Functions, recursion and the call stack.
func minMax(array: [Int]) -> (min: Int, max: Int)? {
guard let first = array.first else {
return nil
}
var currMin = first
var currMax = first
for value in array {
if value < currMin {
currMin = value
} else if value > currMax {
currMax = value
}
}
return (currMin, currMax)
}
print(minMax(array: [4, 1, 3, 11, 9, -89, 3, 0]) ?? (0, 0)) // (min: -89, max: 11)func communityGreeting(_ cohort: String) -> String {
"Hello, \(cohort)!"
}
communityGreeting("iOS") // Hello, iOS!func currentCohort(_ cohort: Double = 6.0) {
print("Current cohort is \(cohort)")
}
currentCohort() // Current cohort is 6.0
currentCohort(7.0) // Current cohort is 7.0func networkingList(_ friends: String...) { // syntax is 3 trailing dots after the Data type
guard !friends.isEmpty else {
print("Le't do some more networking.")
return
}
for friend in friends {
print("\(friend) is now a friend")
}
}
networkingList() // no current network, variadic argument can be omitted
networkingList("Kim") // Kim is now a friend
networkingList("Nancy", "David")
/*
Nancy is now a friend
David is now a friend
*/A function may have at most one variadic parameter.
func updateLastName(_ name: inout String) {
let splitNames = name.split(separator: " ")
let firstName = splitNames[0]
name = "\(firstName) Appleseed"
}
var fullname = "Alex Paul"
print(fullname) // Alex Pual
updateLastName(&fullname)
print(fullname) // Alex AppleseedRecursion is defined as a function that calls iteself.
Recall: Whenever writing a recursive function the most important 2 factors are:
- The base case.
- The recursive call.
input: base number and exponent
output: the power of the given base number
Solution
func power(x: Int, y: Int) -> Int {
// 1
guard y > 1 else {
return x
}
// 2
return x * power(x: x, y: y - 1)
}
print(power(x: 2, y: 3)) // 8- Base case.
- Recursive call.
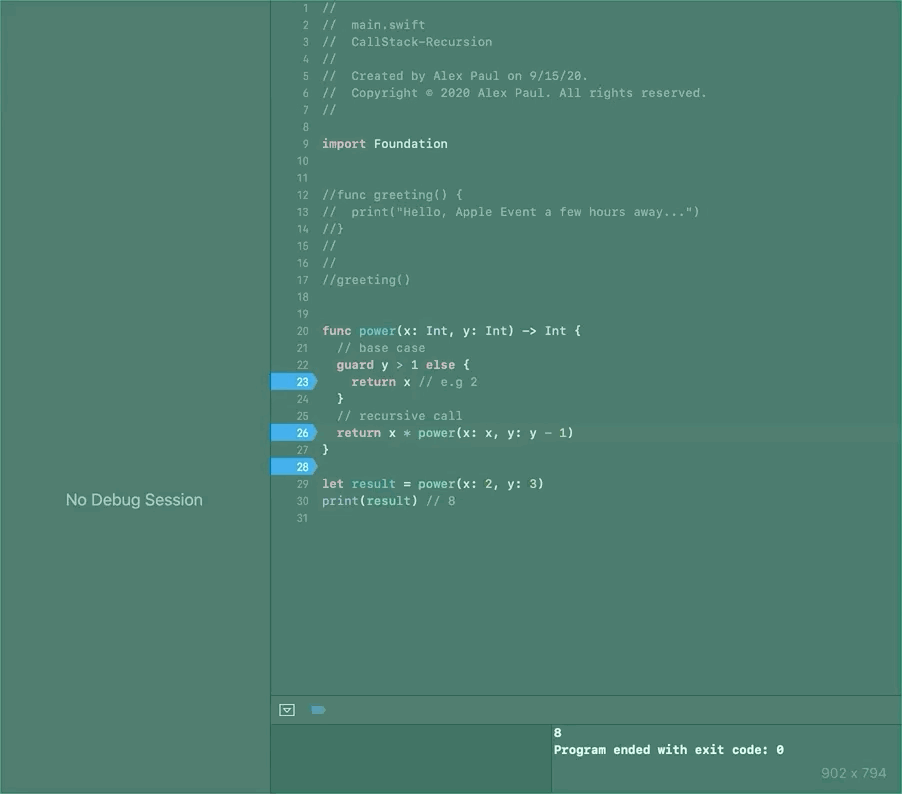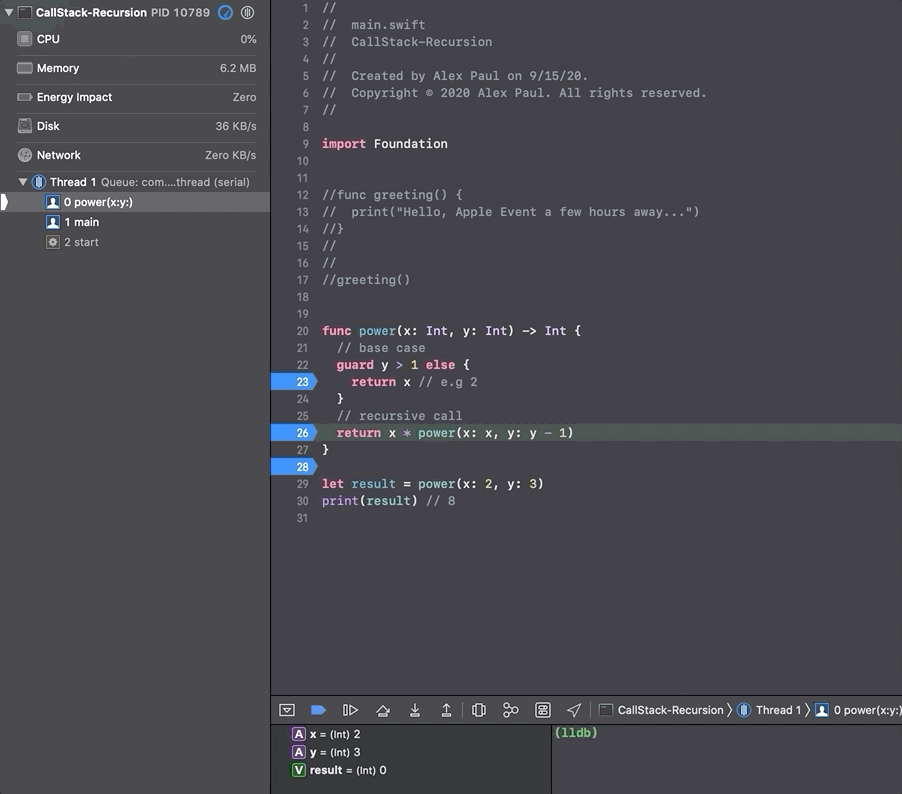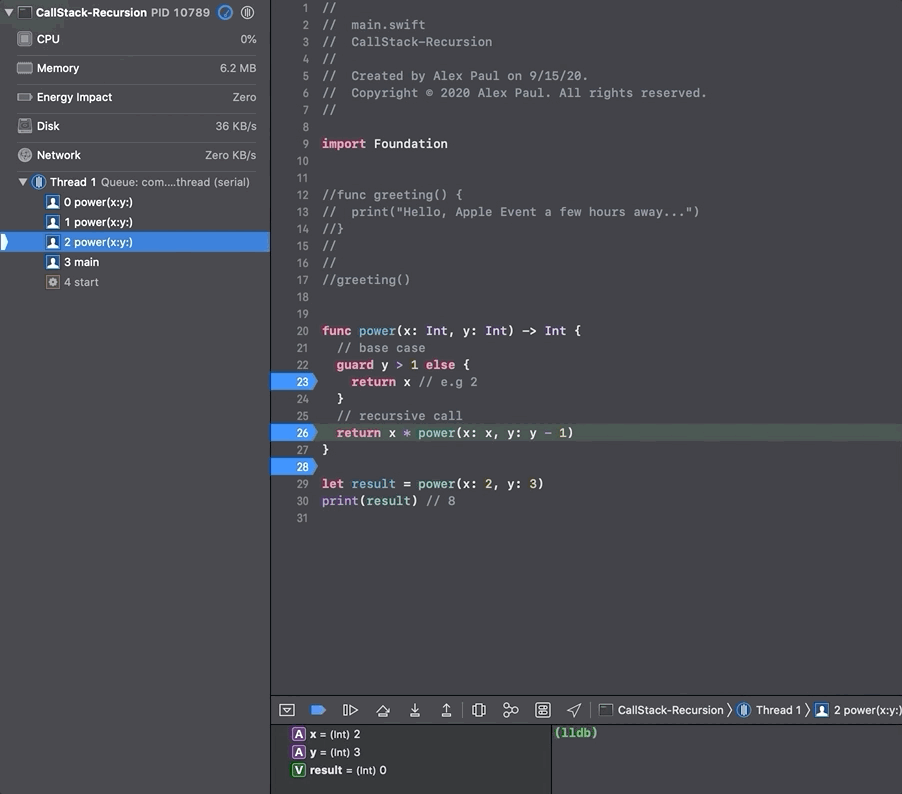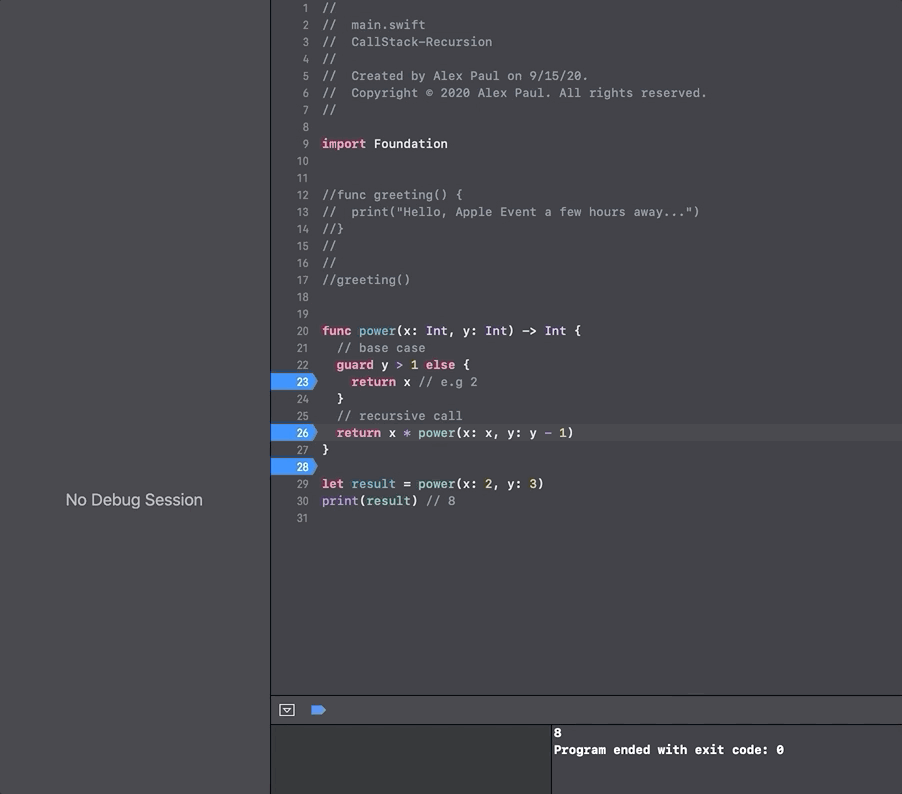
In the gif below we use a command line tool to go through the call stack and visualize the calls from the recursive function power(x_:, y_:) from the sketch above.
Write a function that uses recursion to print the values this given Linked List.
class Node {
var value: Int
var next: Node?
init(_ value: Int) {
self.value = value
}
}
let node1 = Node(1)
let node2 = Node(2)
let node3 = Node(3)
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node3Solution
func printNode(_ node: Node?) {
// 1
guard let node = node else {
return
}
// 3
print("\(node.value)", terminator: " ") // 1 2 3
// 2
printNode(node.next)
// 4
//print("\(node.value)", terminator: " ") // 3 2 1
}
printNode(node1)- Base case
- Recursive call
- Print value of current node
- If we were to print the node values after the function returns at each recursive call the values would be reversed.