- Developers love OpenShift ❤️
- Developers need local OpenShift environment (Solution : CRC (CodeReady Containers) ) 💻
- Developers build Applications, that need Block/File/Object storage 🔨
- ODF provides Block/File/Object storage to OpenShift 👌
- ODF Nano deploys ODF on CRC 🙌 👏
tldr; Watch introduction & Demo Video here
ODF-Nano lets you deploy OpenShift Data Foundation on your Laptop (CRC).
- For dev/test experimentation developers ofter need persistent storage with CRC.
- Currently CRC lacks clean & simple persistent storage solution,
ODF-Nanosolves this problem for CRC. - Devs can now develop/test their apps locally using
CRC+ODF-Nano. Once the app is ready, it could be deployed in productionOCP+ODFwithout any change
- RHEL 8,
- Fedora 34 (tested) [ Feel free to test with other releases ]
- Ubuntu 20.04 (tested) [ Feel free to test with other releases ]
- MacOS ( Need more tests )
- Download CRC and OC binaries from [cloud.redhat.com]((https://cloud.redhat.com/openshift/create/local)
- Create CRC directlry
mkdir ~/.crc - Also get CRC pull secret from [cloud.redhat.com]((https://cloud.redhat.com/openshift/create/local) and save it as
~/.crc/pull-secret.txt
Watch Demo Video here
Note : If you have already deployed CRC using OpenSpot project, you can skip step-1 and move directly to step-2
mkdir ~/.crc
cd ~/.crc
# Get CRC pull secret from [cloud.redhat.com]((https://cloud.redhat.com/openshift/create/local) and save it as `~/.crc/pull-secret.txt`
crc config set consent-telemetry no
crc config set enable-cluster-monitoring true # Enable only if you have enough memory, needs ~4G extra
crc config set cpus 15 #Change as per your HW config
crc config set memory 60000 #Change as per your HW config
crc config set pull-secret-file ~/.crc/pull-secret.txt
crc config view
crc setup
alias crcssh='ssh -i ~/.crc/machines/crc/id_ecdsa core@"$(crc ip)"'
crc start
crcssh uptime
crc console --credentials > crc-creds.txt
- Access https://console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing from client machine
- SSH into the host machine running CRC VM
- Create a few raw devices that
ODF-Nanowill use
## Don't worry this is thin provisioned
sudo -S qemu-img create -f raw ~/.crc/vdb 100G
sudo -S qemu-img create -f raw ~/.crc/vdc 100G
- Attach these devices to CRC VM
crc stop
sudo virsh list --all
sudo virsh dumpxml crc > ~/crc.xml
vim ~/crc.xml
- Add the following section to
crc.xml - Make sure to set the correct disk path
<disk type='file' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw' cache='none'/>
<source file='~/.crc/vdb' index='1'/>
<backingStore/>
<target dev='vdb' bus='virtio'/>
<alias name='virtio-disk1'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</disk>
<disk type='file' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw' cache='none'/>
<source file='~/.crc/vdc' index='2'/>
<backingStore/>
<target dev='vdc' bus='virtio'/>
<alias name='virtio-disk2'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</disk>
- Apply XML file and start CRC
sed -i "s|~|$HOME|g" ~/crc.xml
sudo virsh define ~/crc.xml
crc start
- List devices to verify
crcssh lsblk
Watch Demo Video here
mkdir ~/.crc
cd ~/.crc
# Get CRC pull secret from [cloud.redhat.com]((https://cloud.redhat.com/openshift/create/local) and save it as `~/.crc/pull-secret.txt`
crc config set consent-telemetry no
crc config set enable-cluster-monitoring true # Enable only if you have enough memory, needs ~4G extra
crc config set cpus 9 #Change as per your HW config
crc config set memory 32768 #Change as per your HW config
crc config set disk-size 250 #Don't worry this is thin provisioned
crc config set pull-secret-file ~/.crc/pull-secret.txt
crc config view
crc setup
alias crcssh='ssh -p 2222 -i ~/.crc/machines/crc/id_ecdsa core@"$(crc ip)"'
crc start
crcssh uptime
crc console --credentials > crc-creds.txt
- Access https://console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing from client machine
- SSH into the host machine running CRC VM
- Create a few loopback devices that
ODF-Nanowill use
## Don't worry this is thin provisioned
sudo -i
mkdir -p /var/lib/storage
truncate --size 220G /var/lib/storage/disk1
losetup -P /dev/loop1 /var/lib/storage/disk1
pvcreate /dev/loop1
vgcreate odf /dev/loop1
lvcreate -n disk1 -L 105G odf
lvcreate -n disk2 -L 105G odf
lsblk
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/lvm-odf-losetup.service
[Unit]
Description=LVM ODF loopback device setup
DefaultDependencies=no
Conflicts=umount.target
Requires=lvm2-lvmetad.service systemd-udev-settle.service
Before=local-fs.target umount.target
After=lvm2-lvmetad.service systemd-udev-settle.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/sbin/losetup -P /dev/loop1 /var/lib/storage/disk1
ExecStop=/sbin/losetup -d /dev/loop1
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=local-fs-pre.target
EOF
systemctl enable lvm-odf-losetup
-
Login to CRC using
kubeadminoc login -u kubeadmin -p <PWD> https://api.crc.testing:6443 -
Get
odf-nano
git clone https://github.com/ksingh7/odf-nano.git
cd odf-nano
- Install
odf-nano- LINUX
sh deploy_odf.sh
- Install
odf-nano- MacOS
sh deploy_odf_macos.sh
- Sample output
Setting up environment for ODF - this will take a few minutes
subscription.operators.coreos.com/ocs-subscription created
Waiting for operators to be ready
No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.
.No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.
...
.No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.
...............................
Operators are ready now
Finished up preparing the local storage
ODF is installing now, please be patient
ocsinitialization.ocs.openshift.io/ocsinit patched
pod/rook-ceph-tools-7d95854fb8-b78s2 condition met
ODF is installed now
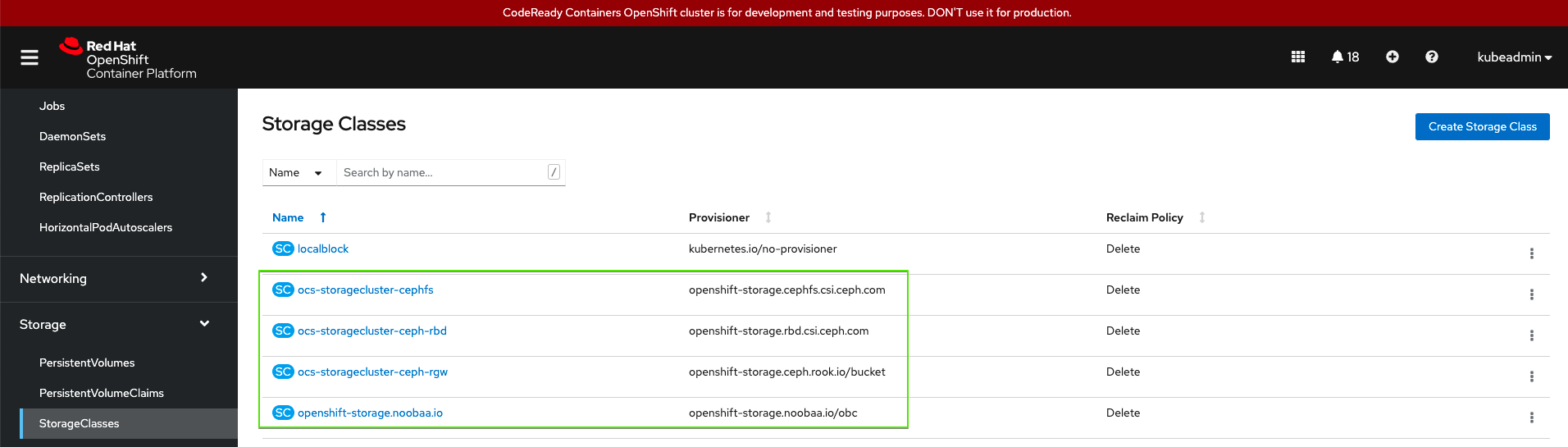
- Verify ODF setup
oc get sc
- You now have File/Block/Object Persistent Storage Classes from ODF. Deploy and Test your app locally, like you do in production (OCP & ODF)
- Resource Footprint
| CPU | Memory |
|---|---|
| 3 vCPU | 2.5G |
- ODF Components
| Component | Count |
|---|---|
| MON | 1 |
| MGR | 1 |
| OSD | 2 |
| MDS | 2 |
| RGW | 1 |
| Ceph-Tools | 1 |
| ocs-metrics-exporter | 1 |
| ocs-operator | 1 |
| noobaa-operator | 1 |
** Reducing MDS count to 1 is WIP **
By default CRC cluster is reachable from localhost. Inorder to access a CRC cluster remotely, we need to add a proxy layer. This setup is useful, when you want to deploy CRC on a remote machine (Home server or a Cloud bare metal), there has to be a way for you to acces CRC cluster remotely. This procedure help you access your CRC remotely.
- Execute on the Host running CRC VM
SERVER_IP=0.0.0.0
CRC_IP=$(crc ip)
sudo cp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg{,.bak}
sudo semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6443
sudo tee /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg &>/dev/null <<EOF
global
log /dev/log local0
defaults
balance roundrobin
log global
maxconn 100
mode tcp
timeout connect 5s
timeout client 500s
timeout server 500s
listen apps
bind 0.0.0.0:80
server crcvm $CRC_IP:80 check
listen apps_ssl
bind 0.0.0.0:443
server crcvm $CRC_IP:443 check
listen api
bind 0.0.0.0:6443
server crcvm $CRC_IP:6443 check
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
sudo systemctl status haproxy
sudo netstat -plunt | grep -i haproxy
- Example output from
netstat
$ sudo netstat -plunt | grep -i haproxy
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9291/haproxy
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9291/haproxy
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9291/haproxy
https://www.stevenrombauts.be/2018/01/use-dnsmasq-instead-of-etc-hosts/
brew install dnsmasq
sudo brew services start dnsmasq
mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/dnsmasq.d
touch /usr/local/etc/dnsmasq.d/crc.conf
vim /usr/local/etc/dnsmasq.d/crc.conf
address=/.testing/192.168.1.6
- verify dns resolution
sudo brew services restart dnsmasq
dig apps-crc.testing @127.0.0.1
dig console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing @127.0.0.1
sudo mkdir /etc/resolver
sudo vim /etc/resolver/testing
nameserver 127.0.0.1
scutil --dns
ping -c 1 foo.api.crc.testing
ping -c 1 foo.apps-crc.testing
ping -c 1 console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing
bash uninstall_odf.sh
- If running out of space, create a symlink for .crc
mkdir /mnt/hdd_space1/.crc
ln -s /mnt/hdd_space1/.crc ~/.crc
- To ssh into crc vm
ssh -i ~/.crc/machines/crc/id_ecdsa core@"$(crc ip)"
- Deep clean previous instance of crc
crc delete -f
crc cleanup
rm -rf ~/.crc/vd* ~/.crc/crc* ~/.crc/bin ~/.crc/machines
sudo virsh list --all
sudo virsh destroy crc
sudo virsh undefine crc
virsh vol-list --pool crc
#virsh pool-destroy crc # generally you can skip this
# virsh vol-list --pool crc # generally you can skip this
- Increase root disk spaced of CRC VM
By defautl CRC vm uses 30G of root disk, you definately need to increase that
crcssh lsblk
# Identify partition name of /sysroot
vda 252:0 0 31G 0 disk
|-vda1 252:1 0 1M 0 part
|-vda2 252:2 0 127M 0 part
|-vda3 252:3 0 384M 0 part /boot
`-vda4 252:4 0 30.5G 0 part /sysroot
vdb 252:16 0 100G 0 disk
vdc 252:32 0 100G 0 disk
crc stop
CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE=${HOME}/.crc/machines/crc/crc.qcow2
# This resize is thin-provisioned
sudo qemu-img resize ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE} +20G
sudo cp ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE} ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE}.ORIGINAL
#increase the /dev/sda4 (known as vda4 in the VM) disk partition size by an additional 20GB
sudo virt-resize --expand /dev/sda4 ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE}.ORIGINAL ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE}
sudo rm ${CRC_MACHINE_IMAGE}.ORIGINAL
crc start
- Refer issue#3