inspectdf 
Overview
inspectdf is collection of utilities for columnwise summary, comparison and visualisation of data frames. Functions are provided to summarise missingness, categorical levels, numeric distribution, correlation, column types and memory usage.
The package has three aims:
- to speed up repetitive checking and exploratory tasks for data frames
- to make it easier to compare data frames for differences and inconsistencies
- to support quick visualisation of data frames
Key functions
inspect_types()summary of column typesinspect_mem()summary of memory usage of columnsinspect_na()columnwise prevalence of missing valuesinspect_cor()correlation coefficients of numeric columnsinspect_imb()feature imbalance of categorical columnsinspect_num()summaries of numeric columnsinspect_cat()summaries of categorical columns
Installation
To install the development version of the package, use
devtools::install_github("alastairrushworth/inspectdf")
# load the package
library(inspectdf)Illustrative data: starwars
The examples below make use of the starwars data from the dplyr package
# some example data
data(starwars, package = "dplyr")For illustrating comparisons of dataframes, use the starwars data and produce two new dataframes star_1 and star_2 that randomly sample the rows of the original and drop a couple of columns.
library(dplyr)
star_1 <- starwars %>% sample_n(50)
star_2 <- starwars %>% sample_n(50) %>% select(-1, -2)Column types
inspect_types() for a single dataframe
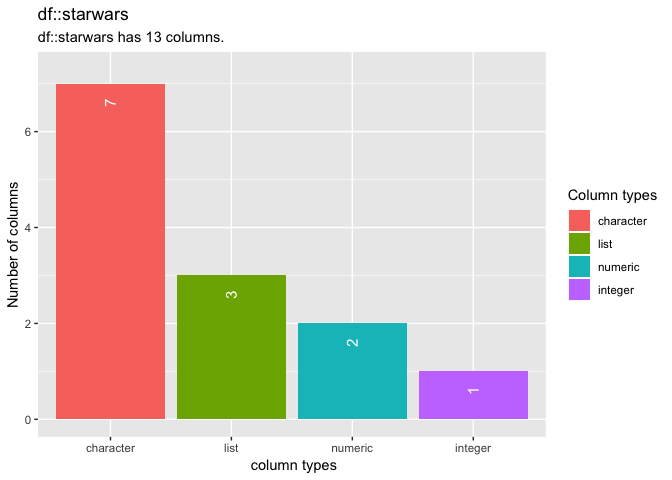
To explore the column types in a data frame, use the function inspect_types(). The command returns a tibble summarising the counts and percentages of columns with particular types. A barplot is also returned when show_plot = TRUE.
# return tibble and visualisation of columns types
inspect_types(starwars, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 4 x 4
## type cnt pcnt col_name
## <chr> <int> <dbl> <list>
## 1 character 7 53.8 <chr [7]>
## 2 list 3 23.1 <chr [3]>
## 3 numeric 2 15.4 <chr [2]>
## 4 integer 1 7.69 <chr [1]>
inspect_types() for two dataframes
When a second dataframe is provided, inspect_types() will create a dataframe comparing the count and percentage of each column type for each of the input dataframes. The summaries for the first and second dataframes are show in columns with names appended with _1 and _2, respectively.
inspect_types(star_1, star_2, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 4 x 5
## type cnt_1 pcnt_1 cnt_2 pcnt_2
## <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 character 7 53.8 6 54.5
## 2 list 3 23.1 3 27.3
## 3 numeric 2 15.4 2 18.2
## 4 integer 1 7.69 0 0
Memory usage
inspect_mem() for a single dataframe
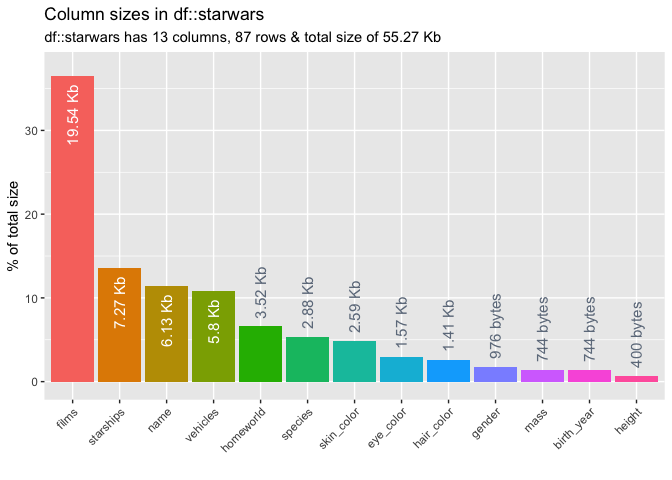
To explore the memory usage of the columns in a data frame, use inspect_mem(). The command returns a tibble containing the size of each column in the dataframe. A barplot is also returned when show_plot = TRUE.
inspect_mem(starwars, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 13 x 3
## col_name size pcnt
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 films 19.54 Kb 36.5
## 2 starships 7.27 Kb 13.6
## 3 name 6.13 Kb 11.5
## 4 vehicles 5.8 Kb 10.8
## 5 homeworld 3.52 Kb 6.58
## 6 species 2.88 Kb 5.39
## 7 skin_color 2.59 Kb 4.85
## 8 eye_color 1.57 Kb 2.93
## 9 hair_color 1.41 Kb 2.63
## 10 gender 976 bytes 1.78
## 11 mass 744 bytes 1.36
## 12 birth_year 744 bytes 1.36
## 13 height 400 bytes 0.730
inspect_mem() for two dataframes
When a second dataframe is provided, inspect_mem() will create a dataframe comparing the size of each column for both input dataframes. The summaries for the first and second dataframes are show in columns with names appended with _1 and _2, respectively.
inspect_mem(star_1, star_2, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 13 x 5
## col_name size_1 size_2 pcnt_1 pcnt_2
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 films 11.2 Kb 11.82 Kb 34.6 40.5
## 2 starships 4.53 Kb 4.7 Kb 14.0 16.1
## 3 name 3.55 Kb <NA> 11.0 NA
## 4 vehicles 3.41 Kb 3.39 Kb 10.5 11.6
## 5 homeworld 2.3 Kb 2.12 Kb 7.11 7.26
## 6 species 1.82 Kb 1.82 Kb 5.63 6.24
## 7 skin_color 1.76 Kb 1.79 Kb 5.44 6.13
## 8 eye_color 1.1 Kb 1.05 Kb 3.41 3.62
## 9 hair_color 960 bytes 1 Kb 2.90 3.43
## 10 gender 616 bytes 624 bytes 1.86 2.09
## 11 mass 448 bytes 448 bytes 1.35 1.50
## 12 birth_year 448 bytes 448 bytes 1.35 1.50
## 13 height 248 bytes <NA> 0.749 NA
Missing values
inspect_na() for a single dataframe
inspect_na() summarises the prevalence of missing values by each column in a data frame. A tibble containing the count (cnt) and the overall percentage (pcnt) of missing values is returned A barplot is also returned when show_plot is set to TRUE.
inspect_na(starwars, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 13 x 3
## col_name cnt pcnt
## <chr> <int> <dbl>
## 1 birth_year 44 50.6
## 2 mass 28 32.2
## 3 homeworld 10 11.5
## 4 height 6 6.90
## 5 hair_color 5 5.75
## 6 species 5 5.75
## 7 gender 3 3.45
## 8 name 0 0
## 9 skin_color 0 0
## 10 eye_color 0 0
## 11 films 0 0
## 12 vehicles 0 0
## 13 starships 0 0
inspect_na() for two dataframes
When a second dataframe is provided, inspect_na() returns a tibble containing counts and percentage missingness by column, with summaries for the first and second data frames are show in columns with names appended with _1 and _2, respectively. In addition, a p-value is calculated which provides a measure of evidence of whether the difference in missing values is significantly different.
inspect_na(star_1, star_2, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 13 x 6
## col_name cnt_1 pcnt_1 cnt_2 pcnt_2 p_value
## <chr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 birth_year 26 52 24 48 0.841
## 2 mass 19 38 14 28 0.395
## 3 homeworld 6 12 2 4 0.269
## 4 height 4 8 NA NA NA
## 5 hair_color 3 6 4 8 1.000
## 6 species 3 6 2 4 1.000
## 7 gender 2 4 2 4 1
## 8 name 0 0 NA NA NA
## 9 skin_color 0 0 0 0 NA
## 10 eye_color 0 0 0 0 NA
## 11 films 0 0 0 0 NA
## 12 vehicles 0 0 0 0 NA
## 13 starships 0 0 0 0 NA
Notes:
- Smaller p-values indicate stronger evidence of a difference in the missingness rate for a single column
- If a column appears in one data frame and not the other - for example
heightappears instar_1but norstar_2, then the correspondingpcnt_,cnt_andp_valuecolumns will containNA - Where the missingness is identically 0, the
p_valueisNA. - The visualisation illustrates the significance of the difference using a coloured bar overlay. Orange bars indicate evidence of equality or missingness, while blue bars indicate inequality. If a
p_valuecannot be calculated, no coloured bar is shown. - The significance level can be specified using the
alphaargument toinspect_na(). The default isalpha = 0.05.
Correlation
inspect_cor() for a single dataframe
inspect_cor() returns a tibble containing Pearson's correlation coefficient, confidence intervals and p-values for pairs of numeric columns . The function combines the functionality of cor() and cor.test() in a more convenient wrapper. A point and whiskers plot is also returned when show_plot = TRUE.
inspect_cor(starwars, show_plot = T)## # A tibble: 3 x 6
## col_1 col_2 corr p_value lower upper
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 birth_year mass 0.478 0.00318 0.130 0.721
## 2 birth_year height -0.400 0.00789 -0.651 -0.0690
## 3 mass height 0.134 0.312 -0.163 0.409
Notes
- The tibble is sorted in descending order of the absolute coefficient |ρ|.
inspect_cordrops missing values prior to calculation of each correlation coefficient.- The
p_valueis associated with the null hypothesis H0 : ρ = 0.
inspect_cor() for for two dataframes
When a second dataframe is provided, inspect_cor() returns a tibble that compares correlation coefficients of the first dataframe to those in the second. The p_value column contains a measure of evidence for whether the two correlation coefficients are equal or not.
inspect_cor(star_1, star_2, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 3 x 5
## col_1 col_2 corr_1 corr_2 p_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 mass height 0.801 NA NA
## 2 birth_year height -0.572 NA NA
## 3 birth_year mass -0.421 0.986 8.03e-46
Notes:
- Smaller
p_valueindicates stronger evidence against the null hypothesis H0 : ρ1 = ρ2 and an indication that the true correlation coefficients differ. - The visualisation illustrates the significance of the difference using a coloured bar overlay. Orange bars indicate evidence of equality of correlations, while blue bars indicate inequality. If a
p_valuecannot be calculated, no coloured bar is shown. - The significance level can be specified using the
alphaargument toinspect_cor(). The default isalpha = 0.05.
Feature imbalance
inspect_imb() for a single dataframe
Understanding categorical columns that are dominated by a single level can be useful. inspect_imb() returns a tibble containing categorical column names (col_name); the most frequently occurring categorical level in each column (value) and pctn & cnt the percentage and count which the value occurs. The tibble is sorted in descending order of pcnt. A barplot is also returned when show_plot is set to TRUE.
inspect_imb(starwars, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 7 x 4
## col_name value pcnt cnt
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int>
## 1 gender male 71.3 19
## 2 hair_color none 42.5 1
## 3 species Human 40.2 1
## 4 eye_color brown 24.1 10
## 5 skin_color fair 19.5 2
## 6 homeworld Naboo 12.6 3
## 7 name Ackbar 1.15 1
inspect_imb() for two dataframes
When a second dataframe is provided, inspect_imb() returns a tibble that compares the frequency of the most common categorical values of the first dataframe to those in the second. The p_value column contains a measure of evidence for whether the true frequencies are equal or not.
inspect_imb(star_1, star_2, show_plot = TRUE)## # A tibble: 7 x 7
## col_name value pcnt_1 cnt_1 pcnt_2 cnt_2 p_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 gender male 72 10 72 11 1.000
## 2 hair_color none 40 1 44 1 1
## 3 species Human 40 1 42 1 1
## 4 eye_color brown 24 8 NA NA NA
## 5 skin_color fair 24 1 20 2 1
## 6 homeworld Tatooine 14. 2 16 1 1
## 7 name Anakin Skywalker 2 1 NA NA NA
- Smaller
p_valueindicates stronger evidence against the null hypothesis that the true frequency of the most common values is the same. - The visualisation illustrates the significance of the difference using a coloured bar overlay. Orange bars indicate evidence of equality of the imbalance, while blue bars indicate inequality. If a
p_valuecannot be calculated, no coloured bar is shown. - The significance level can be specified using the
alphaargument toinspect_imb(). The default isalpha = 0.05.
Numeric summaries
inspect_num() combining some of the functionality of summary() and hist() by returning summaries of numeric columns. inspect_num() returns standard numerical summaries (min, q1, mean, median,q3, max, sd), but also the percentage of missing entries (pcnt_na) and a simple histogram (hist). If show_plot = TRUE a histogram is generated for each numeric feature.
inspect_num(starwars, show_plot = TRUE, breaks = 10)## # A tibble: 3 x 10
## col_name min q1 median mean q3 max sd pcnt_na hist
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <list>
## 1 birth_year 8 35 52 87.6 72 896 155. 50.6 <tibble [1…
## 2 height 66 167 180 174. 191 264 34.8 6.90 <tibble [1…
## 3 mass 15 55.6 79 97.3 84.5 1358 169. 32.2 <tibble [1…
The hist column is a list whose elements are tibbles each containing the relative frequencies of bins for each feature. These tibbles are used to generate the histograms when show_plot = TRUE. For example, the histogram for starwars$birth_year is
inspect_num(starwars)$hist$birth_year## # A tibble: 20 x 2
## value prop
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 [-Inf, 0) 0
## 2 [0, 50) 0.488
## 3 [50, 100) 0.395
## 4 [100, 150) 0.0465
## 5 [150, 200) 0
## 6 [200, 250) 0.0233
## 7 [250, 300) 0
## 8 [300, 350) 0
## 9 [350, 400) 0
## 10 [400, 450) 0
## 11 [450, 500) 0
## 12 [500, 550) 0
## 13 [550, 600) 0
## 14 [600, 650) 0.0233
## 15 [650, 700) 0
## 16 [700, 750) 0
## 17 [750, 800) 0
## 18 [800, 850) 0
## 19 [850, 900) 0.0233
## 20 [900, Inf) 0
Categorical levels
inspect_cat() returns a tibble summarising categorical features in a data frame, combining the functionality of the inspect_imb() and table() functions. If show_plot = TRUE a barplot is generated showing the relative split. The tibble generated contains the columns
col_namename of each categorical columncntthe number of unique levels in the featurecommonthe most common level (see alsoinspect_imb())common_pcntthe percentage occurrence of the most dominant levellevelsa list of tibbles each containing frequency tabulations of all levels
inspect_cat(starwars, show_plot = T)## # A tibble: 7 x 5
## col_name cnt common common_pcnt levels
## <chr> <int> <chr> <dbl> <list>
## 1 eye_color 15 brown 24.1 <tibble [15 × 2]>
## 2 gender 5 male 71.3 <tibble [5 × 2]>
## 3 hair_color 13 none 42.5 <tibble [13 × 2]>
## 4 homeworld 49 Naboo 12.6 <tibble [49 × 2]>
## 5 name 87 Ackbar 1.15 <tibble [87 × 2]>
## 6 skin_color 31 fair 19.5 <tibble [31 × 2]>
## 7 species 38 Human 40.2 <tibble [38 × 2]>
For example, the levels for the hair_color column are
inspect_cat(starwars)$levels$hair_color## # A tibble: 13 x 2
## value prop
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 none 0.425
## 2 brown 0.207
## 3 black 0.149
## 4 <NA> 0.0575
## 5 white 0.0460
## 6 blond 0.0345
## 7 auburn 0.0115
## 8 auburn, grey 0.0115
## 9 auburn, white 0.0115
## 10 blonde 0.0115
## 11 brown, grey 0.0115
## 12 grey 0.0115
## 13 unknown 0.0115
Note that by default, if NA values are present, they are counted as a distinct categorical level.