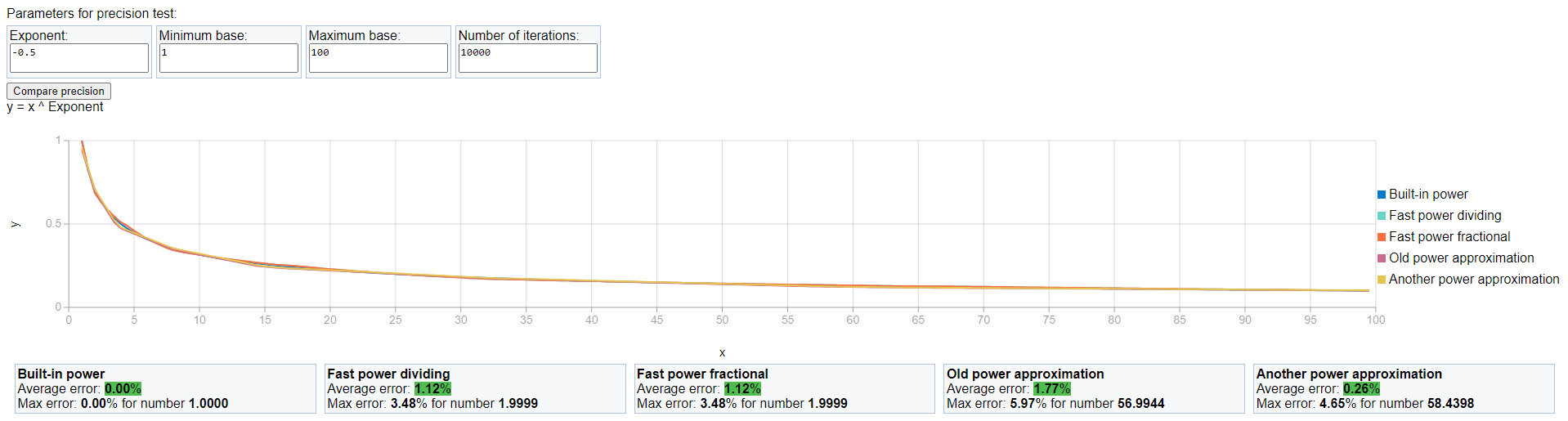
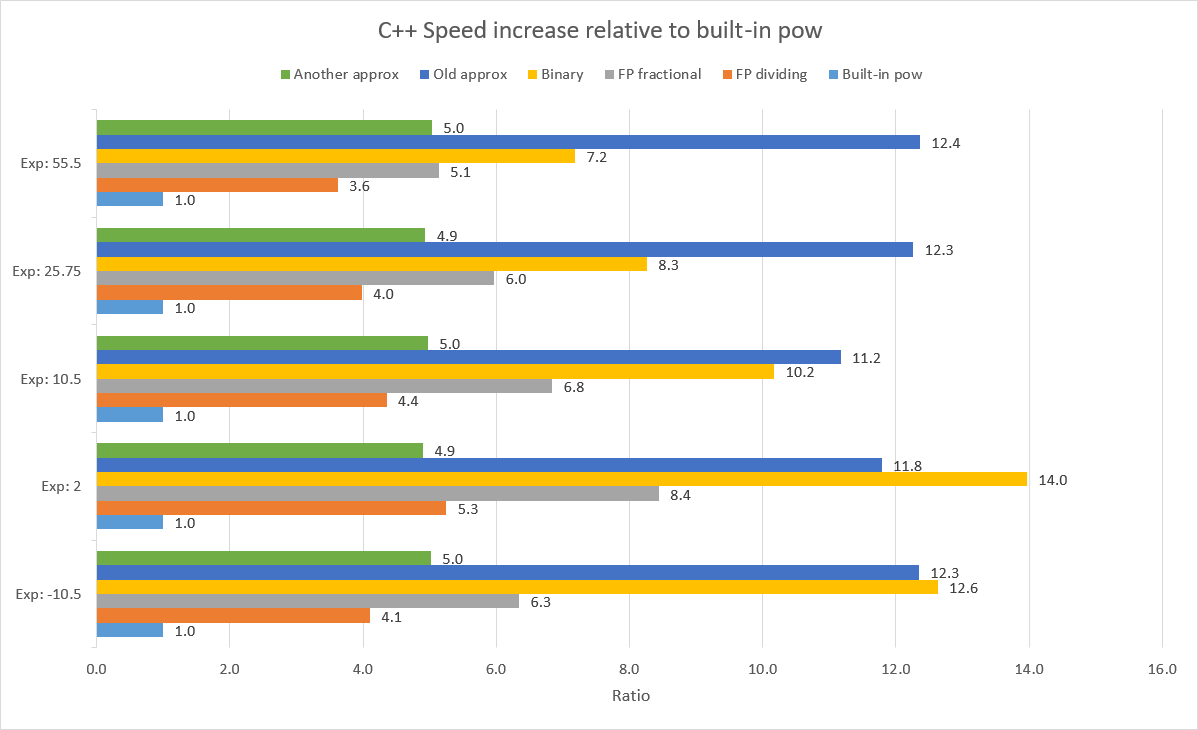
This repository contains realizations of various algorithms for fast exponentiation with small error in C++, C# or Java.
More info: "Ускоряем pow"
- "Old" approximation
- Binary power
- Dividing fast power
- Fractional fast power
- "Another" approximation
There are 9 projects in visual studio solution and 5 java projects used to test custom algorithms, including web page for precision tests.
You can check results of performance measures in this excel table.
Tests ran on: i5-10300H, 19.8 DDR4 GB of usable RAM, 64bit, single threaded
C++: MSVC + /O2 + /Oi + /Ot
C#: "Optimize code" option
In C++
double OldApproximatePower(double b, double e) {
union {
double d;
long long i;
} u = { b };
u.i = (long long)(4606853616395542500L + e * (u.i - 4606853616395542500L));
return u.d;
}In C#
double OldApproximatePower(double b, double e) {
long i = BitConverter.DoubleToInt64Bits(b);
i = (long)(FastMath.doubleApproximator + e * (i - FastMath.doubleApproximator));
return BitConverter.Int64BitsToDouble(i);
}In Java
double OldApproximatePower(double b, double e) {
long i = Double.doubleToLongBits(b);
i = (long) (FastMath.doubleApproximator + e * (i - FastMath.doubleApproximator));
return Double.longBitsToDouble(i);
}In C++
double BinaryPower(double b, unsigned long long e) {
double v = 1.0;
while(e != 0) {
if((e & 1) != 0) {
v *= b;
}
b *= b;
e >>= 1;
}
return v;
}In C#
double BinaryPower(double b, UInt64 e) {
double v = 1d;
while(e != 0) {
if((e & 1) != 0) {
v *= b;
}
b *= b;
e >>= 1;
}
return v;
}In Java
double BinaryPower(double b, long e) {
double v = 1d;
while (e > 0) {
if ((e & 1) != 0) {
v *= b;
}
b *= b;
e >>= 1;
}
return v;
}In C++
double FastPowerDividing(double b, double e) {
// To avoid undefined behaviour near key points,
// we can hardcode results for them, but this
// will make function slightly slower.
if(b == 1.0 || e == 0.0) {
return 1.0;
}
double eAbs = fabs(e);
double el = ceil(eAbs);
double basePart = OldApproximatePower(b, eAbs / el);
double result = BinaryPower(basePart, (unsigned long long)el);
// Because OldApproximatePower gives inaccurate results
// with negative exponent, we can increase precision
// by calculating exponent of a number in positive power
// and then dividing 1 by result of calculation
if(e < 0.0) {
return 1.0 / result;
}
return result;
}In C#
double FastPowerDividing(double b, double e) {
if(b == 1d || e == 0d) {
return 1d;
}
var eAbs = Math.Abs(e);
var el = Math.Ceiling(eAbs);
var basePart = OldApproximatePower(b, eAbs / el);
var result = BinaryPower(basePart, (UInt64)el);
if(e < 0d) {
return 1d / result;
}
return result;
}In Java
double FastPowerDividing(double b, double e) {
if (b == 1d || e == 0d) {
return 1d;
}
var eAbs = Math.abs(e);
var el = Math.ceil(eAbs);
var basePart = OldApproximatePower(b, eAbs / el);
var result = BinaryPower(basePart, (long) el);
if (e < 0d) {
return 1d / result;
}
return result;
}In C++
double FastPowerFractional(double b, double e) {
if(b == 1.0 || e == 0.0) {
return 1.0;
}
double absExp = fabs(e);
unsigned long long eIntPart = (unsigned long long)absExp;
double eFractPart = absExp - eIntPart;
double result = OldApproximatePower(b, eFractPart) * BinaryPower(b, eIntPart);
if(e < 0.0) {
return 1.0 / result;
}
return result;
}In C#
double FastPowerFractional(double b, double e) {
if(b == 1d || e == 0d) {
return 1d;
}
double absExp = Math.Abs(e);
UInt64 eIntPart = (UInt64)absExp;
double eFractPart = absExp - eIntPart;
double result = OldApproximatePower(b, eFractPart) * BinaryPower(b, eIntPart);
if(e < 0d) {
return 1d / result;
}
return result;
}In Java
double FastPowerFractional(double b, double e) {
if (b == 1d || e == 0d) {
return 1d;
}
double absExp = Math.abs(e);
long eIntPart = (long)absExp;
double eFractPart = absExp - eIntPart;
double result = OldApproximatePower(b, eFractPart) * BinaryPower(b, eIntPart);
if(e < 0d) {
return 1d / result;
}
return result;
}In C++
double AnotherApproximatePower(double a, double b) {
union {
double d;
int x[2];
} u = { a };
u.x[1] = (int)(b * (u.x[1] - 1072632447) + 1072632447);
u.x[0] = 0;
return u.d;
}In C#
double AnotherApproxPower(double a, double b) {
int tmp = (int)(BitConverter.DoubleToInt64Bits(a) >> 32);
int tmp2 = (int)(b * (tmp - 1072632447) + 1072632447);
return BitConverter.Int64BitsToDouble(((long)tmp2) << 32);
}In Java
double AnotherApproxPower(double a, double b) {
int tmp = (int)(Double.doubleToLongBits(a) >> 32);
int tmp2 = (int)(b * (tmp - 1072632447) + 1072632447);
return Double.longBitsToDouble(((long)tmp2) << 32);
}