Improving Pretrained Models for Zero-shot Multi-label Text Classification through Reinforced Label Hierarchy Reasoning
This is the PyTorch companion code for the paper:
Hui Liu, Danqing Zhang, Bing Yin, Xiaodan Zhu. Improving Pretrained Models for Zero-shot Multi-label Text Classification through Reinforced Label Hierarchy Reasoning. NAACL-HLT 2021, long paper
If you have any question about the code, please send me an email (hui.liu@queensu.ca) or leave a github issue.
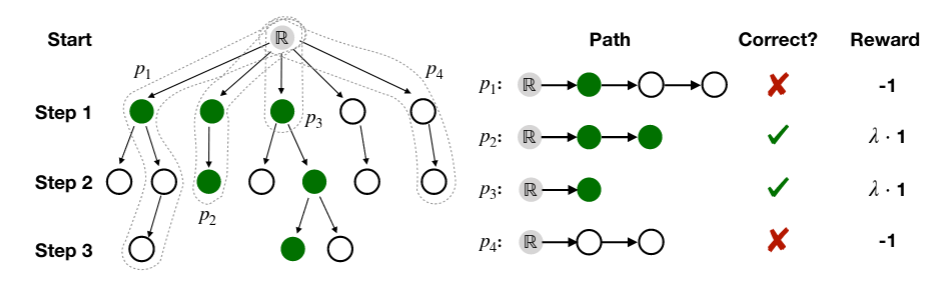
We propose a Reinforced Label Hierarchy Reasoning(RLHR) approach to introduce label structure infor-mation to pretrained models. Instead of regarding labels to be independent, we cast ZS-MTC as a deterministic Markov Decision Process (MDP) overthe label hierarchy. An agent starts from the root label and learns to navigate to the potential labels by hierarchical deduction in the label hierarchy. The reward is based on the correctness of the deduction paths, not simply on the correctness of each label. Thus the reward received by one predicted label will be determined by both the label itself and other labels on the same path, which can helpto strengthen the interconnections among labels. Meanwhile, we find that the hierarchical inferencemethod will broadcast the errors arising at the higher levels of label hierarchies. Thus we further design a rollback algorithm basedon the predicted matching scores of labels to reduce the logical errors in the flat prediction modeduring inference. We apply our approach to different pretrained models and conduct experiments on three real-life datasets. Results demonstrate thatpretrained models outperform conventional non-pretrained methods by a substantial margin. After being combined with our approach, pretrained models can attain further improvement on both the classification metrics and logical error metrics.
- python>=3.6
- PyTorch version=1.4.0
- CUDA version=10.1
- Huggingface Transformers
- apex
- pyyaml
We use three datasets in our experiments, among which Yelp and WOS are publicly available.
There should be six files under the dataset folder:
- train.json: train data file
- dev.json: development data file
- test.json: test data file
- seen_labels.txt: this file contains the seen labels
- unseen_labels.txt: this file contains the unseen labels
- taxonomy.json: this file contains the label taxonomy
We include the split of seen labels, unseen labels and the taxonomy for the two datasets. The path is ./data/(yelp/wos)/. You can download the original versions of the two datasets from the links above. Dev/Test set only contain samples with unseen labels, and the rest samples will be used for training.
The code of our method is under the path ./code.
We support two pretrained models in the code: BERT and DistilBERT.
There are two steps to train a model:
For BERT on Yelp:
python main.py --mode bert --model_config bert-base-uncased --para para.yml --dataset yelp
--save_steps 2500 --logging_steps 500 --num_training_epochs 3 --fp16
For DistilBERT on Yelp:
python main.py --mode distilbert --model_config distilbert-base-uncased --para para.yml --dataset yelp
--save_steps 2500 --logging_steps 500 --num_training_epochs 3 --fp16
The training log will be stored under the path output/{timestamp}/log.txt, and the saved model will be stored under the path output/{timestamp}/cache/, where "timestamp" is a time stamp marking the current train attempt.
For BERT on Yelp:
python main.py --mode bert-rl --model_config bert-base-uncased --para para.yml --dataset yelp
--model_path output/{timestamp}/cache/ckpt-{train-step}/ --learning_rate 0.000001
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 1 --fp16 --num_training_epochs 1 --save_steps 2000
--logging_steps 400 --K 2 --pos_reward 3.0
For DistilBERT on Yelp:
python main.py --mode distilbert-rl --model_config distilbert-base-uncased --para para.yml --dataset yelp
--model_path output/{timestamp}/cache/ckpt-{train-step}/ --learning_rate 0.000001
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 1 --fp16 --num_training_epochs 1 --save_steps 2000
--logging_steps 400 --K 2 --pos_reward 3.0
The training log will be stored under the path output/{timestamp}/rl_log.txt, and the saved model will be stored under the path output/{timestamp}/rl_cache/.
The evaluation code is ./code/inference.py.
An example for BERT on Yelp dev set is:
python inference.py --mode bert --model_config bert-base-uncased --dataset yelp --data_dir ../../data/
--data_type dev --cached_feature_dir cached_input/ --output_dir output/{timestamp}/
--cache_dir rl_cache --eval_all_checkpoints --per_gpu_eval_batch_size 512 --fp16
if all the checkpoints in rl_cache are evaluated. If just one checkpoint is evaluated, it should be:
python inference.py --mode bert --model_config bert-base-uncased --dataset yelp --data_dir ../../data/
--data_type dev --cached_feature_dir cached_input/ --output_dir output/{timestamp}/
--cache_dir rl_cache --checkpoint 7500 --per_gpu_eval_batch_size 512 --fp16
The inference log for the dev dataset will be stored under the path output/{timestamp}/rl_dev_log.txt. The output results will be in output/{timestamp}/rl_result/.
If you want to inference on a BERT model, you can replace the argument --cache_dir rl_cache with --cache_dir cache. Similarly the output results will be in output/{timestamp}/result/.
First select a predicted result file dev_checkpoint_xxxx.json under the dir output/{timestamp}/result/. Then run the code analysis.py to get the metrics. An example with Yelp is:
python analysis.py --mode m --file1 yelp/dev_checkpoint_7500.json --taxonomy data/yelp/taxonomy.json --unseen_labels data/yelp/unseen_labels.txt --seen_labels data/yelp/seen_labels.txt
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License.