Directly comparing and subtracting two networks can result in the loss of a lot of information, while traditional differential network inference algorithms require
To avoid conflicts between packages, we recommend that you first create a brand new virtual environment before proceeding with the package installation:
conda create --name fsdiffnet python=3.10.13and then activate the virtual environment:
conda activate fsdiffnetrpy2 enables the invocation of the BDgraph R package for generating simulation data. We recommend using R-4.3.1.
We recommend you follow the steps below for R package installation:
-
Install R in your conda environment:
conda install -c conda-forge r-base
-
Install
BDgraphR package.conda install -c conda-forge r-BDgraph
Details on the versions of the required packages are provided in requirements.txt
We recommend you follow the steps below for Python package installation:
-
Install pytorch first according to your CUDA version;
or if your CUDA version > 11.3, you can install using the following command:pip install torch==1.12.1+cu113 torchvision==0.13.1+cu113 torchaudio==0.12.1 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
-
Install the dependencies using requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
If you have multiple versions of R installed, specify the version associated with the above packages using:
import os
os.environ["R_HOME"] = "your path to R"One line for installation:
pip install fsdiffnetYou can also install the packages locally by downloading our repository:
git clone https://github.com/amssljc/FSDiffNet.git
cd FSDiffNet
pip install -e .import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from fsdiffnet.infer import infer_differential_graph
from fsdiffnet.generate_data import ExpressionProfiles
from fsdiffnet.utils import show_matrix, remove_diag, keep_largest_k, vec2mat, seed_everything, calculate_flip_error
seed_everything(1)
data_params = {
'p': [30],
'n': 1000,
'sample_n': 10,
'repeats': 1,
'sparsity': [0.1, 0.3],
'diff_ratio': [0.3, 0.7],
'net_rand_mode': 'BA',
'diff_mode': 'hub',
'target_type': 'float',
'usage': 'comparison',
'flip': True,
'withdiag': True,
'sigma_diag': True
}
example_data = ExpressionProfiles(
**data_params
)
(sigma, delta, *X) = example_data[0] # X is a list of expression profiles X1, X2, each with a shape of (n, p), in this case, (1000, 39).
cov1 = np.corrcoef(X[0].T)
cov2 = np.corrcoef(X[1].T)
input = np.stack((cov1, cov2))
input = input[np.newaxis, :]
input = torch.tensor(input).float()
# inferring step
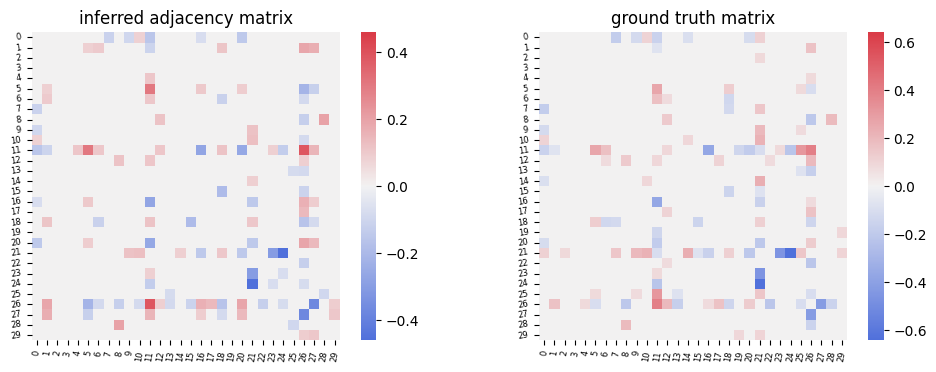
inferred_matrix = infer_differential_graph(input)
inferred_matrix = keep_largest_k(remove_diag(inferred_matrix), data_params['p'][0]*4)
ground_truth = keep_largest_k(vec2mat(delta)[0], data_params['p'][0]*4)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (12,4))
show_matrix(inferred_matrix, ax = axes[0], title='inferred adjacency matrix')
show_matrix(ground_truth, ax = axes[1], title='ground truth matrix')
plt.show()We have provided two real data cases related to the paper as reproducible result notebooks, along with a tutorial notebook verifying that the flip error of FSDiffNet can reach the theoretical lower bound:
We've incorporated pre-trained neural network parameters in the package to facilitate rapid and convenient inference, which can be directly executed with:
inferred_mat = infer_differential_graph(input)Alternatively, you have the option to train your own network parameters by executing main.py.