraform installed
- AWS Account
- Python Environment
Install Python Dependencies
ℹ️ I used Linux/Debian for this project, you might need to adapt the commands to your operating system.
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txtYou might need python3-venv as OS dependency installed.
Deployment
Before Deployment, you should check:
infrastructure/main.tf. The regioninfrastructure/variables.tf. Set the read and write capacity of DynamoDB that you need. Default read-capacity 1, write-capacity 1. Also, prevent destroy for theevent-storeis set to false as default.
At infrastructure folder, execute ./run.sh.
Destroy Infrastructure ⛑️
At infrastructure folder, execute ./destroy.sh.
Solution Design. Trade-offs
- Queue isn't a FIFO (First In-First Out).
It has consequences in the order the events are stored. Even though they contain a timestamp, they might get stored in a different order they have been produced.
In case of low traffic it might not be a real issue. But in case the application starts emitting events intensively that require them to be ordered, you might need to switch from a normal Queue to a FIFO Queue or Kinesis.
- Hash Key and Sort Key
Hash Key = ID
Sort Key = Timestamp
The idea is to have the Events Ordered by Timestamp.
- Items don't expire
I haven't configured the Time to Live (TTL) in DynamoDB. The table will grow in infinitum.w
-
Only one Index
You might want to add more indexes to query the events as you like.-
Info in Terraform to add them in DynamoDB table configuration.
-
Info in AWS About Global Secondary Indexes and why you should define them to perform queries instead of scans.
-
Event Base
All events received by the lambda must follow the next schema:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timestamp | Date | true | Time when event was created |
| EventType | String | true | Event identifier. Format EVENT_EXAMPLE |
| ID | String | true | Id of the entity |
| EmitterId | String | true | Id of the user or system that caused the event |
| EmitterType | String | true | SYSTEM or USER is what we use. It's a free text |
| Data | Object | false | fields of the event |
In case of not following the schema, the event will be rejected.
Example:
{
"Timestamp" : 1596719980,
"EventType" : "EVENT_TEST",
"ID" : "53877b2e-e496-11ea-b678-9b42a44d5e59",
"EmitterId" : "6b04fd08-e496-11ea-8176-9f85e075569c",
"EmitterType": "USER",
"Data" : {
"foo": "bar"
}
}Technical Debt
- AWS Permissions
The different AWS Roles have too much permissions in their policies. It will be convenient that you restricted those to what's really required.
- AWS CloudWatch
It will be convenient to setup a CloudWatch Dashboard with the main metrics to check regularly to know how the system is behaving.