A basic template for a microservice API based on Python FastAPI with CI, CD, Code Formatting, Authentication, and other common practices in Doppler teams.
For the moment, it is only a kind of example. In the future, it could be converted into a Yeoman or dotnet new scaffolding template 🤷♂️.
We base our CI/CD process on Jenkins, Docker Hub, and Docker Swarm.
Jenkins generates the images based on doppler-jenkins-ci.groovy (a renamed Jenkisfile). We refer to these generated images in a Docker Swarm using an auto-redeploy approach. The Doppler Swarm repository stores the configuration of our Docker Swarm.
You can find a detailed description of our Git flow and the relation with Docker Hub in Doppler-Forms repository, but basically, it is the following:
-
Pull Requests generates images with tags like
pr-177(pr-{pull request id}) and (pr-{pull request id}-{commit id}). -
Merging in
main(ormasterin some repositories) generates images with tags likemainandmain-60737d6(main-{commit id}). In general, these images are deployed automatically into the QA environment. -
Resetting the branch
INTgenerates images with tags likeINTandINT-60737d6(INT-{commit id}). In general, these images are deployed automatically into the INT environment. -
Tagging with the format
v#.#.#generates images with tags likev1,v1.3,v1.3.0,v1.3.0_982c388. In general, our Production environment refers to images with tags likev1(only the mayor), so, depends on that, these images could be deployed automatically to the Production environment.
The source of truth related to the build process is doppler-jenkins-ci.groovy (a renamed Jenkisfile). It basically runs docker build, so, you can reproduce jenkins' build process running docker build . or sh ./verify-w-docker.sh.
If you prefer to run these commands without docker, you can read Dockerfile and follow the steps manually.
-
Base conventions for a Python FastAPI project.
-
Normalize to Linux line endings by default for all files (See .editorconfig and .gitattributes).
-
Ignore from git and docker files with the convention that denotes secrets (See .gitignore and .dockerignore).
-
Prettier validation for all supported files.
-
Editor Config validation using
eclint. -
Launch and debug settings for VS Code (.vscode).
-
Custom color (FastAPI based #009485) for VS Code (using Peacock, see settings.json).
-
Python Format, Linting and Test validation
-
Generation of the docker images following Doppler convention and publish them to Docker Hub (See build-n-publish.sh).
-
Generation of
version.txtfile with the image version and expose as a static file. -
demo.http to easily add manual tests for the exposed API with VS Code REST Client.
-
Exposing only HTTP (not HTTPS) because that is the responsibility of our reverse proxy.
-
Expose Swagger (
/openapi.json//docs/redoc). -
Including examples of self-hosting integration tests.
-
Including examples of unit tests.
-
Recommended FastAPI project structure
-
CORS ready
-
JWT and authorization following Doppler standards
We are using the GitHub organizations FromDoppler (for public code) and MakingSense (for private code).
Create a new empty project there, and create a PR to push the updated files. It should start a CI process in our Jenkins server.
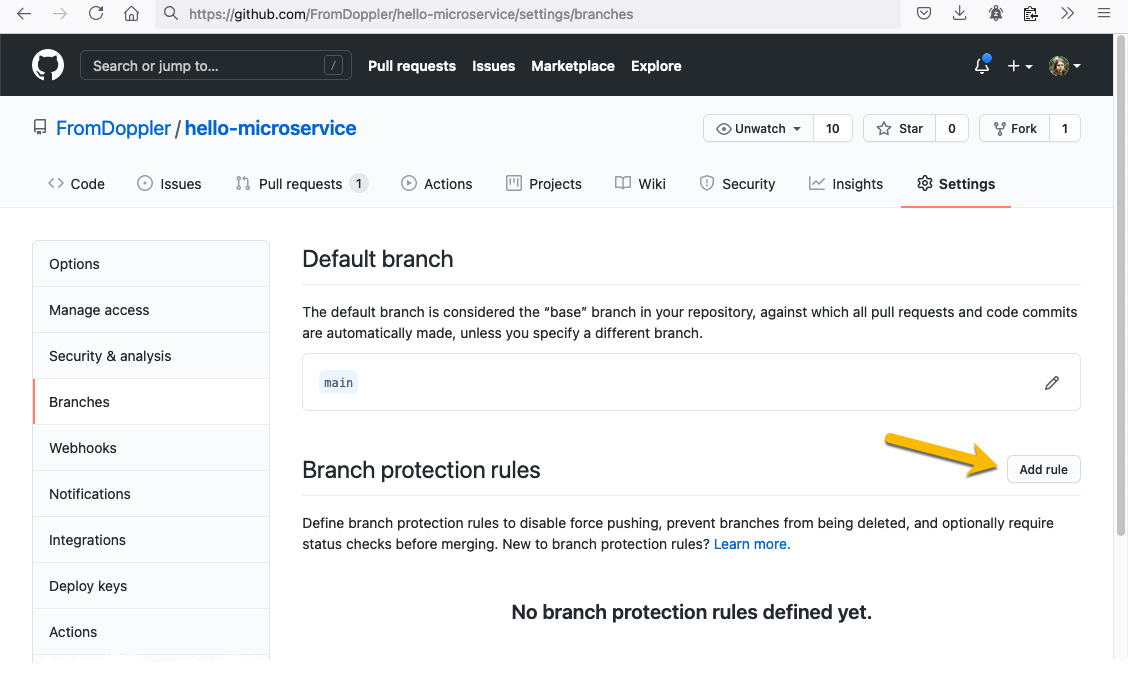
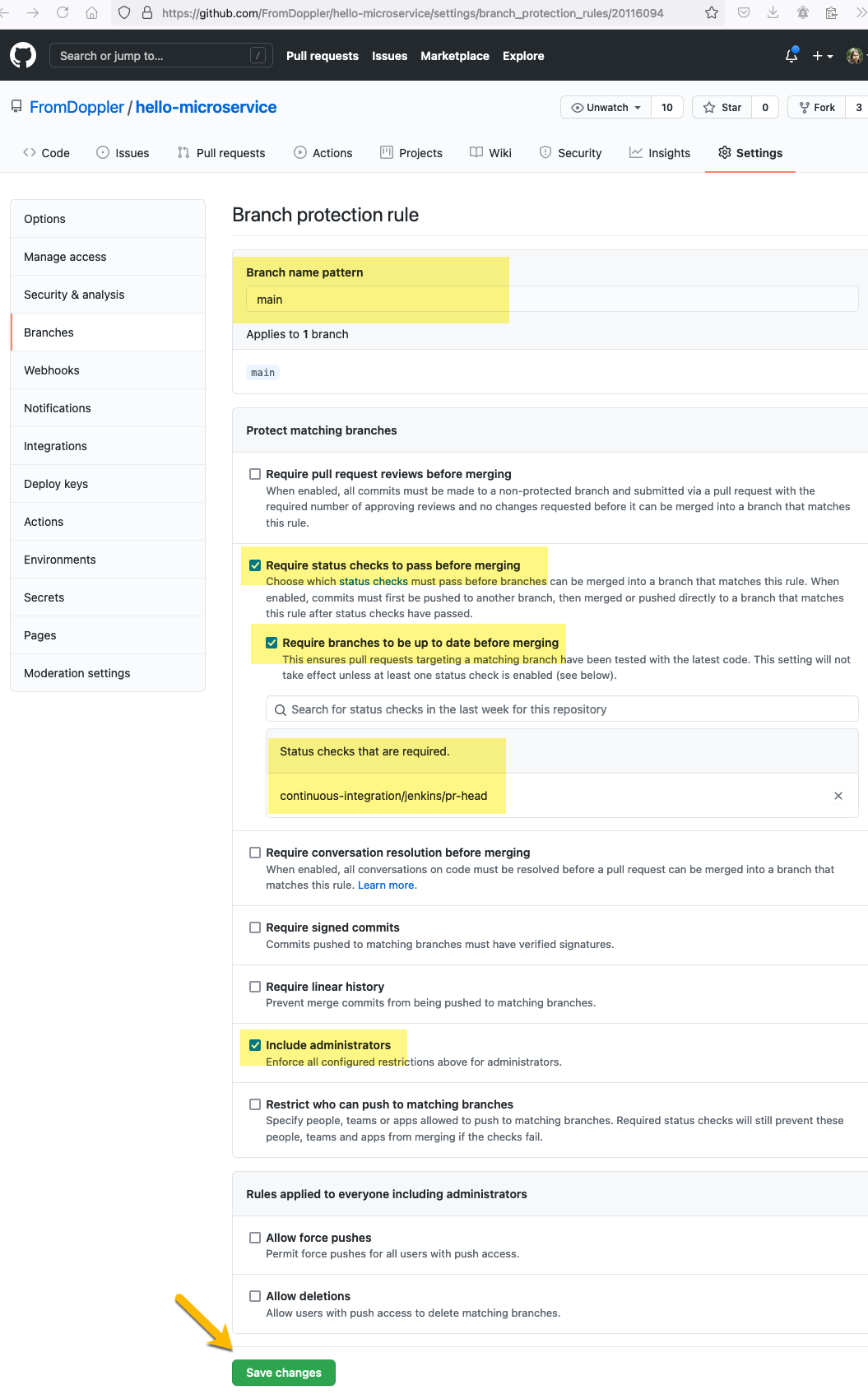
In GitHub Branches Settings add a new protection rule for the main branch.
With the following configuration:
- Branch name pattern:
main - Require status checks to pass before merging: checked
- Require branches to be up to date before merging: checked
- Status checks that are required:
continuous-integration/jenkins/pr-head - Include administrators: checked
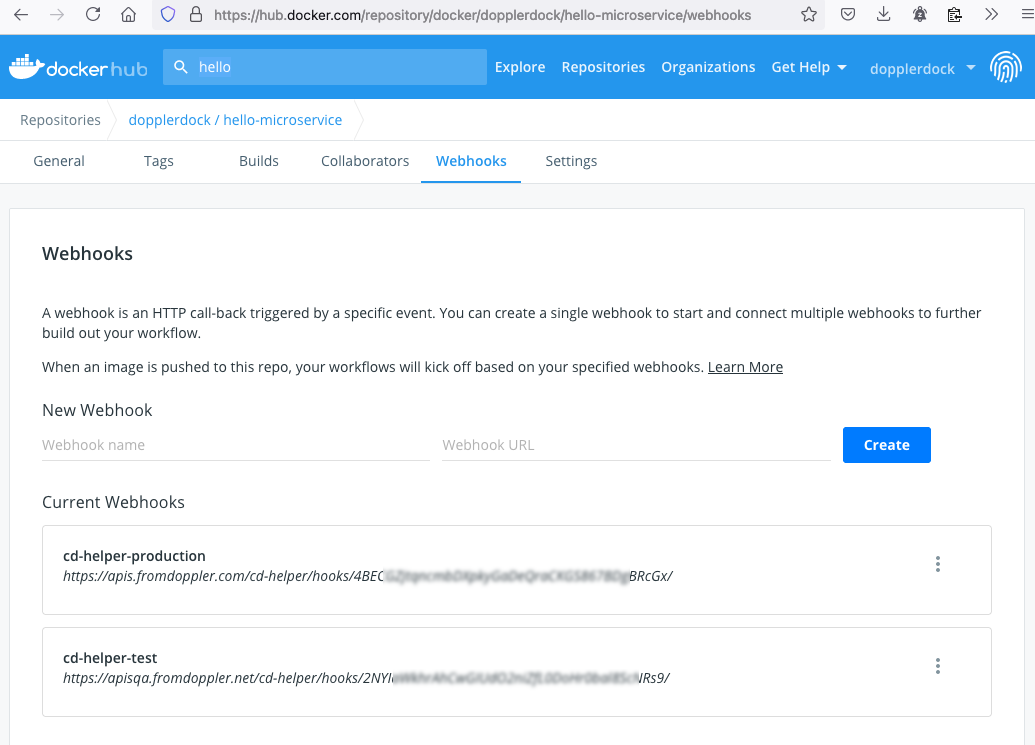
At this point, the CI process already generated a Docker Hub repository and we should configure the WebHooks to enable the auto-redeploy in our environments.
IMPORTANT: You need the credentials of dopplerdock Docker Hub account. Ask for them.
Open the Webhooks configuration page of this new repository (this is the URL for hello-fastapi repository: https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/dopplerdock/hello-fastapi/webhooks) and create the webhooks for production and test environments:
- cd-helper-production
https://apis.fromdoppler.com/cd-helper/hooks/{{REEMPLACE-THE-SECRET-HERE}}/ - cd-helper-test
https://apisqa.fromdoppler.net/cd-helper/hooks/{{REEMPLACE-THE-SECRET-HERE}}/
IMPORTANT: You can see the secrets in other Docker Hub repositories, for example in CD-Helper's one.
We should add the stack to Doppler Swarm repository, it is possible using hello-stack as reference. Using search in files is recommended to find all the places to update.