This is a simple example of how to use connection pooling in MongoDB with OpenFaaS on Kubernetes.
-
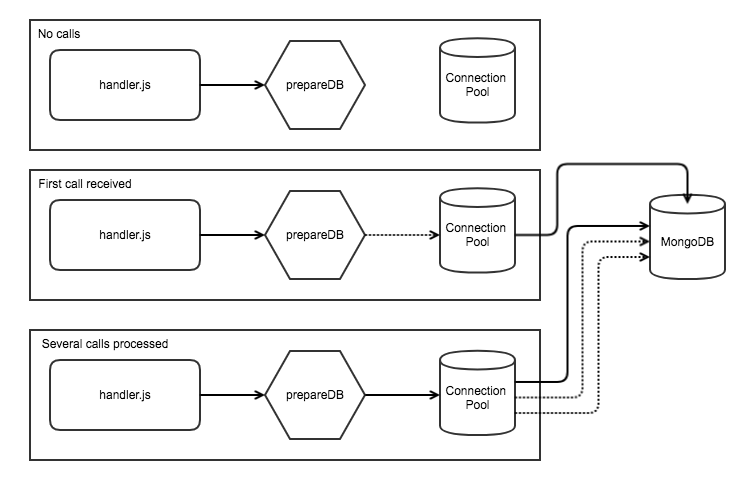
In the first sequence we've had no calls made to the function, so the connection pool is not yet initialized.
prepareDB()was never called. -
In the second sequence
prepareDB()has been called and since there was no instance of a connection in memory, we create one and you see the dotted line shows the connection being established. This will then open a connection to MongoDB in the network. -
In the third sequence we see that subsequent calls detect a connection exists and go straight to the connection pool. We have one active connection and two shown with dotted lines which are about to be closed due to inactivity.
Before we can build and deploy the example we'll set up OpenFaaS on Kubernetes or Swarm followed by MongoDB. This configuration is suitable for development and testing.
- Start by cloning the Github repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/alexellis/mongodb-function
- Install OpenFaaS with
helm
https://docs.openfaas.com/deployment/kubernetes/
- Install the OpenFaaS CLI
curl -sL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh- Set your
OPENFAAS_URLvariable
$ export OPENFAAS_URL=127.0.0.1:31112
If you're using minikube or a remote machine then replace 127.0.0.1 with that IP address.
- Install mongodb via
helm
$ helm install stable/mongodb --name openfaas-db \
--namespace openfaas-fn \
--set persistence.enabled=falseNote down the name of the MongoDB instance i.e. openfaas-db-mongodb
If you want to use the fully-qualified DNS name that would be:
openfaas-db-mongodb.openfaas-fn.svc.cluster.local.
Now skip ahead to "Build and test"
- Install OpenFaaS with Docker
https://docs.openfaas.com/deployment/docker-swarm/
- Install the OpenFaaS CLI
curl -sL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh- Set your
OPENFAAS_URLvariable
$ export OPENFAAS_URL=127.0.0.1:8080
- Create a mongodb Docker Service
$ docker service create --network=func_functions --name openfaas-db-mongodb --publish 27017:27017 mongo mongod
The entry for the stack.yml file will be the IP of your Docker Swarm manager.
-
Update your stack.yml's mongo field with the MongoDB DNS entry/IP from prior steps
-
Replace "alexellis/" prefix from Docker Hub in stack.yml with your own account
-
Build/push/deploy
Pull in the node8-express template:
$ faas template pull https://github.com/openfaas-incubator/node8-express-template
Now build and push / deploy
$ faas build && faas push && faas deploy
- Get a load-testing tool
This requires a local installation of Go.
$ go get -u github.com/rakyll/hey
An alternative tool would be Apache-Bench which is available for most Linux distributions via a package manager.
- Run a test
Let's start by running a single request with curl:
$ curl http://$OPENFAAS_URL/function/insert-user \
--data-binary '{"first":"Alex", "last": "Ellis"}' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
Now run a load-test with hey:
$ ~/go/bin/hey -m POST -d '{"first":"Alex", "last": "Ellis"}' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-n 1000 -c 10 http://$OPENFAAS_URL/function/insert-user
This test posts in a JSON body with 1000 requests with 10 of those being concurrent.
Here's an abridged output from hey with the function running on a remote server with the test being run from my laptop:
Summary:
Requests/sec: 1393.2083
...
Status code distribution:
[200] 10000 responses
If you look at the logs of the Mongo deployment or service you will see the connection count is between 1-10 connections only during the load-test. This shows that the connection-pool is being used by our function.
On Kubernetes:
$ kubectl logs deploy/openfaas-db-mongodb -f -n openfaas-fn
On Swarm:
$ docker service logs openfaas-db-mongodb -f