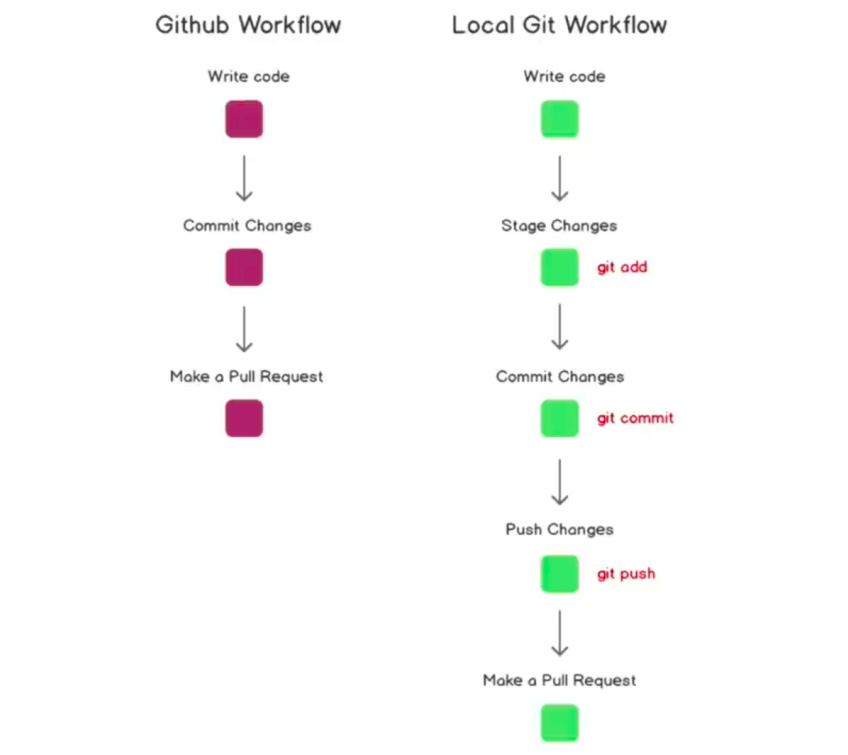
To list hidden files:
ls -la
To check status:
git status
To stage a file:
git add file.txt
To unstage a file:
git restore file.txt
Commit the changes locally:
git commit -m "made first commit" -m "Added index.html and Made some changes to README.md"
To connect your local machine to github account to PUSH changes: Generate a ssh key locally
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "abc@gmail.com"
key.pub will be uploaded using cat key.pub, which is okay to be public
Only the private key could have generated the public key.
Start ssh-agent:
OR, ssh-agent -s
Add private SSH key:
ssh-add mykey
git push origin main
set upstream:
git push -u origin main
Note: Use SSH, not HTTPS The main reason for any problem is mistakenly git clone the HTTPS URL; we need the SSH URL to use the SSH keys. The solution is to update the .git/config file, url value to SSH instead of HTTPS. How to Update the URL of origin remote using SSH instead of HTTPS:
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:username/repo.git
- Use Git Bash
eval `ssh-agent -s`- ssh-add /c/users/hp/documents/../key
- git clone <>
To Check:
git remote -v
To add origin manually: (When push a locally created repo to github)
git remote add origin git@github.com:username/repo.git
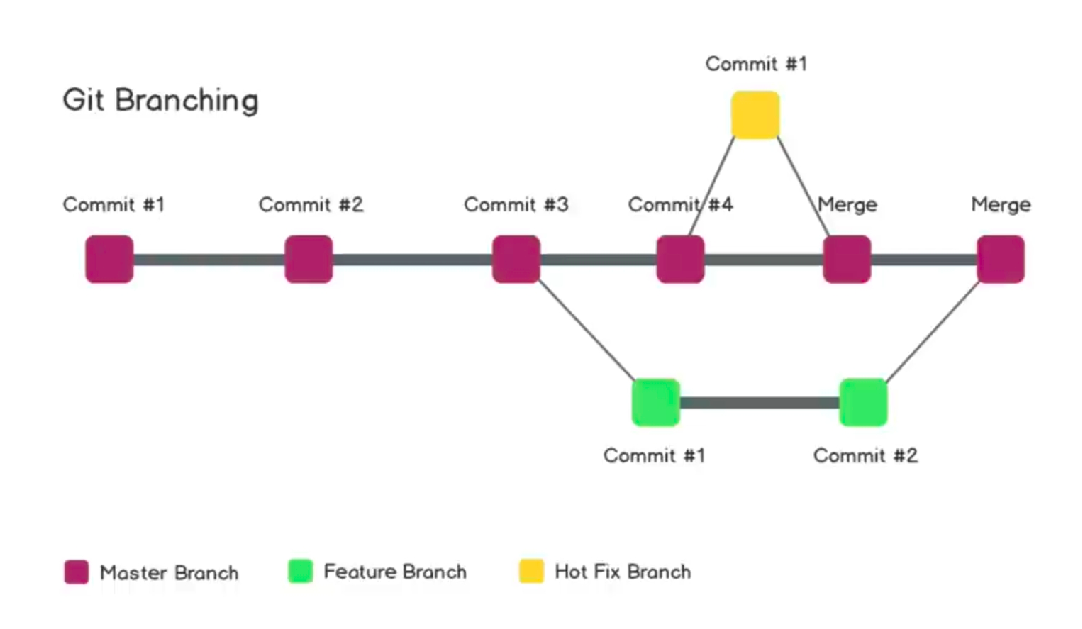
$ git branch
$ git checkout -b feature
Switched to a new branch 'feature'
To Find difference in two branches:
git diff branch-name
NOTE: Merge will work locally but most seen approach is to push both the branches to the github and then make a pull request.
git merge branch-name
Pushing on a different branch: (first checkout that branch)
git push origin branch-name
Then try making a pull request from github, You can also add comments, resolve issues.
You may add more commits to the same pull request before it is merged to the main branch. After it is merged, you have to manually fetch the changes in your local main branch.
git pull origin main
To Delete a branch (like feature) after it is merged to the main:
git branch -d feature
To add & commit at the same time:
git commit -am "modified index.html" -m "description"
Note: only works on modified files, because for new file you need to track/stage the files first.
$ git checkout quick-test
error: Your local changes to the following files would be overwritten by checkout:
index.html
Please commit your changes or stash them before you switch branches.
Aborting
Commiting changes to main branch first,
$ git commit -am "commiting changes to main branch " -m "commiting changes to main branch first to avoid conflict, will then later compare the main branch with the other (quick-test) branch "
$ git checkout quick-test
$ git diff main
$ git merge main
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in index.html
Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
Now you need to use editor like vscode to manually edit the code merge
To Unstage a file or all files:
$ git reset
$ git reset file-name
HEAD is pointer to the last commit:
git reset HEAD~1
above code resets the last commits (or say undo it)
Log of all commits with hashcode:
$ git log
$ git reset hash-of-commit
$ git reset --hard hash-of-commit
Complete copy of some repo (including the branches)
- to make a pull request
- to branch off a repo
- complete control over code of repo
To get our change to get in the original repo, we need to pull request.
In short, this should do it:
$ git remote set-url origin user@example.com:PATH/REPOSITORY
Example:
$ git remote set-url origin git@github.com:alwaysanshul/FitHub.git
- Create a
.gitignorefile in the root directory of your Git repository, if it doesn't already exist. - Open the
.gitignorefile in a text editor. - Add the file or directory pattern that you want to ignore. For example, if you want to ignore a file named
example.txtsimply add the following line to your.gitignorefile:
example.txt
- Save and close the .gitignore file.
- Commit and push the .gitignore file to your Git repository. Note: If you have already committed the file that you want to ignore, you will need to remove it from the repository and create a new commit before the changes in .gitignore take effect. You can use the following Git commands to remove the file from the repository while keeping it in your local working directory:
git rm --cached example.txt
git commit -m "Removed example.txt from version control"
The git rm --cached command removes the file from the repository but keeps it in your local working directory. The subsequent git commit command creates a new commit with the changes.
To ignore all files with a particular extension in a Git repository, you can add a wildcard pattern to your .gitignore file. Here's how you can do it:
- Open your .gitignore file in a text editor.
- Add the following line to ignore all files with the extension .ext:
*.ext
These notes made from course by Gwen Faraday(@faradayacademy)