Leverage gRPC's powerful bidirectional streaming capabilities with a simple Python drawing app and GoLang backend service.
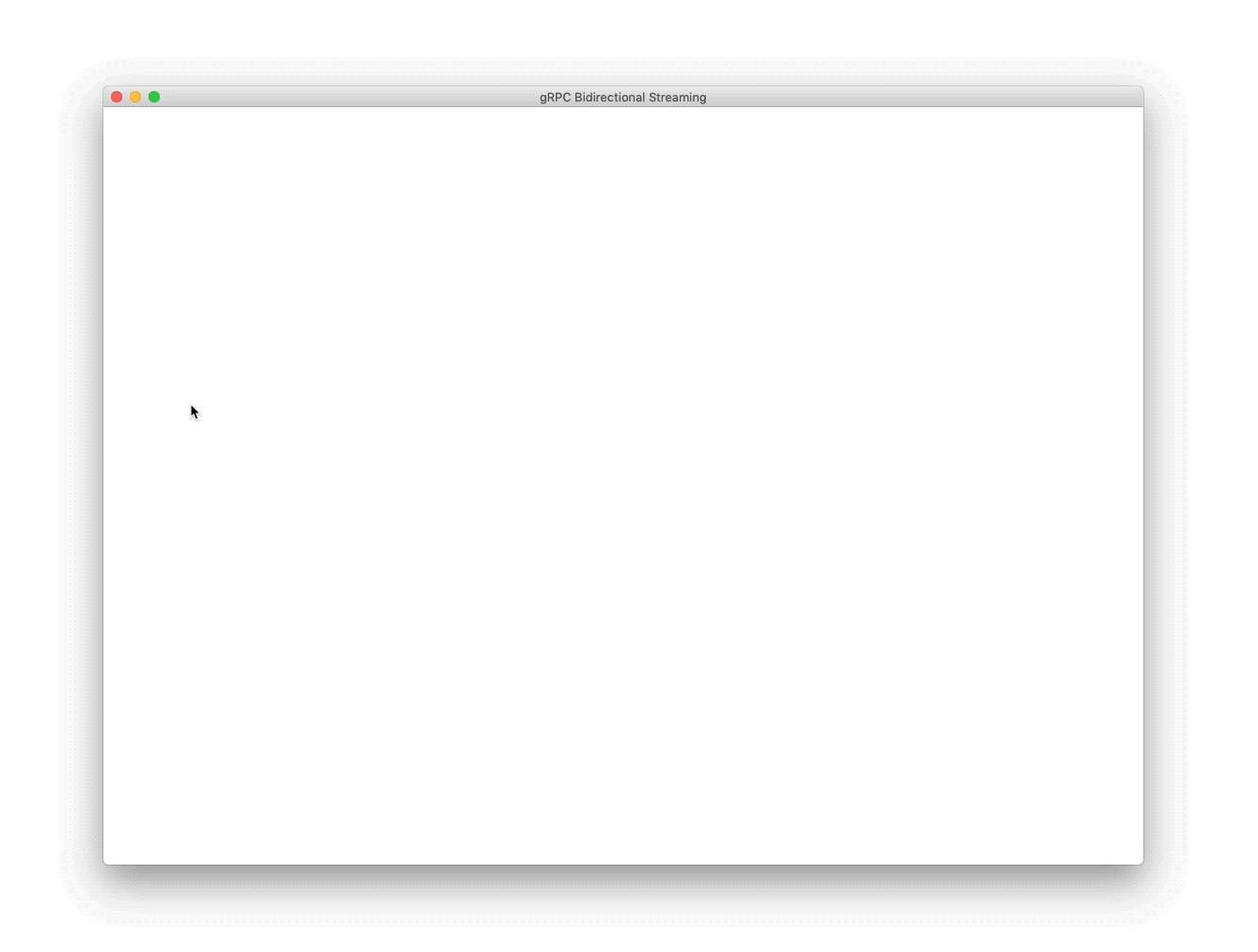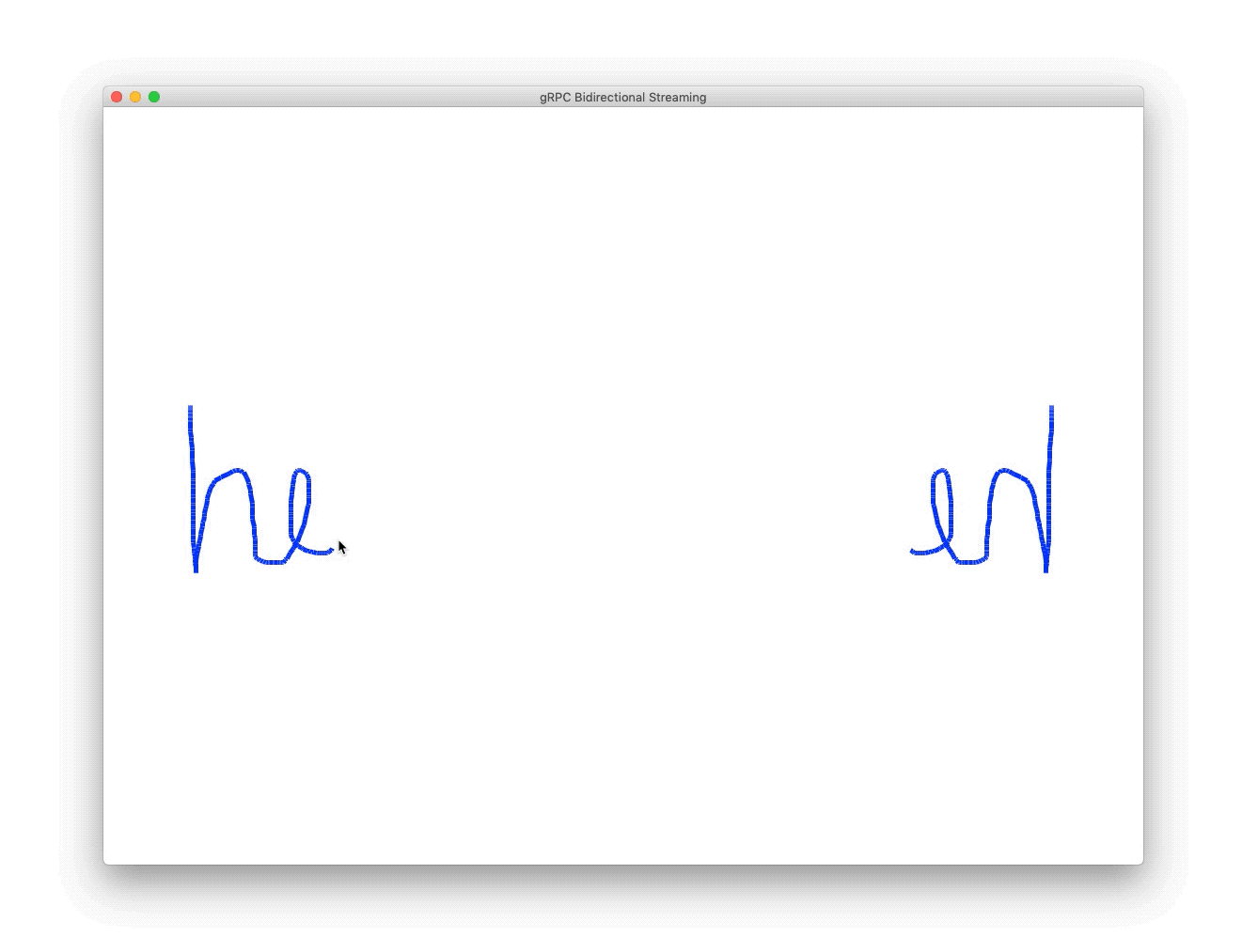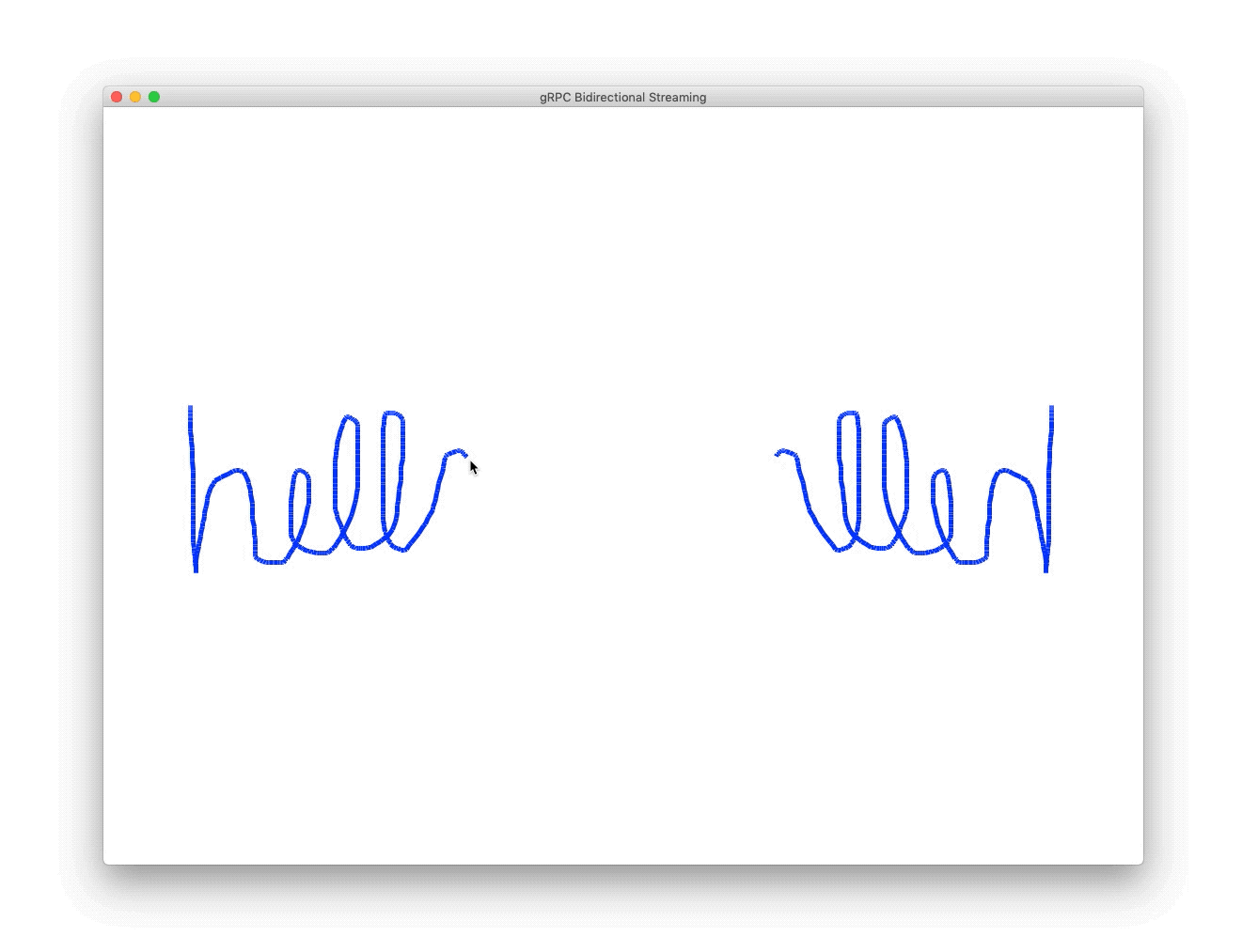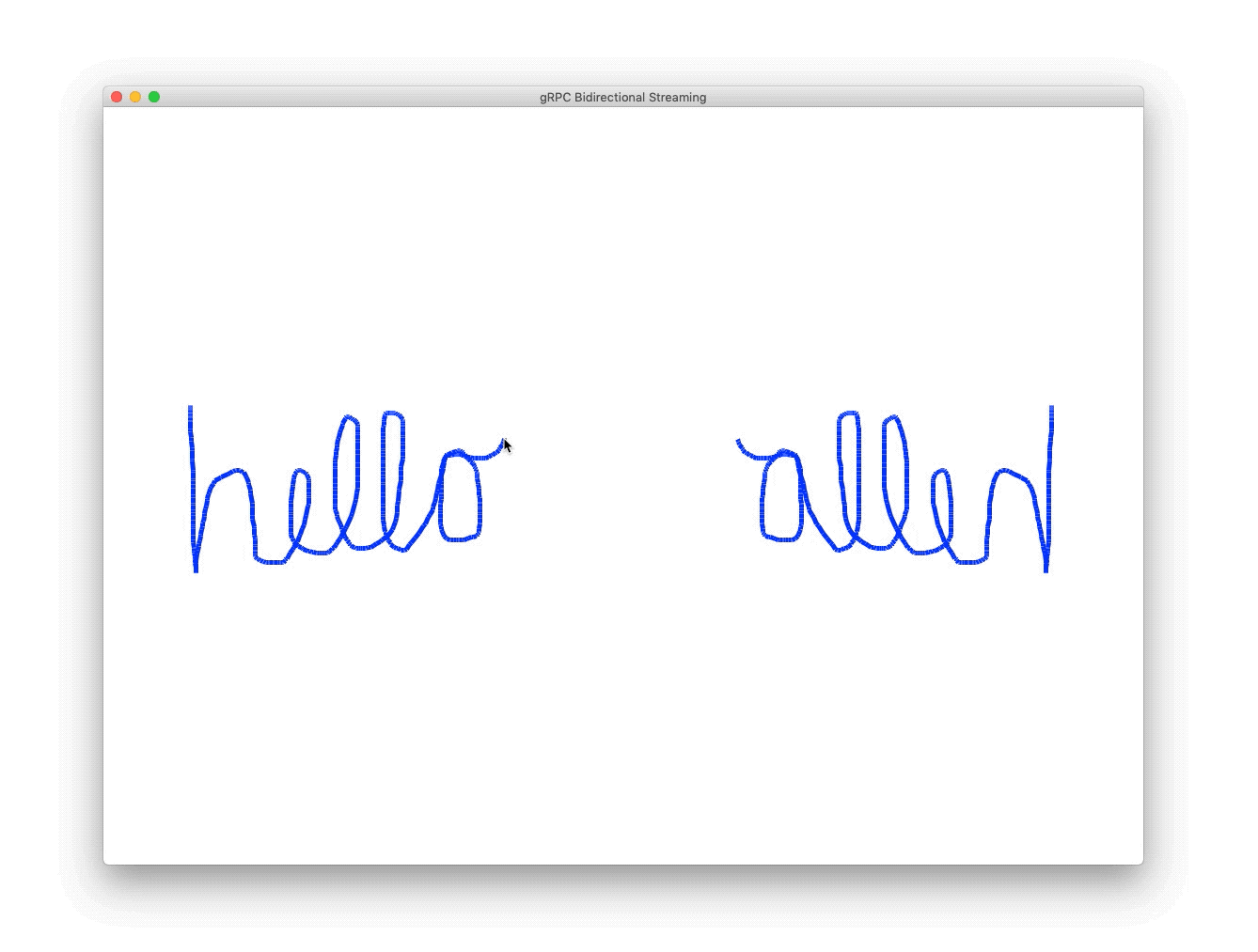
The front-end Python application streams the mouse X and Y coordinates via gRPC to the backend transform service, which flips the coordinates along a horizontal axis, and streams them back to the front end service to be displayed.
The contract between services is defined in the demo.proto file, with flip being the lone RPC call, that both receives and returns a gRPC stream of Point messages.
service Transform {
rpc flip(stream Point) returns (stream Point) {}
}
message Point {
double x = 1;
double y = 2;
Canvas canvas = 3;
}
message Canvas {
int64 width = 1;
int64 height = 2;
}The Point message is received by the backend transform service, which flips the X and Y values along the horizontal axis.
func (s *Server) Flip(stream pb.Transform_FlipServer) error {
for {
in, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
return err
}
if (in.X >= 0) && (in.Y >= 0) {
out := gfx.Mirror(in)
err := stream.Send(&out)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
}On mouse-down, the front-end Python application draws a line from the user's previous mouse location to its current mouse location, and sends the current mouse location the backend to the transform service, and draws a line from the previous mirror point to the current mirror point.
for flip_point in stub.flip(send([event_point])):
if len(flip_points) > 1:
draw_line(flip_points[-2],flip_points[-1])
flip_points.append(flip_point)
From the /transform directory, pull all dependencies.
$ go getServe up transform service on :9901
$ go run server.goFrom the /draw directory, run pip install grpcio && pip install protobuf. Then start up the application:
$ python main.py
Go
$ protoc -I . demo.proto --go_out=plugins=grpc:transform/protos/Python
$ python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I . demo.proto --python_out=draw/protos/ --grpc_python_out=draw/protos/