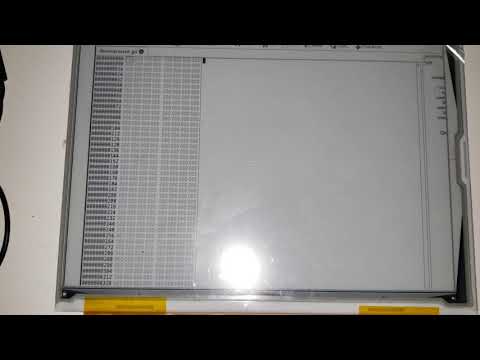
Epdiy Eink Pc Monitor
Description:
This repository contains the source code for a client a host application that allow a Epdiy eink display controller board to mirror the image of a monitor, allowing the eink display to be used as a pc monitor. Video:
Supported platforms:
It has been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 and Windows 10 version 20H2
How it works:
The Python module mss is used to capture the screen and Pillow is used to convert the capture to black and white. The black and white image is piped to a C++ program that generates the eink framebuffer, compresses it with RLE compression and sends it wirelessly to the Epdiy board using TCP protocol.The ESP32 application for the board receives the compressed framebuffer, extracts it and uses the Epdiy driver to write it to the display.
Notes on development:
- Framerate and draw time depend on settings, on how much screen has changed and speed of wifi, with default settings full frame draw time including the wifi transfer can be between 60ms to 160ms.
- Ghosting can be a problem in particular when drawing white letters on black background. Is recommended to use black letters on white background.
- It is necessary to have at least 1 real monitor plugged in to a port of the pc, and the application will mirror an area of that monitor, a dummy hdmi plug could be used to bypass this limitation.
- Because the mss module does not capture the mouse cursor, it is added manually
Dependencies:
This project requires a Epdiy controller board, to get one is necessary to order a pcb from a pcb manufacturers and solder the components. Some pcb manufacturers also offer to solder them. For more info go: https://github.com/vroland/epdiy
Required Python modules:
pip install mss
pip install pyautogui
pip install numpyFor Windows 10:
pip install pywin32
Installation:
-
Once you have the board, flash the demo example on the example folder of the Epdiy repository to verify that it is working correctly.
-
Get the repositories: On linux:
cd
git clone -b v5 https://github.com/vroland/epdiy
git clone https://github.com/amadeok/Epdiy-Eink-PC-monitor
cp -R ~/Epdiy-Eink-PC-monitor/pc_monitor ~/epdiy/examples
On windows' command prompt:
cd c:\
git clone -b v5 https://github.com/vroland/epdiy
git clone https://github.com/amadeok/Epdiy-Eink-PC-monitor
Xcopy /E /I C:\Epdiy-Eink-PC-monitor C:\epdiy\examples
-
The computer and board should connect to the same wifi network. Go to ~/epdiy/examples/pc-monitor/main/, open main.c , go to line 31 and insert the SSID of the wifi network you are going to use in the WIFI_SSID variable and the password of the wifi in the WIFI_PASS variable.
-
Build and flash the client application for the board: On linux:
cd ~/epdiy/examples/pc_monitor
idf.py build && idf.py flash -b 921600 && idf.py monitorOn windows:
cd c:\epdiy\examples\pc_monitor
idf.py build && idf.py flash -b 921600 && idf.py monitor6)After the flashing finishes, the terminal will start displaying some messages, look for the message:
IP Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx(where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is an ip address)
Note it down.
- Add the ip address to a display configuration file:
Open example_display.conf in ~/epdiy/examples/pc_monitor/pc_host_app/ with a text editor and change the IP address in the first line to the one you noted down before, and, if needed, change the values width and height to the witdh and height resolution of your display
- Build the pc-host application and the C shared library: On a new terminal: On Linux:
cd ~/epdiy/examples/pc_monitor/pc_host_app/
g++ main.cpp generate_eink_framebuffer.cpp rle_compression.cpp utils.cpp -o process_capture -I include
g++ dither_.cpp invert_.cpp -o dither_.so -shared -fPICOn Windows(requires MinGW installed and on PATH):
cd C:\epdiy\examples\pc_monitor\pc_host_app\
g++ main.cpp generate_eink_framebuffer.cpp rle_compression.cpp utils.cpp -static -o process_capture.exe -I "C:\Epdiy-Eink-PC-monitor\pc_monitor\pc_host_app\include" -lws2_32
g++ dither_.cpp invert_.cpp -o dither_.dll -shared -fPIC
- Now the pc is ready to start the mirroring. If the board is ready to start mirroring it will display a message saying "Socket listening ". To start the mirroring execute:
python screen_capture.py example_display.confIf you want to hide the terminal output run it like this:
python screen_capture.py example_display.conf -silentImportant: always exit the pc host application by pressing the letter q
Creating configuration files and settings:
The pc host application reads the settings from a .conf file passed as an argument when running screen_capture.py. Inside a display configuration file there are the following settings:
-
ip_address : the IP address of the ESP32 module to connect to
-
id: Number to identify each display. Has to be different for each display
-
width : the resolution width of the display
-
height: the resolution height of the display
-
x_offset and y_offset
They set how many pixels away for the top left corner the screen will be captured. ie. if the resolution is 1200x825, setting both to zero will capture 1200x825 pixels from the extreme top left corner of the screen. setting them to 100 and 50 will capture 1200x825 pixels 100 pixels to the right and 50 pixels from the top left corner of the screen. If you have 2 monitors of 1920x1080 pixels and you want to capture from the top left corner of the monitor on the right, x_offset should be 1920 and y_offset should be 0. More info on mss: https://python-mss.readthedocs.io/examples.html -
rotation: can be set to 180 to if using a display upside down
-
grey_monochrome_threshold: When converting the capture from 256 greyscale shades to black and white monochrome a threshold is used to determine which shades will become plain black and which plain white. The default is 200 and it improves drawing black letters on white background. Minimum value is 0 and maximum is 255
-
sleep_time: Amount of time in miliseconds to pause the program after capturing a frame. Can be used to reduce the framerate artificially. Set it to 50 or less for fast refresh rate
-
refresh_every_x_frames: Refreshes the display every the specified number of frame draws. A frame draw is not counted if less than 85 lines have changed (such as when moving the mouse)
-
framebuffer_cycles: Defines the number of times to write the current eink framebuffer to the display. Because of the way that eink displays work, writing the same framebuffer to the display has the effect of getting deeper blacks and whites. Increases draw time.
-
rmt_high_time: Defines the high tick time of the CKV signal. A higher value makes blacks blacker and whites whiter. Increases draw time. It is defined in rmt_pulse.h
-
mode: there are 10 modes: monochrome, PIL_dither(Floyd-Steinberg dither) and 8 more dithering modes: Bayer16, Bayer8 Bayer4, Bayer3, Bayer2, FS, SierraLite, Sierra which are defined in Dither.h
-
invert: if set to -1 invert is always off, if set to 0 it's always on, if it's greater than zero it acts as a threshold for smart invert, which activates. smart invert inverts the whole image only when most of it is black, otherwise it doesn't invert at all. maximum value is 255
-
selective_invert if set to 1 detects black regions on the screen and inverts them (can create some artifacts). smart invert and selective_invert can help improve overall usability for text based office work by forcing almost always black letters on white background
-
color, contrast, brightness, sharpness: the Pillow module has the option to apply these enhancements to the capture. They are applied before converting the image to 1 bit per pixel. more info: https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/ImageEnhance.html (experimental)
-
draw_white_first makes the program draw to the display first the white pixels of the image and then the black ones
-
enhance_before_greyscale: choose wether to apply the Pillow enhancements before or after converting to 8bpp greyscale
-
do_full_refresh: calls epd_clear() to refresh screen
Advanced settings:
-
selective_compression sets a maximum percentage of eficiency for the rle compression. if that percentage is not met, the framebuffer will be sent without compression to the board
-
esp32_multithread starts downloading next frame while the current is being drawn
-
enable_skipping: makes the driver call epd_skip() instead of epd_output_row() with an empty buffer. It can reduce draw time significantly but may introduce some artifacts. To avoid the artifacts but mantain low draw time when moving the cursor epd_skip_threshold can be set to 75.
-
epd_skip_threshold: if less than epd_skip_threshold rows have changed skipping is enabled for the current frame draw.
-
framebuffer_cycles_2 and framebuffer_cycles_2_threshold: If less than framebuffer_cycles_2_threshold number of rows have changed, the current framebuffer will be written framebuffer_cycles_2 times instead of the value set by framebuffer_cycles. Can be used to reduce the draw time when just a few lines have changed such as when moving the cursor. This is only active is the mouse is moving
Hotkeys:
It is possible to change the following settings while the application is running by pressing their hotkey on the terminal: -1 decreases color by 0.1
-2 increases color by 0.1
-3 decreases contrast by 0.1
-4 increases contrast by 0.1
-5 decreases brightness by 0.1
-6 increases brightness by 0.1
-7 decreases sharpness by 0.1
-8 increases sharpness by 0.1
-9 increases grey_monochrome_threshold by 10
-0 decreases grey_monochrome_threshold by 10
-b toggles enhance_before_greyscale
-i toggles invert
-u increases smart invert threshold by 10 and activates it
-y decreases smart invert threshold by 10 and activates it
-s toggles selective_invert
-d switches to the mode specified in the configuration file
-m switches to monochrome mode
Using multiple displays at the same time
The application supports using multiple displays at the same time. For each display it is required to create a configuration file. Once the configuration files are created run them as
python3 screen_capture.py display0.confpython3 screen_capture.py display1.confpython3 screen_capture.py display2.confEach from a different terminal. If you want that a hotkey press has an effect on all the running instances, append -common to each command:
python3 screen_capture.py display0.conf -commonSupport for other displays
- The project has been tested using a board revision 4 and a ED097TC2 display. Check for the list of other displays supported by the Epdiy board on https://github.com/vroland/epdiy . Those displays should work but are untested. If the display you want to try has the same resolution of the ED097TC2, that is 1200x825, it should be enough to select the correct display type in the menuconfig Epdiy section. If the display you want to try has a different resolution, other than selecting it in the menuconfig before flashing the board, you should also specify its resolution on its display configuration file.
To do list:
- Organize the code better
- Improve ghosting
- Optimize data transfer between pc and board