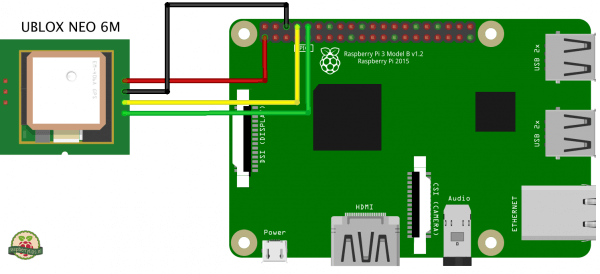
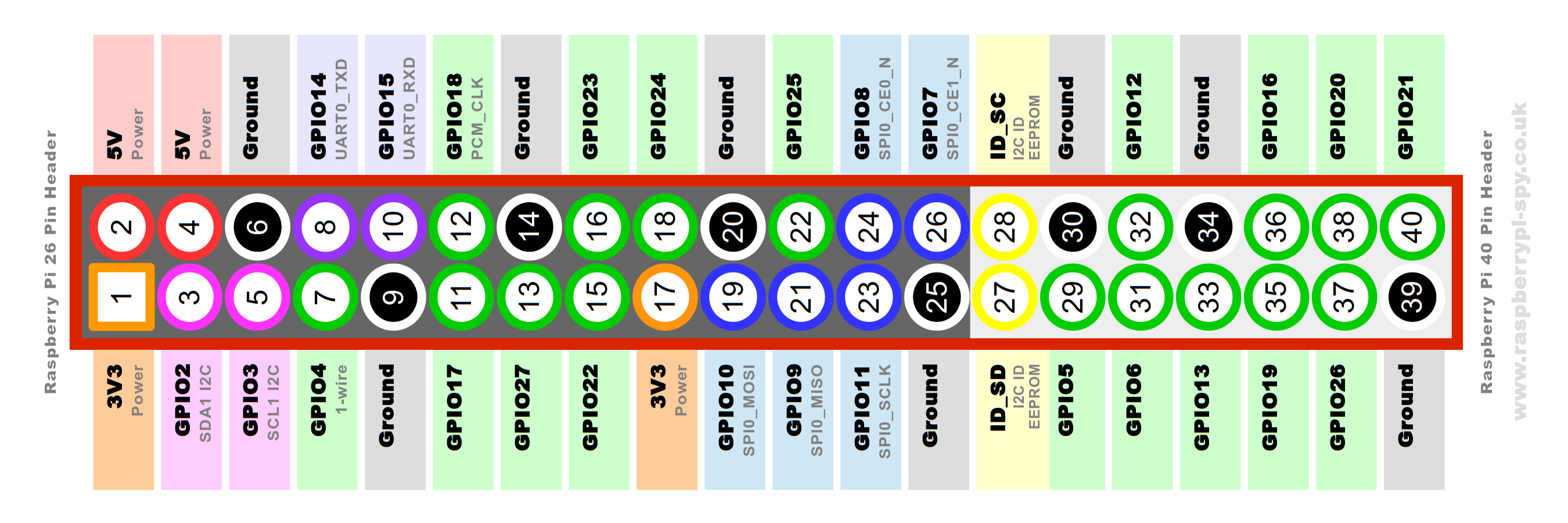
Python script for the NEO-6M GPS module on the Raspberry Pi
- pip installed.
sudo apt-get install python-pip
- you will need pynmea2.
sudo pip install pynmea2
- You need the GPS software
sudo apt-get install gpsd gpsd-clients python-gps minicom
- Serial port modify cmdline.txt:
sudo nano /boot/cmdline.txt
and replace all with the following lines:
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait quiet splash plymouth.ignore-serial-consoles
- Change startup settings:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
and at the end of the file add the following lines:
dtparam=spi=on
dtoverlay=pi3-disable-bt
core_freq=250
enable_uart=1
force_turbo=1
init_uart_baud=9600
- reboot the system:
sudo reboot now
- Configure the module for the 9600 rate:
stty -F /dev/ttyAMA0 9600
- Connect AMA0 to the GPS Software First kill the process and add the device to gpsd tool
sudo killall gpsd
sudo nano /etc/default/gpsd
Edit the file /etc/default/gpsd and add your serial port in DEVICES, like
DEVICES="/dev/ttyAMA0"
- Restart the Software
sudo systemctl enable gpsd.socket
sudo systemctl start gpsd.socket
sudo cgps -s
These instructions will get you a quick start with the script and please check before if you have the dependencies installed. Also connect the raspberry like the obove schemata.
- Look if the terminal output of the sensor works
cat /dev/ttyAMA0
or use:
cgps -s
- Run the script
cd Python-NEO-6M-GPS-Raspberry-Pi
sudo python Neo6mGPS.py
import serial
import pynmea2
def parseGPS(str):
if str.find('GGA') > 0:
msg = pynmea2.parse(str)
print "Timestamp: %s -- Lat: %s %s -- Lon: %s %s -- Altitude:
%s %s" %
(msg.timestamp,msg.lat,msg.lat_dir,msg.lon,msg.lon_dir,msg.altitude,m
sg.altitude_units)
serialPort = serial.Serial("/dev/ttyAMA0", 9600, timeout=0.5)
while True:
str = serialPort.readline()
parseGPS(str)