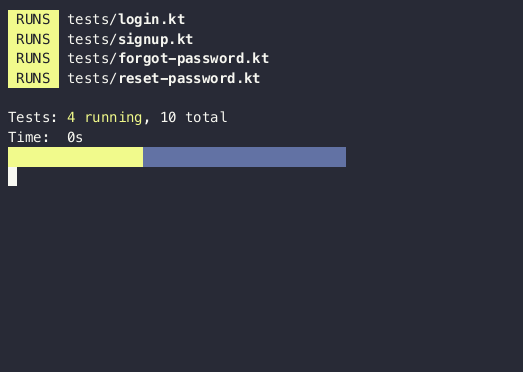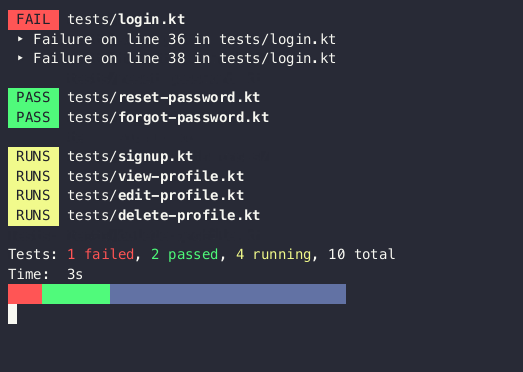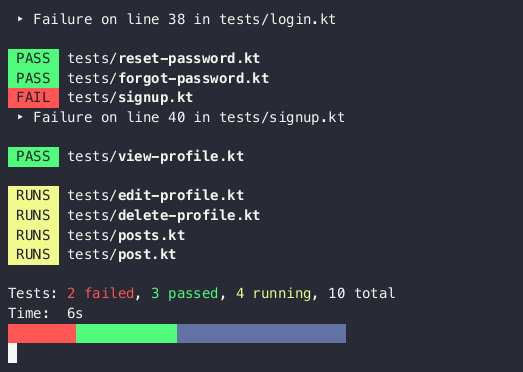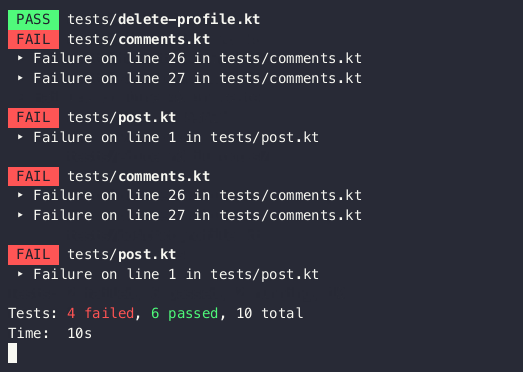
An experimental tool for building console UI in Kotlin using the Jetpack Compose compiler/runtime. Inspired by Ink.
Jump to: Introduction | Usage | Samples | FAQ | License
The entrypoint to Mosaic is the runMosaic function.
The lambda passed to this function is responsible for both output and performing work.
Output (for now) happens through the setContent function.
You can call setContent multiple times, but as you'll see you probably won't need to.
fun main() = runMosaic {
setContent {
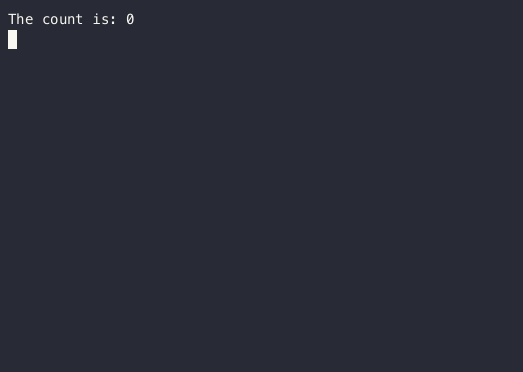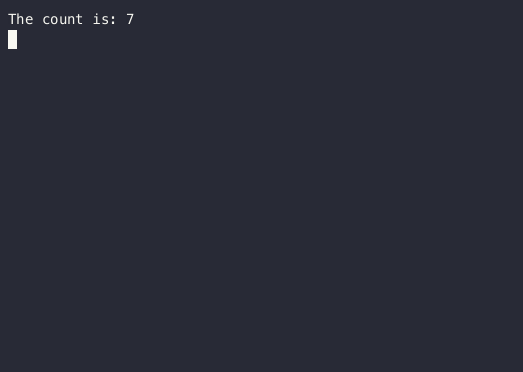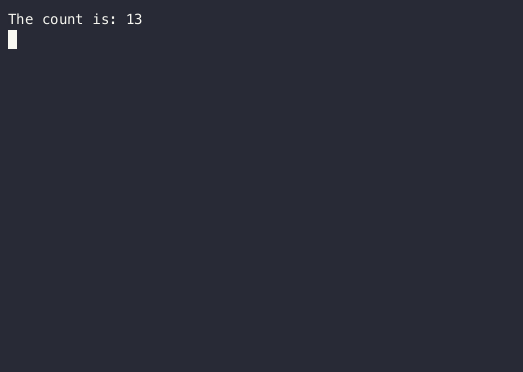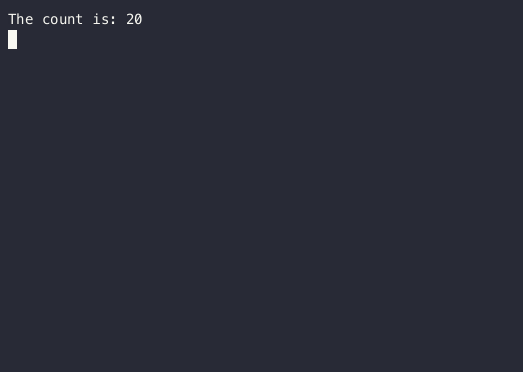
Text("The count is: 0")
}
}To change the output dynamically we can use local properties to hold state. Let's update our counter to actually count to 20.
fun main() = runMosaic {
var count = 0
setContent {
Text("The count is: $count")
}
for (i in 1..20) {
delay(250)
count = i
}
}This will not work! Our count stays at 0 for 5 seconds instead of incrementing until 20.
Instead, we have to use Compose's State objects to hold state.
-var count = 0
+var count by mutableStateOf(0)Now, when the count value is updated, Compose will know that it needs to re-render the string.
fun main() = runMosaic {
var count by mutableStateOf(0)
setContent {
Text("The count is: $count")
}
for (i in 1..20) {
delay(250)
count = i
}
}(Note: You may need to add imports for androidx.compose.runtime.getValue and import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue manually.)
In order to use Mosaic you must write your code in Kotlin and must apply the Compose Kotlin compiler plugin.
For Gradle users, the Mosaic Gradle plugin will take care of applying the compiler plugin.
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:1.9.22'
classpath 'com.jakewharton.mosaic:mosaic-gradle-plugin:0.11.0'
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm'
apply plugin: 'com.jakewharton.mosaic'The runtime APIs will be made available automatically by applying the plugin. Documentation is available at jakewharton.github.io/mosaic/docs/0.x/.
Note: Any module which contains a @Composable-annotated function or lambda must apply the
Mosaic plugin. While the runtime dependency will be available to downstream modules as a
transitive dependency, the compiler plugin is not inherited and must be applied to every module.
Since Kotlin compiler plugins are an unstable API, certain versions of Mosaic only work with certain versions of Kotlin.
| Kotlin | Mosaic |
|---|---|
| 1.9.22 | 0.11.0 |
| 1.9.20 | 0.10.0 |
| 1.9.10 | 0.9.1 |
| 1.9.0 | 0.8.0 - 0.9.0 |
| 1.8.22 | 0.7.1 |
| 1.8.21 | 0.7.0 |
| 1.8.20 | 0.6.0 |
| 1.8.10 | 0.5.0 |
| 1.8.0 | 0.3.0 - 0.4.0 |
| 1.7.10 | 0.2.0 |
| 1.5.10 | 0.1.0 |
Versions newer than those listed may be supported but are untested.
Snapshots of the development version are available in Sonatype's snapshots repository.
buildscript {
repository {
mavenCentral()
maven {
url 'https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/'
}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:1.9.22'
classpath 'com.jakewharton.mosaic:mosaic-gradle-plugin:0.12.0-SNAPSHOT'
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm'
apply plugin: 'com.jakewharton.mosaic'Snapshot documentation is available at jakewharton.github.io/mosaic/docs/latest/.
Run ./gradlew installDist to build the sample binaries.
-
Counter: A simple increasing number from 0 until 20.
./samples/counter/build/install/counter/bin/counter -
Demo: A playground for demonstrating many features of Mosaic.
./samples/demo/build/install/demo/bin/demo -
Jest: Example output of a test framework (such as JS's 'Jest').
./samples/jest/build/install/jest/bin/jest -
Robot: An interactive, game-like program with keyboard control.
./samples/robot/build/install/robot/bin/robot -
rrtop: An example inspired by rrtop.
./samples/rrtop/build/install/rrtop/bin/rrtop
Compose is, at its core, a general-purpose runtime and compiler for tree and property manipulation which is trapped inside the AndroidX monorepo and under the Jetpack marketing department. This core can be used for any tree on any platform supported by Kotlin. It's an amazing piece of technology.
Compose UI is the new UI toolkit for Android (and maybe Desktop?). The lack of differentiation between these two technologies has unfortunately caused Compose UI to overshadow the core under the single "Compose" moniker in an unforced marketing error.
If you want another example of a non-Compose UI-based Compose project checkout JetBrains' Compose for Web project.
This is the goal. It is currently blocked by issuetracker.google.com/178904648.
When that change lands, and Mosaic is updated, the counter sample will look like this:
fun main() = runMosaic {
var count by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
Text("The count is: $count")
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
for (i in 1..20) {
delay(250)
count = i
}
}
}Each version of Mosaic ships with a specific JetBrains Compose compiler version which works with a single version of Kotlin (see version table above). Newer versions of the Compose compiler or alternate Compose compilers can be specified using the Gradle extension.
To use a new version of the JetBrains Compose compiler version:
mosaic {
kotlinCompilerPlugin.set("1.4.8")
}To use an alternate Compose compiler dependency:
mosaic {
kotlinCompilerPlugin.set("com.example:custom-compose-compiler:1.0.0")
}Copyright 2020 Jake Wharton
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.