Simple Beer Service Setup Guide
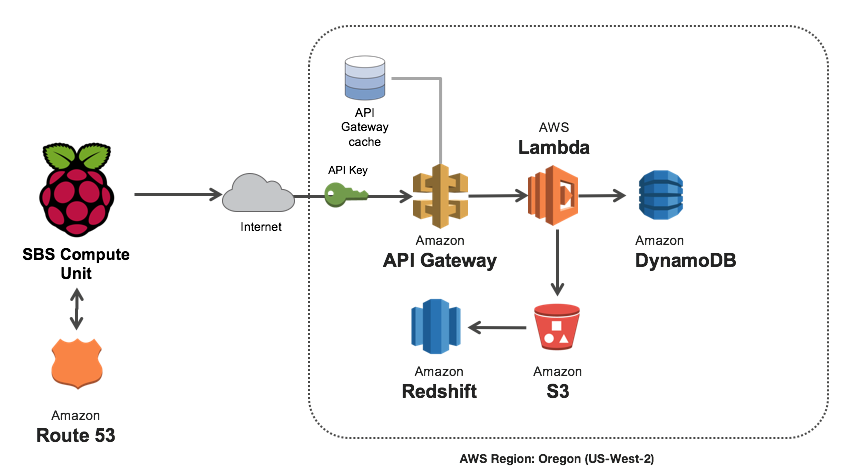
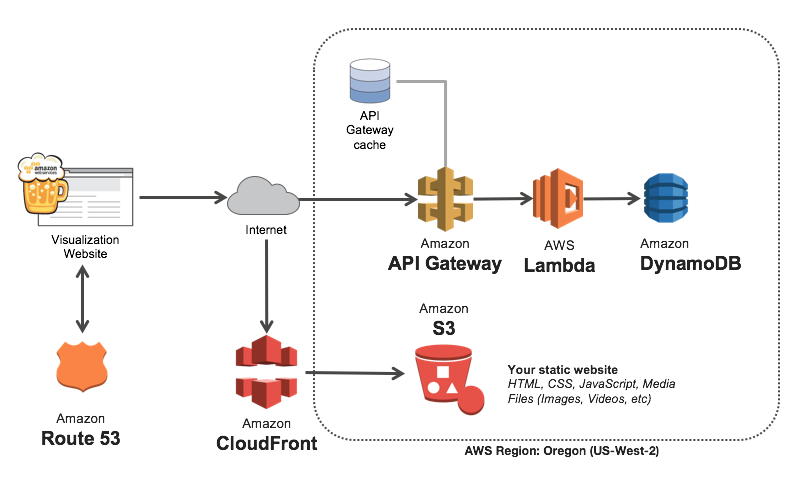
Simple Beer Service (SBS) is a cloud-connected kegerator that sends sensor data (beer flow, temperature, humidity, sound levels and proximity) to an Amazon API Gateway endpoint. The API Gateway endpoint invokes an AWS Lambda function that writes sensor data to an Amazon DynamoDB table. A serverless static S3 website displays the data in real-time as it streams in through Amazon API Gateway and AWS Lambda.
SBS Device Architecture
Real-time Dashboard Architecture
Pre-requisites
Hardware
Before getting started, check to ensure you have the following components:
- Raspberry Pi - Purchase
- GrovePi Shield - Purchase
- Seeed Studio: Flow Meter, DHT PRO, Ultrasonic Sensor, Button, 3 LEDS, Speakers and whatever else you want! More Info
Getting your AWS environment up and running.
- Purchase a domain for your SBS website and create a new hosted zone associated with the domain.
- Launch the CloudFormation script include in the cfn/ directory. Reference the hosted zone used in Step 1.
- Once completed, in the outputs of your CloudFormation stack, you will see the name of two DynamoDB tables. One, is the unit table used to hold the information about all SBS units in your fleet. The other, is the SBS data table. All sensor data from your SBS fleet is written into this table. Secondly, you will see the name of the three lambda functions in here as well. We will reference these names in the application files.
- In the SBS code base, you will need to change a few things:
- deploy/lambda.sh -> replace the FCT_NAMES with the actual Lambda function names from the outputs above.
- web/Gruntfile.js -> find the task "publish" and replace with <S3_BUCKET> with your bucket name. Also, change the IAM profile from default to your profile name if required, as well as the default region.
- lambda/getSBSFleet, lambda/readSBSData, lambda/writeSBSData -> Add in your DynamoDB table names to these files.
- Deploy your lambda functions using the script /deploy/lambda.sh.
- Next, create a new API Gateway endpoint and wire up the Lambda functions. [Coming Soon, Swagger File]
- ENDPOINT/data -> GET -> Query String Parameters (timestamp) -> readSBSData lambda function.
- ENDPOINT/fleet -> GET -> getSBSFleet lambda function.
- ENDPOINT/{sbsid} -> GET -> getSBSFleet lambda function.
- ENDPOINT/{sbsid}/data -> GET -> Query String Parameters (timestamp) -> readSBSData lambda function.
- ENDPOINT/{sbsid}/data -> POST -> writeSBSData lambda function.
- For the resources that require the query string parameter timestamp, include the following Mapping Template in the integration response:application/json -> { "timestamp": "$input.params('timestamp')" }
- For more information on how to setup API Gateway and wire them up to Amazon API Gateway, click here
- You will also need to enable CORS support for API Gateway, to do this click here
- Once completed, take your deployed API Gateway endpoint and add it the following file. You will also need to reference this when installign the device code.
- web/app/scripts/main.js
Software
Flashing the Raspberry Pi with Raspbian
- Follow the instructions on the Raspberry Pi website to flash a new SD card with Raspbian [1].
- Once complete, put the SD card into the Raspberry Pi, connect the ethernet cable, external monitor and keyboard.
- Start the Rasberry Pi. After following the instructions above, you should see a command prompt.
Installing the software
-
Update the OS:
sudo apt-get install rpi-update sudo rpi-update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo reboot -
Configure the linux distribution:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure keyboard-configuration sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata sudo apt-get update sudo reboot -
Copy over SBS files to the Raspberry-Pi. A recommended directory to install SBS is:
sudo su cd /opt/ mkdir sbs -
Run the install script from the SBS directory:
sudo ./install.sh -
During the install process, you will be prompted for some configuration variables. You will need to input:
- A Gateway ID: The identifier of your new SBS unit.
- An AWS API Gateway Endpoint.
- An AWS API Gateway Key.
- The content type (default is application/json)
- The location of the sensors. For example, flow-sensor = 5 would mean that the flow sensor is connected to D5 on the GrovePi sheild. You can connect your sound sensor to A0 and your RGB LCD screen to any I2C port.
- The location of the LEDS.
- The location of the button.
- Threshold values. You can leave these as the default values.
-
Once your Raspberry Pi has restarted, go back to your install directory and install grove through pip:
cd /opt/sbs/ sudo pip install grovepi -
Set-up WiFi
a. Open the WPA Supplicant File:
sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confb. Add the following to the supplicant file (using the connection details of your WiFi network):
network={ ssid="YOURSSID" psk="YOURPASSWORD" # Protocol type can be: RSN (for WP2) and WPA (for WPA1) proto=WPA # Key management type can be: WPA-PSK or WPA-EAP (Pre-Shared or Enterprise) key_mgmt=WPA-PSK # Pairwise can be CCMP or TKIP (for WPA2 or WPA1) pairwise=TKIP #Authorization option should be OPEN for both WPA1/WPA2 (in less commonly used are SHARED and LEAP) auth_alg=OPEN }c. Open the network interfaces file:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfacesd. Add the following (or replace if it is already there):
allow-hotplug wlan0 iface wlan0 inet dhcp wpa-conf /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf iface default inet dhcp -
Run python SBS.py to start the application.
Kegerator Setup
Included in this respository is the 3D printable .stl files. Bring these files to your favourite 3D printer (or print them yourself!) and build the SBS compute unit.
- Once the compute unit has been created, attach it to the top of your kegerator tower. Drop the wires for the flow sensor and the digital humidity and temperature sensor down the tower into the fridge.
- Ensure you have two couplers for your flow meter, and they are the right size for the line in your kegerator. If all is good, cut the line from the keg coupler to the tower, attaching each end of the tube to the two small couplers on each end of the flow meter.
- Plug in the fridge, and the SBS unit and let it cool down for an hour or so.
- Buy a keg and have it shipped to your address. Once it arrives, ensure it is the right kind of beer that you were expecting. Tap the keg by attaching the keg coupler to the keg and put it in the refrigerator.
- The flow meter will add resistance to your line, which might mean you have to increase the pressure in the system. However, finding the right pressure is an art. Take a look at Draft Beer Made Easy [2] for more detailed instructions if you are finding your beer is a) pouring really slowly - pressure is too low, or b) you have really foamy beer - pressure is too high.