This directory contains an example of a Jenkins setup that is configured to demonstrate the CI/pipeline workflow for the sample-app application using the Jenkins Master/Slave setup and automation done on OpenShift v3.
To start, you have to manually enter following commands in OpenShift:
## Create project and allow Jenkins to talk to OpenShift API
# Create all necessary projects 'ci', 'stage', 'prod'
$ oc new-project ci
$ oc new-project stage
$ oc new-project prod
# Allow the CI user where the Jenkins runs access all projects
$ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:ci:default -n ci
$ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:ci:default -n stage
$ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:ci:default -n prod
# Add roles for 'stage' and 'prod' projects
$ oc project prod
$ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:prod:default -n stage
# Create the sample application in the 'stage' and 'prod' namespaces:
$ oc create -n stage -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arilivigni/openshift-ci-pipeline/master/sample-app/sample-app-template.json
$ oc create -n prod -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arilivigni/openshift-ci-pipeline/master/sample-app/sample-app-template.json
# Now create the Jenkins Master and Slave templates in the 'ci' namespace:
$ oc create -n ci -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arilivigni/openshift-ci-pipeline/master/examples/master/jenkins-with-k8s-plugin.json
$ oc create -n ci -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arilivigni/openshift-ci-pipeline/master/examples/slave/s2i-slave-template.jsonNavigate to the OpenShift UI and choose the ci project we created in the previous
step. Now click Add to Project button and then click Show All
Template. You should see jenkins-master template and s2i-to-jenkins-slave.
Note: To continue, you have to first create your Jenkins Slave image. Please see the instructions here.
This template defines a BuildConfig that use the Docker Strategy to rebuild the official OpenShift Jenkins Image. This template also defines a Deployment Configuration that will start just one instance of the Jenkins server.
When you choose the jenkins-master template, you have to specify these parameters:
- JENKINS_SERVICE_NAME - The name of the Jenkins service (default: jenkins)
- JENKINS_IMAGE - The name of the original Jenkins image to use
- JENKINS_PASSWORD - The Jenkins 'admin' user password
Once you instantiate this template, you should see a new service jenkins in the overview page and a route https://jenkins-ci.router.default.svc.cluster.local/.
Optionally, you can configure your own repository with Jenkins plugins, configuration, etc by changing these parameters:
- JENKINS_S2I_REPO_URL - The Git repository with your Jenkins configuration
- JENKINS_S2I_REPO_CONTEXTDIR - The directory inside the repository
- JENKINS_S2I_REPO_REF - Specify branch or Git ref
You have to wait until OpenShift rebuilds the original image to include all plugins and configuration needed.
The last step is to instantiate the sample-app template. The sample
app is a simple Ruby application
that runs Sinatra and has one unit test defined to exercise the CI flow.
You have to instantiate the template in both ci and stage projects.
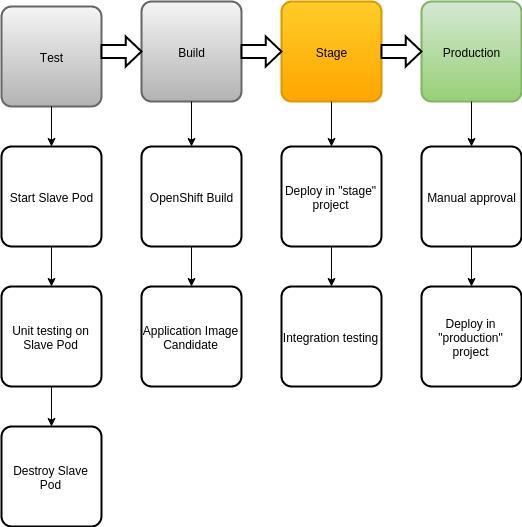
You can watch the youtube video that shows the full workflow. What happens in the video is:
-
When the
sample-app-testjob is started it fetches the sample-app sources, installs all required rubygems using bundler and then executes the sample unit tests. In the job definition, we restricted this job to run only on slaves that have the ruby-22-centos7 label. This will match the Kubernetes Pod Template you see in the Kubernetes plugin configuration. Once this job is started and queued, the plugin connects to OpenShift and starts the slave Pod using the converted S2I image. The job then runs entirely on that slave. When this job finishes, the Pod is automatically destroyed by the Kubernetes plugin. -
If the unit tests passed, the
sample-app-buildis started automatically via the Jenkins promoted builds plugin. This job will leverage the OpenShift Jenkins plugin and start build of the Docker image which will contain 'sample-app'. -
Once the new Docker image for the
sample-appis built, thesample-app-stageproject will automatically deploy it intostageproject and notify the QA team about availability for testing. -
If the
sample-appimage passes thestagetesting, you have to manually promote thesample-app-buildbuild to be deployed to OpenShift. Since re-deploying the application replaces the existing running application, human intervention is needed to confirm this step. -
Once the build is promoted, the
sample-app-deployjob is started. This job will scale down the existing application deployment and redeploy it using the new Docker image.