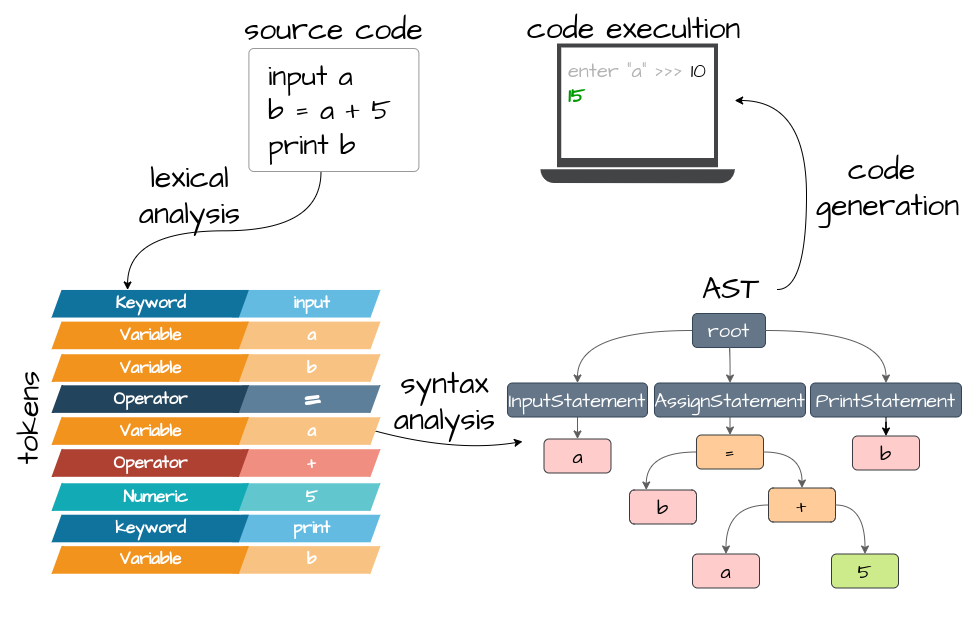
This is a simple toy language implementation. More details: Building Your Own Programming Language From Scratch
- Variables declaration
# plain types
<variable_name> = <expression>
a1 = 123
a2 = "hello world"
# class instance
<variable name> = new <class_name> [ <argument_expression_1>, <argument_expression_2>, ... ]
left_tree_node = new TreeNode [ 1 ]
right_tree_node = new TreeNode [ 2 ]
tree_node = new TreeNode [ 3, left_tree_node, right_tree_node ]
tree_node = new TreeNode [ 3, new TreeNode [ 1 ], null ]
# array
<array> = { <value1>, <value2>, ... }
example_array = { 1, 2, "three", new TreeNode [ 4 ] }
empty_array = {}
- Conditions
if <condition>
# statements
elif <condition>
# statements
else
# statements
end
if a1 > 5 and tree_node :: value == 3
# statements
elif a2 == "hello" or a3 == "world"
# statements
else
# statements
end
- Print to console
print <expression>
print a1 + a2 + tree_node :: value
- Input from console
input <variable_name>
input number
- Functions
fun <function_name>
<body>
end
fun <function_name> [ <argument1, argument2>, ... ]
<body>
return <expression>
end
fun fibonacci_number [ n ]
if n < 2
return n
end
return fibonacci_number [ n - 1 ] + fibonacci_number [ n - 2 ]
end
- Loops
# For loop
loop <variable> in <lower_bound>..<upper_bound>
# statements
end
# Specify the step
loop <variable> in <lower_bound>..<upper_bound> by <step>
# statements
# seed increment statement
end
# While loop
loop <condition>
# statements
end
# Iterable loop (for-each)
loop <variable> in <iterable>
# statements
end
# terminate the loop
loop <variable> in <lower_bound>..<upper_bound> by <step>
if <other_condition>
break
end
end
# jump to the next iteration
loop <variable> in <lower_bound>..<upper_bound> by <step>
if <other_condition>
next
end
end
- Exceptions
# raise (throw) an exception
raise "Error"
# raise a class instance
class MyException [message]
end
raise new MyException ["Error message"]
# rescue (catch) exception
begin
raise new MyException ["Error message"]
rescue err
print "Rescue block"
# access property of raised (thrown) object
print err :: message
end
# ensure (finally)
begin
raise new MyException ["error message"]
rescue error
print "Rescue block"
print error :: message
ensure
print "Ensure block"
end
There are the following data types currently supported:
- Numeric
number1 = 1
number2 = 2.
number3 = 3.21
number4 = 0.432
number5 = .543
number6 = -1
- Text
text = "hello world"
print text{1}
text{1} = "a"
print text
- Logical
logical1 = true
logical2 = false
- Class
class <class_name>
end
class <class_name> [ <property1>, <property2>, ... ]
# inner statements
print <property1>
fun <function_name> [ <property1>, <property2> ]
# function statements
this :: <property1> = <property1>
end
end
# derived classes
class <derived_class_name>: <base_class_name1>, <base_class_name2>
end
class <derived_class_name> [ <derived_property>, ... ]: <base_class_name> [ <derived_property>, ... ]
end
class Lamp [ type, is_on ]
fun turn_on
is_on = true
end
fun turn_off
is_on = false
end
fun set_is_on [ is_on ]
this :: is_on = is_on
end
end
lamp_instance = new Lamp [ "Halogen", false ]
# get/set class's property
lamp_is_on = lamp_instance :: is_on
lamp_instance :: type = "Led"
# invoke class's function
lamp_instance :: turn_off []
- Arrays
<array> = { <value1>, <value2>, ... }
example_array = { 1, 2, "three", new TreeNode [ 4 ] }
empty_array = {}
# get an array's value
<value> = <array> { <index> }
value = items{1}
# set an array's value
<array> { <index> } = <value>
items{1} = 123
# append a value to array
<array> << <value>
items = {1,2}
items << 3 #{1,2,3}
- Null
value = null
To calculate a complex expression in the proper order, each of the supported operators has its own precedence:
| Operator | Value | Precedence | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assignment | = |
1 | a = 5 |
| Append value to array | << |
1 | array << "value" |
| Logical OR | or |
2 | true or false |
| Logical AND | and |
3 | true and true |
| Left Paren | ( |
4 | |
| Right Paren | ) |
4 | |
| Equals | == |
5 | a == 5 |
| Not Equals | != |
5 | a != 5 |
| Greater Than Or Equals | >= |
5 | a >= 5 |
| Greater Than | > |
5 | a > 5 |
| Less Than Or Equals | <= |
5 | a <= 5 |
| Less Than | < |
5 | a < 5 |
| Addition | + |
6 | a + 5 |
| Subtraction | - |
6 | a - 5 |
| Exponentiation | ** |
7 | a ** 5 |
| Multiplication | * |
7 | a * 5 |
| Division | / |
7 | a / 5 |
| Floor Division | // |
7 | a // 5 |
| Modulo | % |
7 | a % 5 |
| NOT | ! |
8 | !false |
| Class Instance | new |
8 | type = new Type [ value ] |
| Nested Class Instance | :: new |
8 | type :: new NestedType |
| Class Property | :: |
8 | type_value = type :: value |
| Class Cast | as |
8 | type as Supertype |
| Class Instance Of | is |
8 | type is Supertype |
Firstly, compile and package the program into a uber jar, go to the ./target folder and then run the following command
java -cp toy-language.jar org.example.toylanguage.RunToyLanguage ../src/test/resources/stack.toy