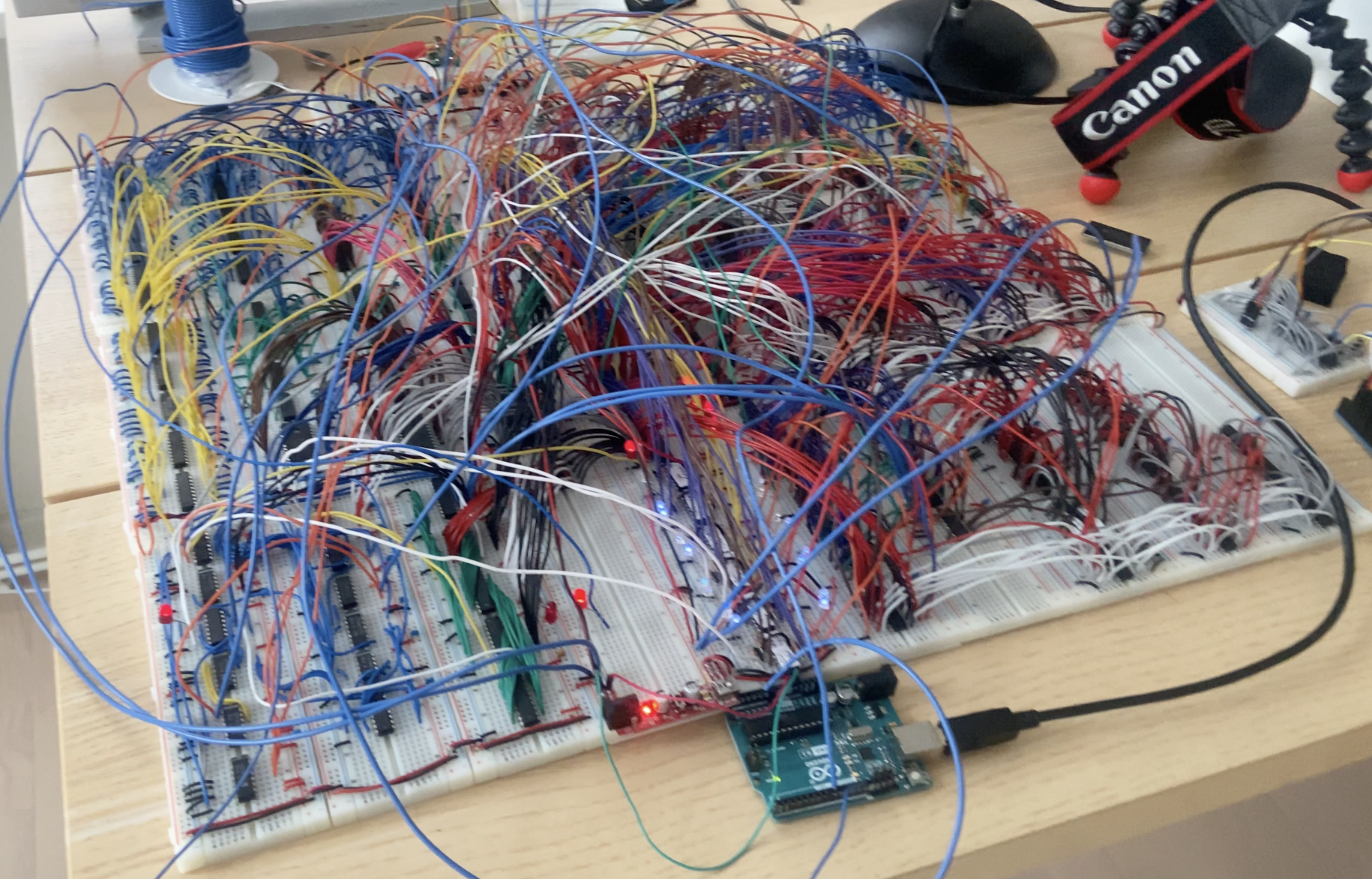
An fully custom 8-bit minicomputer with a unique architecture.
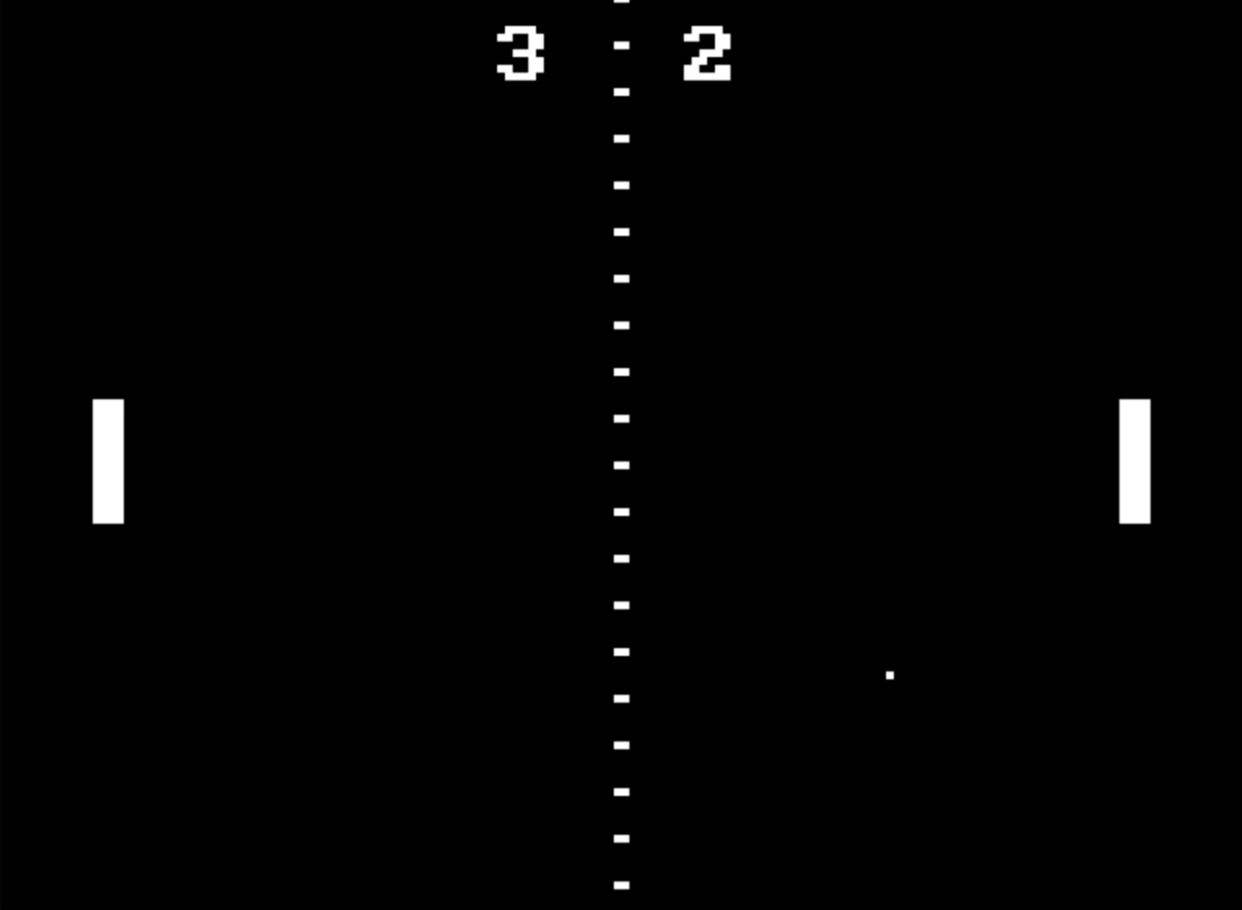
The program above is running in the emulator, see programs/pong.asm for the source.
See the video on the design.
and the video on the build.
- 8-bit data width
- 16-bit address bus (64 KiB available memory + banking)
- 8 fully general purpose registers (5 normal + 2 indirect address + 1 flags)
- 16 instruction RISC architecture
- Port mapped I/O for device communication
0: MW reg, imm8/reg -> reg = imm8/reg
1: LW reg, [HL/imm16] -> reg = [HL/imm16]
2: SW [HL/imm16], reg -> [HL/imm16] = reg
3: PUSH imm8/reg -> [SP--] = imm8/reg
4: POP reg -> reg = [++SP]
5: LDA [imm16] -> HL = imm16
6: JNZ imm8/reg -> imm8/reg != 0 ? PC = HL : NOP
7: INB reg, imm8/reg -> reg = PORT[imm8/reg]
8: OUTB imm8/reg, reg -> PORT[imm8/reg] = reg
9: ADD* reg, imm8/reg -> reg = reg + imm8/reg
A: ADC* reg, imm8/reg -> reg = reg + imm8/reg + c
B: AND reg, imm8/reg -> reg = reg & imm8/reg
C: OR reg, imm8/reg -> reg = reg | imm8/reg
D: NOR reg, imm8/reg -> reg = ~(reg | imm8/reg)
E: CMP* reg, imm8/reg -> f = compare reg, imm8/reg (see below)
F: SBB* reg, imm8/reg -> reg = reg - imm8/reg - b
*these instructions load the carry/borrow bits in the (F)lags register
A (0): GP register/arg 0
B (1): GP register/arg 1
C (2): GP register/arg 2
D (3): GP register/arg 3
L (4): GP register/(L)ow index register
H (5): GP register/(H)igh index register
Z (6): GP register/return value
F (7): flags (LSB to MSB)
LESS
EQUAL
CARRY
BORROW
See the spec for more information.
The schematic requires a modified version of Logisim Evolution to view, see here. You will need to build it from source.
Compile with $ make
- Install MSYS2 (msys2.org)
- Install MinGW-W64 from MSYS2
- Get 64-bit SDL2 development tools (libsdl.org)
- LIBPATH to your SDL location (
Makefileautomatically specifies C:/cdevlibs) - Change CC and LD to the location of GCC (including the executable name) in your MinGW-W64 install or add
gccandldto PATH - Install xxd for Windows (https://sourceforge.net/projects/xxd-for-windows/)
- Change variable XXD in
Makefileto the location of XXD (including the executable name) or addxxdto PATH - Run mingw32-make inside project directory
Assembler (asm)
./bin/asm [-h] [--help] [-v] [--verbose] [-n] [--no-builtin-macros] [-o file] file
Emulator (emu)
./bin/emu [-m/--mod module] [-r/--run] [-l/--load file address] [ROM file]
SET <register> <data>: set register dataGET <register>: get register valuePEEK <address>: get memory valuePOKE <address> <data>: set memory dataINB <port>: get port dataOUTB <port> <data>: write port dataSTEP: step one instructionDUMP: print current machine stateLOAD <ROM file> <address>: load ROM at addressMODS: list modulesMOD <module>: load moduleDEVICES: list devicesRUN <speed?>: run at speed (hz) until haltQUIT: quit