This repository contains smart contracts constituting Ambrosus protocol, in particular:
- Smart contracts constituting Ambrosus protocol
- Amber - ERC20 Token representing powering Ambrosus protocol
- ICO Contribution contract
To add ambrosus to your project:
npm i -S ambrosus
And import to module in your application:
import ambrosus from 'ambrosus'
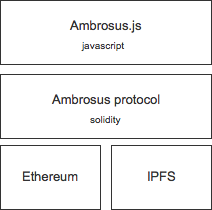
Ambrosus architecture consists of 3 main layers:
- dependencies - to run properly Amborsus requires Ethereum and IPFS
- smart contracts - building blocks of Ambrosus protocol
- javascript library - that allows to create and operate Ambrosus contracts and objects
All 3 parts are stored in this repository. Following is a description of 3 layers introduced above.
Smart contracts are the core of ambrosus protocol. The system of contracts is written in Solidity and compiled to EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). Contracts are combined together to co-operate and create services around quality assurance in food and pharma supply chains. They are abstract building blocks for different applications.
There are some basic abstractions in the protocol, including:
- Measurements - a contract abstraction used to store measurements - a basic unit of a history of an item in supply chain
- Requirements - a basic way to describe expectations about product in supply chain
- Validator - a way to check if given product's history (list of measurements) meets specific validation rules (e.g. meet requirements)
- Agreement - represents agreement between Parties, with specific rules considering product in supply chain
In a top of those abstractions are build implementations for specific use cases. They are more concrete building blocks. Examples are:
- MeasurementsOnChain - allows measurements devices to store measurements on the Ethereum blockchain, note: this might very inefficient and therefore one should for production purposes use the following contract.
- MeasurementsOffChain - allows measurements devices to store measurements off the blockchain, in this case on the IPFS. Measurements can be later verified using this contract on their origin (e.g. if they come from authorized devices) and completeness (if any thing is missing)
- Range requirements - allow expressing expectations in future or past measurements
In the top of that we build more complete solutions per use case e.g.:
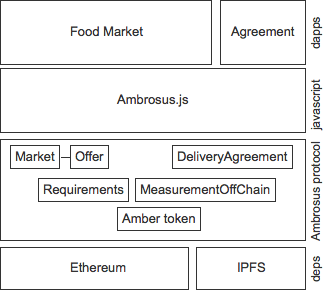
- Market - a marketplace for buying and selling food. Suppliers can create profiles using their Ethereum wallets. Buyer can sellers can make agreements directly on the market.
- DeliveryAgreement - allows parties to make a delivery agreement in the form of contract on Ethereum. Agreement uses building blocks like Requirements to define the quality standard of food agreed upon. Measurements to store information delivered by measurement devices along the way. The agreement can use escrow, so the money for the supplier is automatically released if all conditions from the agreement are met. On the other hand, the buyer can reimburse if delivered food did not meet quality standard agreed upon.
Ambrosus comes with a javascript library that makes using protocol easy and straight forward. Eg. to create a new offer on the market on can use following code:
let exampleOffer = {
name: 'Tune',
origin: 'Japan',
category: 'Fish',
packageWeight: 100,
pricePerUnit: 100,
pricePerPackage: 100,
imageHash: 'QmWWQSuPMS6aXCbZKpEjPHPUZN2NjB3YrhJTHsV4X3vb2t', //Image hash on IPFS
seller: ..., // Seller wallet address
measurementsAddress: ..., // Measurements contract address
requirementsAddress: ..., // Requirements contract address
validatorAddress: ..., // Validator contract address
};
And to put in on the market:
offerRepo = new OfferRepository(OfferContract);
marketRepo = new MarketRepository(MarketContract);
market = ...;
await offerRepo.save(market.getAddress(), exampleOffer);
Or to create a new market:
await marketRepo.create(accounts[0]);
Below is an example architecture overview for two apps build in top of Ambrosus protocol.
Detailed documentation coming soon.
-
Clone repository
git clone git@github.com:ambrosus/Ambrosus.git cd Ambrosus -
Install global dependencies, such as Truffle (requires NodeJS 5.0+) and Testrpc, then install local dependencies:
npm install -
Before running tests make sure testrpc is up:
testrpc -
Running tests
truffle test
Contribution and token contracts have been influenced by the work of MelonPort and by Condition-Orientated Programming approach.