GoVector is a vector clock logging library written in Go. The vector clock algorithm is used to order events in distributed systems in the absence of a centralized clock. GoVector implements the vector clock algorithm and provides feature rich logging, and encoding infrastructure.
Vector clock events
are generated using 3 key functions PrepareSend, UnpackReceive,
and LogLocalEvent. PrepareSend encodes messages for network
transport, updates GoVectors local time, and logs a sending event.
UpackReceive decodes messages from the network, merges GoVectors local
clock with the received clock, and logs a receiving event. LogLocalEvent
event ticks the clock, and logs a message.
This library can be added to a Go project to generate a ShiViz-compatible vector-clock timestamped log of events in a concurrent or distributed system. This library can also be used to generate TSViz-compatible log of events. GoVector is compatible with Go 1.4+
- govec/ : Contains the Library and all its dependencies
- govec/vclock : Pure vector clock library
- govec/vrpc : Go's rpc with GoVector integration
- example/ : Contains some examples instrumented with different features of GoVector
To install GoVector you must have a correctly configured go development environment, see How to write Go Code
Once you set up your environment, GoVector can be installed with the go tool command:
go get -u github.com/DistributedClocks/GoVector
gofmt will automatically add imports for GoVector. If you do not have a working version of gofmt GoVector can be imported by adding:
The following is a basic example of how this library can be used
package main
import "github.com/DistributedClocks/GoVector/govec"
func main() {
//Initialize GoVector logger
Logger := govec.InitGoVector("MyProcess", "LogFile")
//Encode message, and update vector clock
messagepayload := []byte("samplepayload")
vectorclockmessage := Logger.PrepareSend("Sending Message", messagepayload)
//send message
connection.Write(vectorclockmessage)
//In Receiving Process
connection.Read(vectorclockmessage)
//Decode message, and update local vector clock with received clock
Logger.UnpackReceive("Receiving Message", &messagepayload, vectorclockmessage)
//Log a local event
Logger.LogLocalEvent("Example Complete")
}For complete documentation and small examples see GoVectors GoDoc,
- Client-Server GoVector insturmentation Examples/ClientServer.go
- RPC Client-Server program Examples/RpcClientServer.go
GoVector was initially developed as a pedagogical tool for students attending UBC's computer science course on distributed systems (CPSC 416). Students new to the development of distributed systems can reason about event orderings by visualizing their executions with ShiViz. Furthermore GoVectors marshaling functionality reduces student effort in writing networking code which is largely boiler plate.
As a result of student requests GoVector transformed into a general purpose logging tool. Additional features include optimized IO, priority logging, TSViz compatibility and RPC instrumentation.
GoVector has the following dependencies :
- Ivan Beschastnikh
- Mike Fink
- Stewart Grant
- Clement Fung
- Fabian Ruffy
- Vaastav Anand
The source code from the useage example produces the following log into a file named "LogFile.txt" :
MyProcess {"MyProcess":1}
Initialization Complete
MyProcess {"MyProcess":2}
Sending Message
MyProcess {"MyProcess":3}
Receiving Message
MyProcess {"MyProcess":4}
Example Complete
Here is a sample output of the priority logger
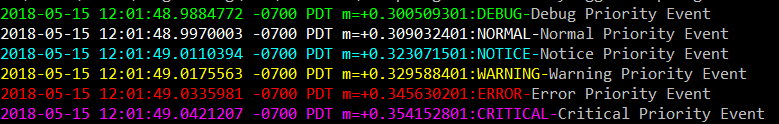
Here is an example of ShiViz output generated by an RPC client server
interaction