This repository contains O-RAN Alliance compliant E2 Node Agent emulators, a nearRT-RIC, and xApps written in C/C++ and Python. It implements various service models (O-RAN standard KPM v2.01/v2.03/v3.00 and RC v1.03, as well as customized NG/GTP, PDCP, RLC, MAC, SC and TC). Depending on the service model, different encoding schemes have been developed (ASN.1, flatbuffer, plain). The indication data received in the xApp uses as persistence mechanism an sqlite3 database for enabling offline processing applications (e.g., ML/AI). Moreover it supports E2AP v1.01/v2.03/v3.01 for all the SMs.
If you want to know more about FlexRIC and its original architecture, you can find more details at: Robert Schmidt, Mikel Irazabal, and Navid Nikaein. 2021. FlexRIC: an SDK for next-generation SD-RANs. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies (CoNEXT '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 411–425. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3485983.3494870. A pdf copy is available at https://bit.ly/3uOXuCV
Below is the list of features available in this version divided per component and per service model:
| OAI-5g | SRS-5g | E2 Agent emulator | Near RT-RIC | xApp c/c++ SDK | xApp python SDK | O-RAN standardized | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KPM | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y |
| RC | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y |
| MAC | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
| RLC | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
| PDCP | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
| SLICE | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
| TC | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N |
| GTP | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N |
1.1 Install prerequisites
-
A recent CMake (at least v3.22).
On Ubuntu, you might want to use this PPA to install an up-to-date version.
-
SWIG (at least v.4.1).
We use SWIG as an interface generator to enable the multi-language feature (i.e., C/C++ and Python) for the xApps. Please, check your SWIG version (i.e,
swig -version) and install it from scratch if necessary as described here: https://swig.org/svn.html or via the code below:git clone https://github.com/swig/swig.git cd swig git checkout release-4.1 ./autogen.sh ./configure --prefix=/usr/ make -j8 make install -
Flatbuffer encoding(optional).
We also provide a flatbuffers encoding/decoding scheme as alternative to ASN.1. In case you want to use it, follow the instructions at https://github.com/dvidelabs/flatcc and provide the path for the lib and include when selecting it at
ccmake ..from the build directory
1.2 Download the required dependencies.
Below an example of how to install it in ubuntu
sudo apt install libsctp-dev python3.8 cmake-curses-gui libpcre2-dev python3-dev1.3 Clone the FlexRIC project, build and install it.
-
Download the code
Check the release page and read the release notes for deciding which release you want to install. You can download directly the code from the web or use git in the following way:
# i.e.: $ git clone https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/mosaic5g/flexric.git # i.e. git checkout v1.0.0 # There are rolling updates on `dev` branch that we consider unstable before releasing and tagging into master branch. # You can play with new features on dev branch checking it out with $git checkout dev instead of the command below $ git checkout <here put the release tag>
-
Build
$ cd flexric && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make -j8
Note: Supported E2AP versions: v1.01/v2.03/v3.01 Supported KPM SM versions: v2.01/v2.03/v3.00 By default, FlexRIC will build the nearRT-RIC with E2AP v2.03 and KPM v2.03. If you are interested in other available versions, please, execute this command:
mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DE2AP_VERSION=<e2ap_version> -DKPM_VERSION=<kpm_version> && make -j8-
Install
You can install the Service Models (SM) in your computer via:
sudo make install
By default the service model libraries will be installed in the path
/usr/local/lib/flexricwhile the configuration file in/usr/local/etc/flexric.Note: Command
sudo make installinstalls shared libraries that represent Service Models. Every time E2AP or/and KPM versions are modified, this command must be executed afterwards.Check that everything went fine running the tests:
ctest
1.4 Test (optional step)
There are some tests you can run. Precisely:
- 3 nodes test. See directory
build/examples/xApp/c/monitor. This test simulates an scenario with an E2 node, a nearRT-RIC and an xApp. Data is randomly filled. Example running in 3 terminals.
# terminal 1: start E2 Node agent
./build/examples/emulator/agent/emu_agent_gnb
# terminal 2: start nearRT-RIC
./build/examples/ric/nearRT-RIC
# terminal 3
./build/examples/xApp/c/monitor/xapp_gtp_mac_rlc_pdcp_moni1.5 Docker (optional step)
We build regularly FlexRIC using docker files for Ubuntu20 and Ubuntu22. You can find the Dockerfile at
cd test/docker/Before starting the nearRT-RIC, check that the IP address where your nearRT-RIC will be listening is the desired one at /usr/local/etc/flexric/flexric.conf.
Infact the default configuration assumes all the components are located in the same localhost.
Start the nearRT-RIC with:
$ ./build/examples/ric/nearRT-RICStart one or multiple E2 node Agent emulators using default configuration
$ ./build/examples/emulator/agent/emu_agent_gnb_cu
$ ./build/examples/emulator/agent/emu_agent_gnb_duor a customized one, i.e.:
$ ./build/examples/emulator/agent/emu_agent_gnb_cu -c ~/flexric1.conf &
$ ./build/examples/emulator/agent/emu_agent_gnb_du -c ~/flexric2.conf &where, for example, flexric1.conf is:
[NEAR-RIC]
NEAR_RIC_IP = 127.0.0.1
[XAPP]
DB_PATH = /tmp/
DB_NAME = xapp_db1
flexric2.conf is:
[NEAR-RIC]
NEAR_RIC_IP = 127.0.0.1
[XAPP]
DB_PATH = /tmp/
DB_NAME = xapp_db2
Next, you can fetch some statistics from the E2 Agents using python xApps via $ python3 build/examples/xApp/python3/xapp_mac_rlc_pdcp_gtp_moni.py, while in other window you can start a second xApp developed in c $ ./build/examples/xApp/c/monitor/xapp_kpm_moni
At this point, FlexRIC is working correctly in your computer and you have already tested the multi-agent, multi-xApp and multi-language capabilities.
The latency that you observe in your monitor xApp is the latency from the E2 Agent to the nearRT-RIC and xApp. In modern computers the latency should be less than 200 microseconds or 50x faster than the O-RAN specified minimum nearRT-RIC latency i.e., (10 ms - 1 sec) range. Therefore, FlexRIC is well suited for use cases with ultra low-latency requirements. Additionally, all the data received in the xApp is also written to /tmp/xapp_db in case that offline data processing is wanted (e.g., Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence applications). You browse the data using e.g., sqlitebrowser. Please, check the example folder for other working xApp use cases.
Follow the instructions https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/oai/openairinterface5g/-/blob/develop/openair2/E2AP/README.md
Follow the instructions https://docs.srsran.com/projects/project/en/latest/tutorials/source/flexric/source/index.html
The nearRT-RIC has been successfully tested with Keysight's RICtest RAN emulator https://www.keysight.com/us/en/product/P8828S/rictest-ran-intelligent-controller-test-solutions.html,
as demonstrated at O-RAN PlugFest Fall 2023. Specifically, the nearRT-RIC with the xApp flexric/examples/xApp/c/keysight/xapp_keysight_kpm_rc.c were tested.
Before running the various components (RAN/nearRT-RIC/xApps), you probably want to align the machines' clock. For this aim, you can use ptp4l in all the machines
involved (if you have for example deployed the various components on different hosts)
sudo ptp4l -m -i InterfaceName #for master
sudo ptp4l -m -i InterfaceName -s #for slavesFollowing make sure that no ntpd, chrondy or timesyncd is running in the system (e.g., sudo systemctl stop systemd-timesyncd).
sudo phc2sys -m -s InterfaceName -w-
Start some gNodeB
Below an example with 5G OAI gNodeB
# gNB $ cd oai/cmake_targets/ran_build/build $ sudo ./nr-softmodem -O ../../../targets/PROJECTS/GENERIC-NR-5GC/CONF/gnb.sa.band78.fr1.106PRB.usrpb210.conf --rfsim --sa -E
-
Start the nearRT-RIC
$ ./build/examples/ric/nearRT-RIC
-
Start different xApps
e.g, start the kpm monitoring xApp via
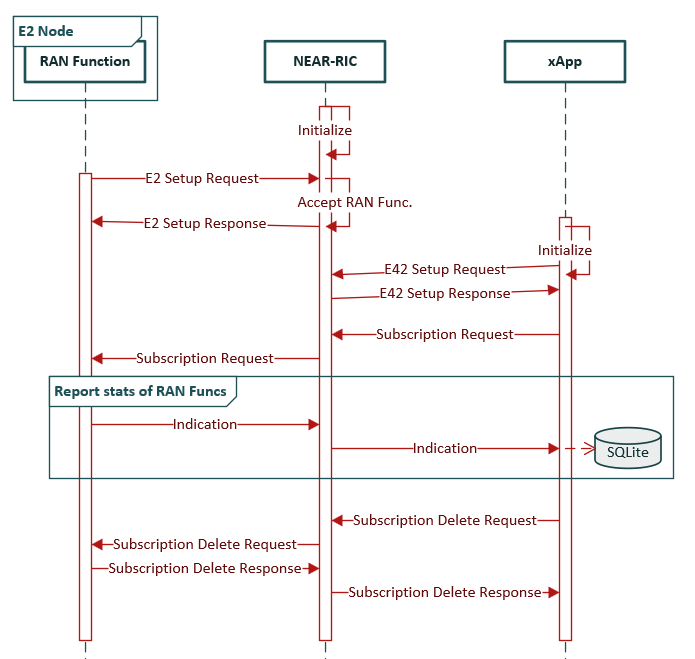
$ ./build/examples/xApp/c/monitor/xapp_kpm_moni. The controlling sequence diagram is represented below:
FlexRIC's E2 Agent (and OAI RAN that is embedded on it) has also been successfully tested using O-RAN's OSC nearRT-RIC H Release as shown at https://openairinterface.org/news/openairinterface-will-showcase-3-demos-at-the-o-ran-f2f-meeting-in-phoenix/ and https://openairinterface.org/joint-osc-oai-workshop-end-to-end-open-source-reference-designs-for-o-ran/
Follow OSC nearRT-RIC installation guide. The xApp can be found at https://github.com/mirazabal/kpm_rc-xapp. Please, note that we do not give support for the OSC nearRT-RIC.
Recorded presentation at Phoenix, October 2023 (4th minute): https://zoom.us/rec/play/N5mnAQUcEVRf8HN6qLYa4k7kjNq3bK4hQiYqHGv9KUoLfcR6GHiE-GvnmAudT6xccmZSbkxxYHRwTaxk.Zi7d8Sl1kQ6Sk1SH?canPlayFromShare=true&from=share_recording_detail&continueMode=true&componentName=rec-play&originRequestUrl=https%3A%2F%2Fzoom.us%2Frec%2Fshare%2FwiYXulPlAqIIDY_vLPQSGqYIj-e5Ef_UCxveMjrDNGgXLLvEcDF4v1cmVBe8imb4.WPi-DA_dfPDBQ0FH
- Mailing list: if you need help or have some questions, you can subscribe to the mailing list
techs@mosaic-5g.iothat you can find at https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/mosaic5g/mosaic5g/-/wikis/mailing-lists. The emails are archived and available publicly. - Demo for flexric in July 2022
- The Wiki space contains tutorials and presentations
- Original FlexRIC paper ACM CoNEXT 2021
Check https://openairinterface.org/projects/oam-project-group/
Check on https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/mosaic5g/flexric/-/milestones and in https://openairinterface.org/mosaic5g/