Detectron2 is one of the most widely adopted open source projects and implements state-of-the-art object detection, semantic segmentation, panoptic segmentation, and human pose prediction. D2Go is powered by PyTorch 1.8, torchvision 0.9, and Detectron2 with built-in SOTA networks for mobile - the D2Go model is very small (only 2.7MB) and runs very fast on Android (~50ms per inference on Pixel 3, also due to the use of the native torchvision-ops library).
This D2Go Android demo app shows how to prepare and use the D2Go model on Android. The code is based on a previous PyTorch Android Object Detection demo app that uses a pre-trained YOLOv5 model, with modified pre-processing and post-processing code required by the D2Go model.
- PyTorch 1.10.0 and torchvision 0.11.1 (Optional)
- Python 3.8 or above (Optional)
- Android Pytorch library pytorch_android_lite 1.10.0, pytorch_android_torchvision_lite 1.10.0, torchvision_ops library 0.10.0
- Android Studio 4.0.1 or later
This section shows how to create and use the D2Go model and the pre-built torchvision-ops library in a completed Android app. To just build and run the app without creating the D2Go model yourself, go directly to Step 4.
- Install PyTorch 1.10.0 and torchvision 0.11.1, for example:
conda create -n d2go python=3.8.5
conda activate d2go
pip install torch torchvision
- Install Detectron2, mobile_cv, and D2Go
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/mobile-vision.git'
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/d2go
cd d2go & python -m pip install .
- Create the D2Go model
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/android-demo-app
cd android-demo-app/D2Go
python create_d2go.py
This will create the quantized D2Go model and save it at android-demo-app/D2Go/ObjectDetection/app/src/main/assets/d2go.pt.
The size of the quantized D2Go model is only 2.6MB.
- Build and run the D2Go Android app
If you have not gone through Step 3, simply run git clone https://github.com/pytorch/android-demo-app first.
In Android Studio, open android-demo-app/D2Go (not android-demo-app/D2Go/ObjectDetection). If an error "Gradle’s dependency may be corrupt" occurs, go to Android Studio - File - Project Structure... , change Gradle Version to 4.10.1.
The main changes needed to use the D2Go model and the required and pre-built torchvision-ops library are adding
implementation 'org.pytorch:pytorch_android_lite:1.10.0'
implementation 'org.pytorch:pytorch_android_torchvision_lite:1.10.0'
implementation 'org.pytorch:torchvision_ops:0.10.0'
in the build.gradle file and
static {
if (!NativeLoader.isInitialized()) {
NativeLoader.init(new SystemDelegate());
}
NativeLoader.loadLibrary("pytorch_jni");
NativeLoader.loadLibrary("torchvision_ops");
}
in the MainActivity.java.
Select an Android emulator or device to run the app. You can go through the included example test images to see the detection results. You can also select a picture from your Android device's Photos library, take a picture with the device camera, or even use live camera to do object detection - see this video for a screencast of the app running.
One quick note about the model performance. In the MainActivity.java, the following code snippet shows how fast the D2Go model runs:
final long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
IValue[] outputTuple = mModule.forward(IValue.listFrom(inputTensor)).toTuple();
final long inferenceTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTime;
Log.d("D2Go", "inference time (ms): " + inferenceTime);
On a Pixel 3 phone, it takes about 50ms to infer an image, compared with the 550ms taken by the YOLOv5 model in the Object Detection demo app.
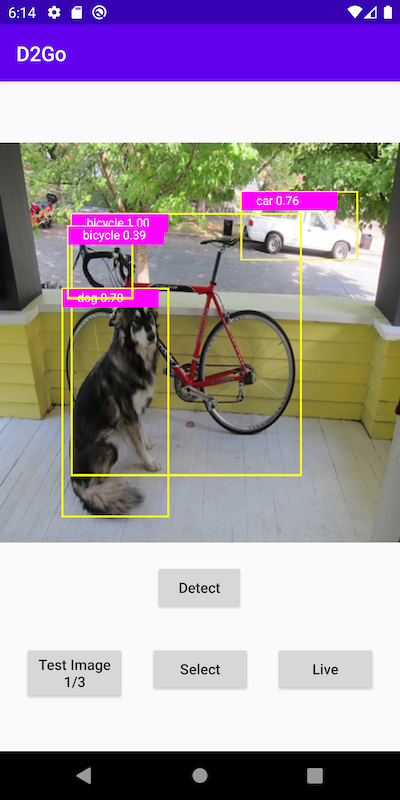
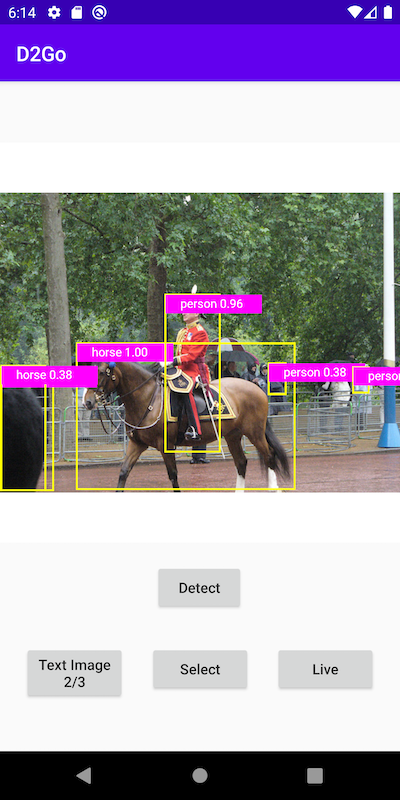
Some example images and the detection results are as follows: