This repository serves as a demonstration illustrating the process of file import through batch processing. You can find a comprehensive video tutorial on this topic available on YouTube via the following link. The tutorial has been created by Ali Bouali, also known as Alibou.
Spring Batch is a framework for building robust and scalable batch processing applications in Java. It simplifies the development of batch jobs by providing reusable building blocks.
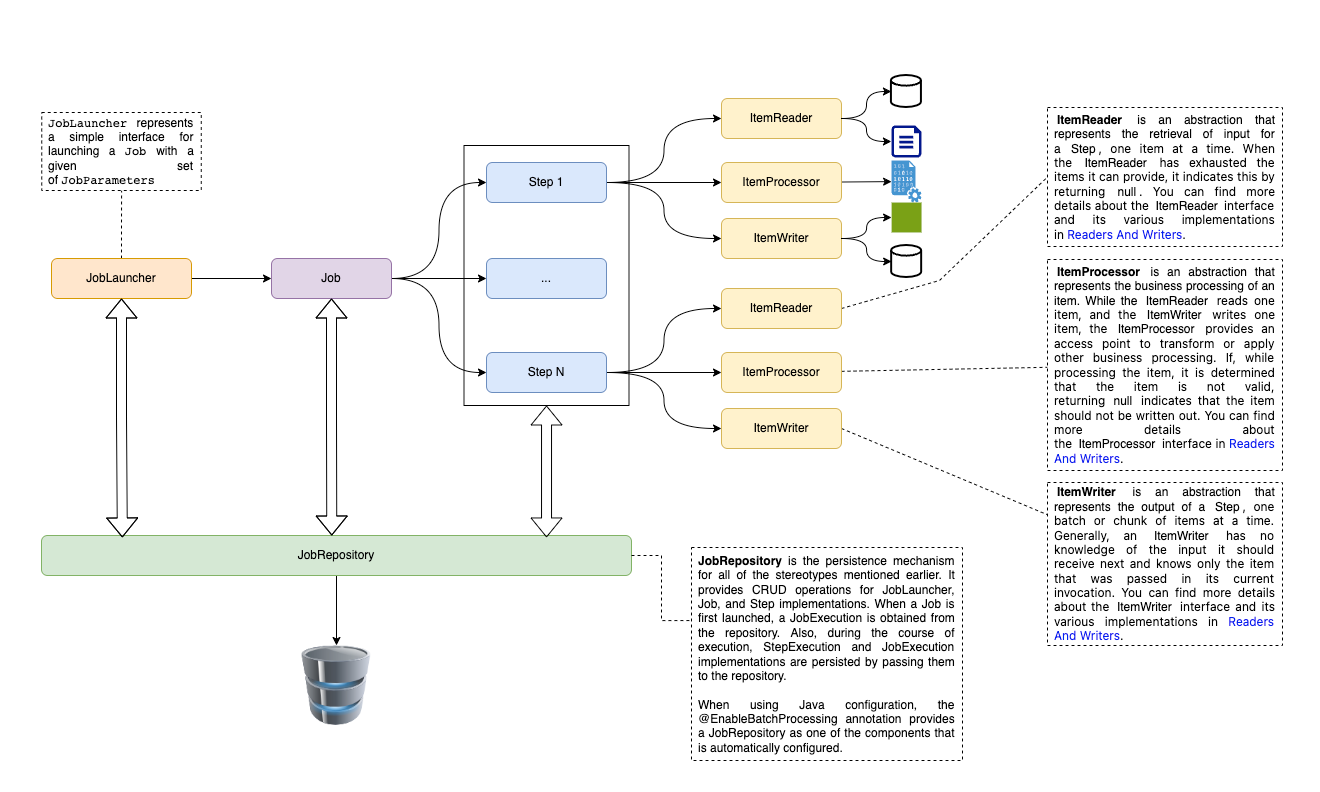
A Job in Spring Batch is the top-level entity that encapsulates an entire batch process. It is configured using either XML or Java-based configuration. A Job is a container for Step instances, grouping logically related steps together. It allows for global configuration, such as restartability.
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class BatchConfig {
private final JobRepository jobRepository;
private final PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
private final StudentRepository repository;
@Bean
public FlatFileItemReader<Student> reader() {
FlatFileItemReader<Student> itemReader = new FlatFileItemReader<>();
//...
return itemReader;
}
@Bean
public StudentProcessor processor() {
return new StudentProcessor();
}
@Bean
public RepositoryItemWriter<Student> writer() {
RepositoryItemWriter<Student> writer = new RepositoryItemWriter<>();
writer.setRepository(repository);
writer.setMethodName("save");
return writer;
}
@Bean
public Step step1() {
return new StepBuilder("csvImport", jobRepository)
.<Student, Student>chunk(1000, platformTransactionManager)
.reader(reader())
.processor(processor())
.writer(writer())
.taskExecutor(taskExecutor())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Job runJob() {
return new JobBuilder("importStudents", jobRepository)
.start(step1())
.build();
}
@Bean
public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor();
asyncTaskExecutor.setConcurrencyLimit(10);
return asyncTaskExecutor;
}
private LineMapper<Student> lineMapper() {
DefaultLineMapper<Student> lineMapper = new DefaultLineMapper<>();
DelimitedLineTokenizer lineTokenizer = new DelimitedLineTokenizer();
lineTokenizer.setDelimiter(",");
lineTokenizer.setStrict(false);
lineTokenizer.setNames("id", "firstName", "lastName", "age");
BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Student> fieldSetMapper = new BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<>();
fieldSetMapper.setTargetType(Student.class);
lineMapper.setLineTokenizer(lineTokenizer);
lineMapper.setFieldSetMapper(fieldSetMapper);
return lineMapper;
}
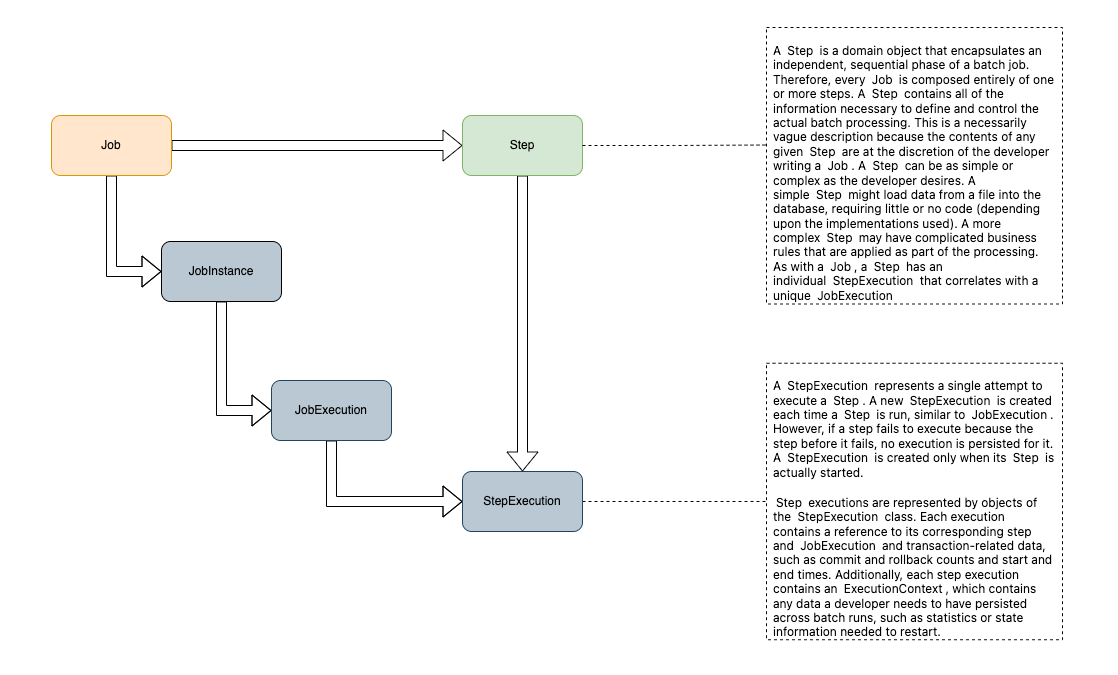
}A Step is a fundamental building block within a Job. It represents a single phase of the batch processing and consists of an ItemReader, ItemProcessor, and ItemWriter. Steps are organized within a Job to create a flow, and each step can be configured individually.
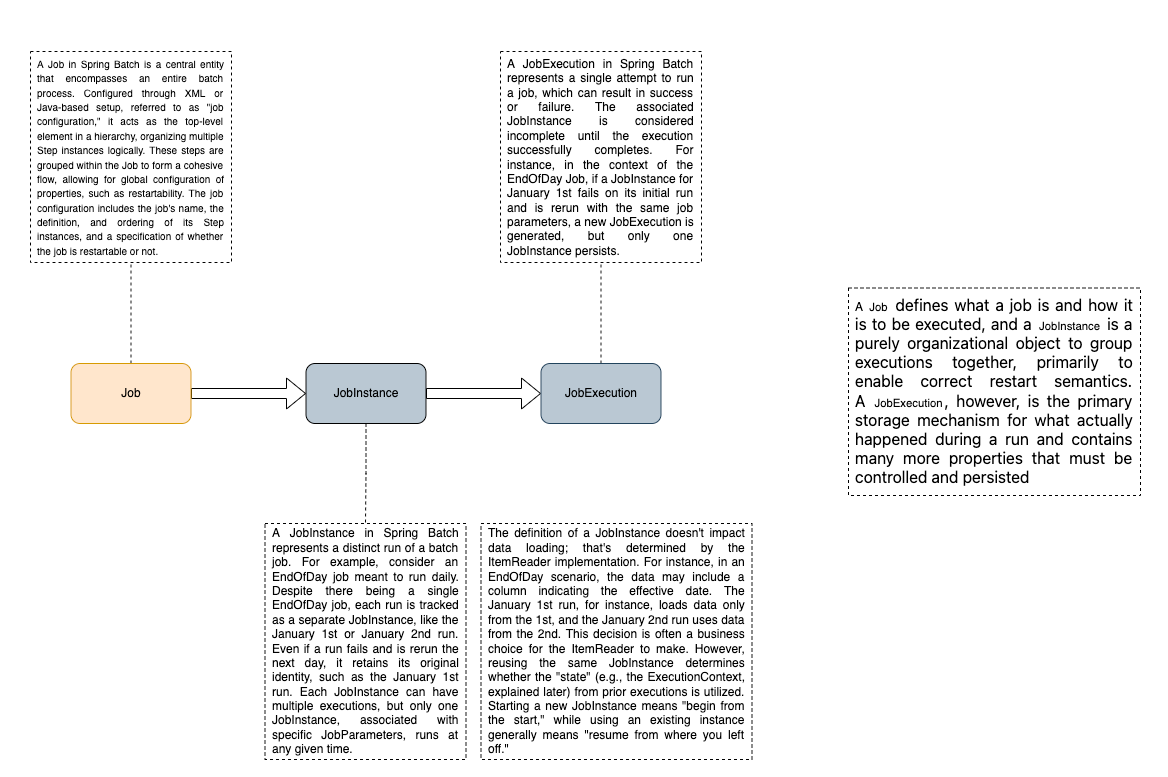
A JobInstance represents a logical run of a batch job. For example, if you have a daily job, each run on a specific day is a separate JobInstance. It helps track and manage individual job runs. Each JobInstance can have multiple JobExecutions, but only one JobInstance can run at a given time.
- January 1st run
- January 2nd run
A JobExecution represents a single attempt to run a Job. It can end in success or failure. A JobInstance is considered incomplete until the JobExecution successfully completes. Even if a JobInstance is rerun, a new JobExecution is created. A JobExecution is the primary storage for the details of what happened during a run.
- January 1st run (initial run)
- January 1st run (rerun)
To get started with Spring Batch, you can follow these steps:
- Define your Job and configure its steps.
- Implement ItemReader, ItemProcessor, and ItemWriter for your specific use case.
- Configure your database and set up any necessary infrastructure.
- Run your Spring Batch job and monitor the JobExecution details.
For more details, please refer to the Spring batch official documentation Visit the official Spring Batch Documentation