After about only one day of training the agent was able to score about at least 15 points in a game and win some of the games.
More training is needed for the agent to able to win all the games.
With few minor changes the code can be used in other gym environments as well.
 |
|---|
| The right player is the RL agent |
numpy (1.16.4)
tensorflow (1.14.0)
keras (2.2.4)
gym (0.10.11)
Reinforcement learning is a branch of machine learning which concerned with learning from experience in an environment and maximize a reward signal.
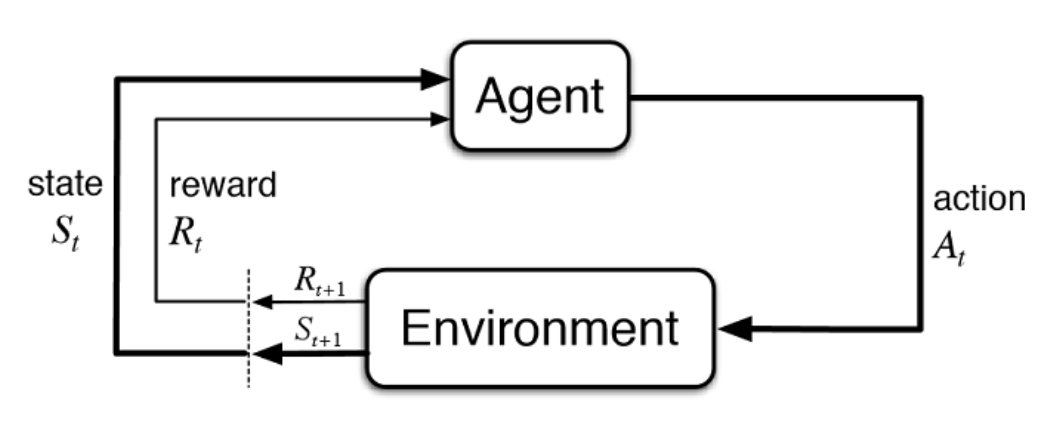 |
|---|
| From Sutton & Barto Book |
So as the above picture illustrates, in each time step, the agent receives the state of the environment and will take an action accordingly, then the environment will give him the reward of his action and the next state.
One case of these kinds of environment which an agent want to maximize its reward is video games.
The environment which I used in this project is the Pong game in OpenAI Gym.
In this environment, the state is an RGB image (210x160) and each action "repeatedly performed for a duration of k frames, where k is uniformly sampled from {2,3,4}" (there are 6 actions).
Who ever first reaches 21 will win the game.
To create an agent that will make a decision based on only the pixels of the given image(the state). I used the Deep Q-Network architecture which was proposed by the DeepMind paper.
The architecture of the network is as follow:
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_4 (Conv2D) (None, 20, 20, 32) 8224
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_5 (Conv2D) (None, 10, 10, 64) 32832
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_6 (Conv2D) (None, 10, 10, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_2 (Flatten) (None, 6400) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 512) 3277312
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 6) 3078
=================================================================
Total params: 3,358,374
Trainable params: 3,358,374
Non-trainable params: 0
You can test the code by only loading the model with following code:
import gym
import cv2
import numpy as np
from keras.models import load_model
def downsample(observation):
s = cv2.cvtColor(observation[30:,:,:], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
s = cv2.resize(s, (80,80), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
s = s/255.0
return s
def update_state(state,observation):
ds_observation = downsample(observation)
state.append(ds_observation)
if len(state) > 4:
state.pop(0)
def sample_action(model,s):
return np.argmax(model.predict(np.array([np.stack((s[0],s[1],s[2],s[3]),axis=2)]))[0])
env = gym.make('Pong-v0')
model = load_model('model.h5')
done = False
state = []
observation = env.reset()
update_state(state,observation)
while not done:
env.render()
if len(state) < 4:
action = env.action_space.sample()
else:
action = sample_action(model,state)
observation, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
update_state(state,observation)