The goal of heRmes is to standardise the heart failure phenotyping of collections of electronic health records.
You can install the latest version of heRmes like so:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("nicksunderland/heRmes")The code lists underpinning the various phenotypes are stored in text
files within the package structure at: inst/extdata/ukhdr_phenotypes.
The format of the file matches that used by the UKHDR Phenotype
Library, but the important
columns are: code, description, coding_system.name, phenotype_id
and phenotype_name. Below is an example of how to view the available
phenotypes and obtain the codes.
For example, view the first 5 phenotypes.
get_phenotypes()[1:5]
#> CCU002_02 Cardiomyopathy
#> "PH1002"
#> Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI)
#> "PH1024"
#> Heart Failure (fatal/non-fatal)
#> "PH1028"
#> Congestive heart failure - Charlson primary care
#> "PH1055"
#> Myocardial infarction - Charlson primary care
#> "PH1062"View the codes for PH1645 corresponding to the HERMES Heart Failure
phenotype.
# top 5 codes
get_codes(pheno_id = "PH1645")[1:5, c("phenotype_id", "phenotype_name", "coding_system.name", "code")]
#> phenotype_id phenotype_name coding_system.name code
#> <char> <char> <char> <char>
#> 1: PH1645 Heart failure ICD9 codes 40201
#> 2: PH1645 Heart failure ICD9 codes 42832
#> 3: PH1645 Heart failure ICD9 codes 42821
#> 4: PH1645 Heart failure ICD9 codes 42823
#> 5: PH1645 Heart failure ICD9 codes 42820Create sample data. This can be in long (only one column containing diagnosis codes) or wide format (multiple columns containing diagnosis codes). n.b. prioritising coding based on diagnosis code position (e.g. primary vs. secondary vs. tertiary positions) is not currently supported.
set.seed(2020)
n <- 10
dat <- data.frame(ids = paste0("ID_", c(1:(n/2), 1:(n/2))),
codes = sample(c("I420", "foo", "bar", "baz"), n, replace = TRUE),
codes1 = sample(c("I420", "foo", "bar", "baz"), n, replace = TRUE))
dat
#> ids codes codes1
#> 1 ID_1 baz I420
#> 2 ID_2 baz I420
#> 3 ID_3 bar baz
#> 4 ID_4 foo baz
#> 5 ID_5 baz baz
#> 6 ID_1 I420 foo
#> 7 ID_2 I420 foo
#> 8 ID_3 baz baz
#> 9 ID_4 foo foo
#> 10 ID_5 foo I420Phenotype the individuals with phenotype PH1643 (heart failure
syndrome) or PH1646 (cardiomyopathy), excluding phenotypes PH1637
(congenital heart disease) and PH1636 (myocardial infarction). There
can be multiple included or excluded phenotypes given in a list.
result <- phenotype(x = dat,
id_col = "ids",
code_cols = list("ICD10 codes" = c("codes", "codes1")),
include = list("PH1645"),
exclude = list("PH1637"))
#> Phenotyping...
#> [i] processing 10 records
#> [i] pivoting data longer
#> [i] getting inclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1645
#> [i] getting exclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1637
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1645
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1637
#> [i] summarising phenotyping of participants
#> [i] finishedresult[]
#> ids PH1645 PH1637 none include exclude overall
#> <char> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl>
#> 1: ID_1 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 2: ID_2 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 3: ID_3 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 4: ID_4 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 5: ID_5 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSEMany of the coding systems have slight formating differences - for
example an ICD-10 code may appear as I509 or I50.9 in a dataset. The
phenotype() provides a way to clean these codes through use of the
gsub argument. This takes a 3 element list: [[1]] is a string
representing the regular expression pattern, [[2]] is the
replacement string, and [[3]] is a character or character vector
which can be one or more of: x (apply to codes in x), pheno (apply
to all codes in phenotypes), both (apply to everything), or a valid
phenotype ID found in include or exclude (apply to specific
phenotype datasets). Other arguments can be passed to gsub through
....
It is important to inspect your dataset (x) and phenotype coding (use
get_codes()) prior to running the phenotyping to avoid join issues
related to formatting differences.
Output formatting can be changed by altering the inputs. If the
phenotype IDs are named, these names are used as column names in the
result. The overall result is given in the column overall, although
this can be renamed by giving the name parameter.
# change format
dat[10, "codes1"] <- "I42.0"
dat[]
#> ids codes codes1
#> 1 ID_1 baz I420
#> 2 ID_2 baz I420
#> 3 ID_3 bar baz
#> 4 ID_4 foo baz
#> 5 ID_5 baz baz
#> 6 ID_1 I420 foo
#> 7 ID_2 I420 foo
#> 8 ID_3 baz baz
#> 9 ID_4 foo foo
#> 10 ID_5 foo I42.0# without dealing with the error ID_5 is incorrectly classified as no HF.
wrong <- phenotype(x = dat,
id_col = "ids",
code_cols = list("ICD10 codes" = c("codes", "codes1")),
include = list(HF = "PH1645"),
exclude = list(congHD = "PH1637"),
name = "Heart Failure")
#> Phenotyping...
#> [i] processing 10 records
#> [i] pivoting data longer
#> [i] getting inclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1645
#> [i] getting exclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1637
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1645
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1637
#> [i] summarising phenotyping of participants
#> [i] finishedwrong[]
#> ids HF congHD none include exclude Heart Failure
#> <char> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl>
#> 1: ID_1 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 2: ID_2 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 3: ID_3 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 4: ID_4 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 5: ID_5 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE# deal with formatting issue using gsub
pheno <- phenotype(x = dat,
id_col = "ids",
code_cols = list("ICD10 codes" = c("codes", "codes1")),
include = list(HF = "PH1645"),
exclude = list(congHD = "PH1637"),
gsub = list("\\.", "", c("x")),
name = "Heart Failure")
#> Phenotyping...
#> [i] processing 10 records
#> [i] pivoting data longer
#> [i] cleaning input codes with regex [ \. ], replacement [ ]
#> [i] getting inclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1645
#> [i] getting exclusion phenotype codes from PhenoID(s) PH1637
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1645
#> [i] assessing phenotype PH1637
#> [i] summarising phenotyping of participants
#> [i] finishedpheno[]
#> ids HF congHD none include exclude Heart Failure
#> <char> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl> <lgcl>
#> 1: ID_1 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 2: ID_2 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 3: ID_3 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 4: ID_4 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 5: ID_5 FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSEThis package’s phenotype library can be updated from the UKHDR
Phenotype Library API
using the below function. This queries the library for phenotypes
matching enteries in the search_terms argument.
update_library(search_terms = c("heart failure", "cardiomyopathy", "myocardial infarction"))
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH25 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH182 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH530 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH531 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH631 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH687 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH968 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH993 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1028 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1055 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1074 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1603 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH129 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH145 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH185 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH961 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1002 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH215 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH356 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH481 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH530 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH611 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH612 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH613 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH741 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH886 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH942 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH949 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH988 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1024 - skipping, already exists
#> [i] reading phenotype id: PH1062 - skipping, already existsThis package’s phenotype library can be updated with
unpublished/development phenotypes from the UKHDR Phenotype Library
API using the below
function. However, since unpublished phenotypes are not searchable by
name, we need to pass the exact ID and also login details for the
website (stored in a local .Renviron file in this example.)
# development phenotypes, ids named for readability only
hermes_phenos <- c(`Congenital heart disease` = "PH1637",
`Heart failure` = "PH1645")
# update
update_library(search_terms = c(),
ids = hermes_phenos,
UKHDR_UN = Sys.getenv("UKHDR_UN"),
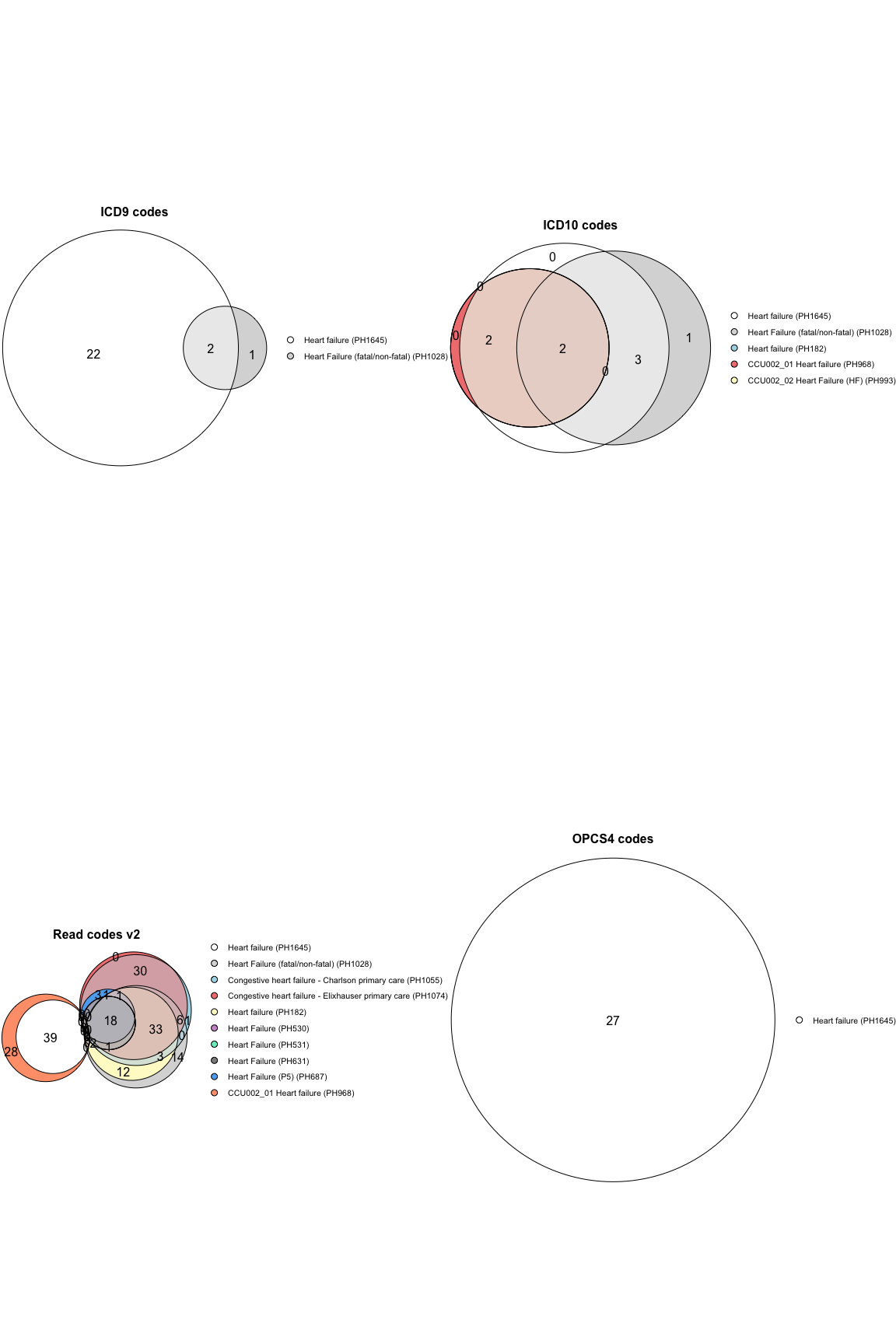
UKHDR_PW = Sys.getenv("UKHDR_PW"))To see the intersection of the codes in two or more phenotype files use
the plot_code_overlap() function.
plot_code_overlap(pheno_ids = c("PH1645", "PH1028", "PH1055", "PH1074", "PH182", "PH25", "PH530", "PH531", "PH631", "PH687", "PH968", "PH993"),
types = c("ICD10 codes", "ICD9 codes", "OPCS4 codes", "Read codes v2"))The primary cardiomyopathy phenotypes described in the ESC cardiomyopathy guidelines.