Official code for the paper "GCondNet: A Novel Method for Improving Neural Networks on Small High-Dimensional Tabular Data", published in Transactions of Machine Learning Research (TMLR) August 2024
Authored by Andrei Margeloiu, Nikola Simidjievski, Pietro Lio, Mateja Jamnik, University of Cambridge, UK
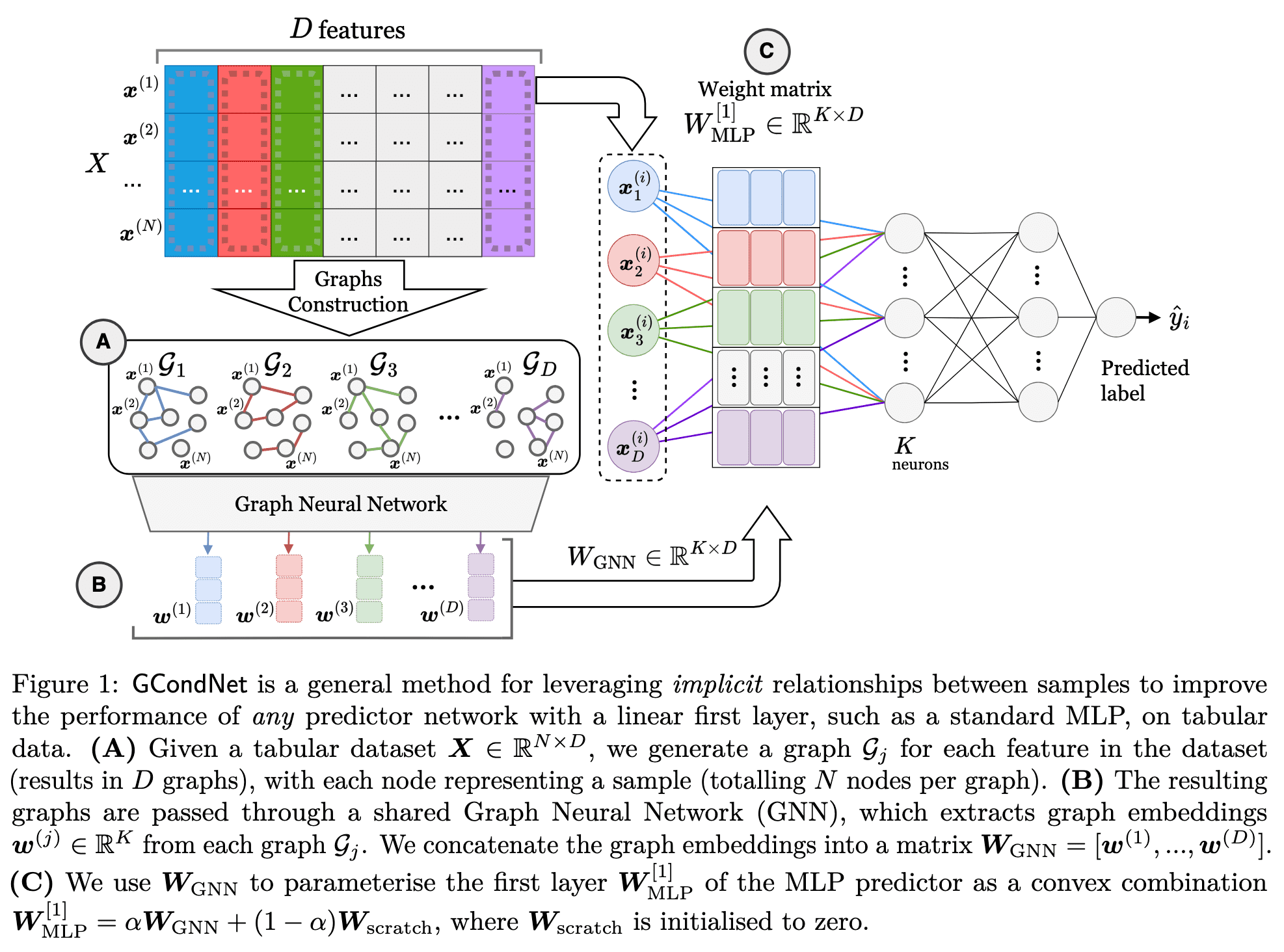
Abstract: Neural networks often struggle with high-dimensional but small sample-size tabular datasets. One reason is that current weight initialisation methods assume independence between weights, which can be problematic when there are insufficient samples to estimate the model's parameters accurately. In such small data scenarios, leveraging additional structures can improve the model's performance and training stability. To address this, we propose GCondNet, a general approach to enhance neural networks by leveraging implicit structures present in tabular data. We create a graph between samples for each data dimension, and utilise Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to extract this implicit structure, and for conditioning the parameters of the first layer of an underlying predictor network. By creating many small graphs, GCondNet exploits the data's high-dimensionality, and thus improves the performance of an underlying predictor network. We demonstrate GCondNet's effectiveness on 12 real-world datasets, where it outperforms 14 standard and state-of-the-art methods. The results show that GCondNet is a versatile framework for injecting graph-regularisation into various types of neural networks, including MLPs and tabular Transformers.
For attribution in academic contexts, please cite this work as:
@article{margeloiu2024gcondnet,
title={GCondNet: A Novel Method for Improving Neural Networks on Small High-Dimensional Tabular Data},
author={Andrei Margeloiu and Nikola Simidjievski and Pietro Lio and Mateja Jamnik},
journal={Transactions on Machine Learning Research},
issn={2835-8856},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=y0b0H1ndGQ},
note={Reproducibility Certification}
}
You must have conda and cuda 11.7 installed locally.
conda create python=3.10 --name gcondnet
conda activate gcondnet
pip install -r requirements.txt
Change BASE_DIR from /src/_config.py to point to the project directory on your machine.
pip install lightgbm --install-option=--gpu --install-option="--opencl-include-dir=/usr/local/cuda/include/" --install-option="--opencl-library=/usr/local/cuda/lib64/libOpenCL.so"
reproduce_figure_2.ipynb: notebook to reproduce Figure 2 from the paper- src
main.py: code for running experimentsmodels.py: GCondNet, WPFS, DietNetworks, FsNet and CAEgraph.py: the GNN as part of GCondNet, and code to compute the SRD/KNN/Random graphsdataset.py: loading the datasetsgnn_classification: GCN and GATv2 bechmark models
- data
- cll, lung, prostate, smk, toxicity
- Train GCondNet using
train_gcondnet.sh - Run
analyze_experiments.ipynb