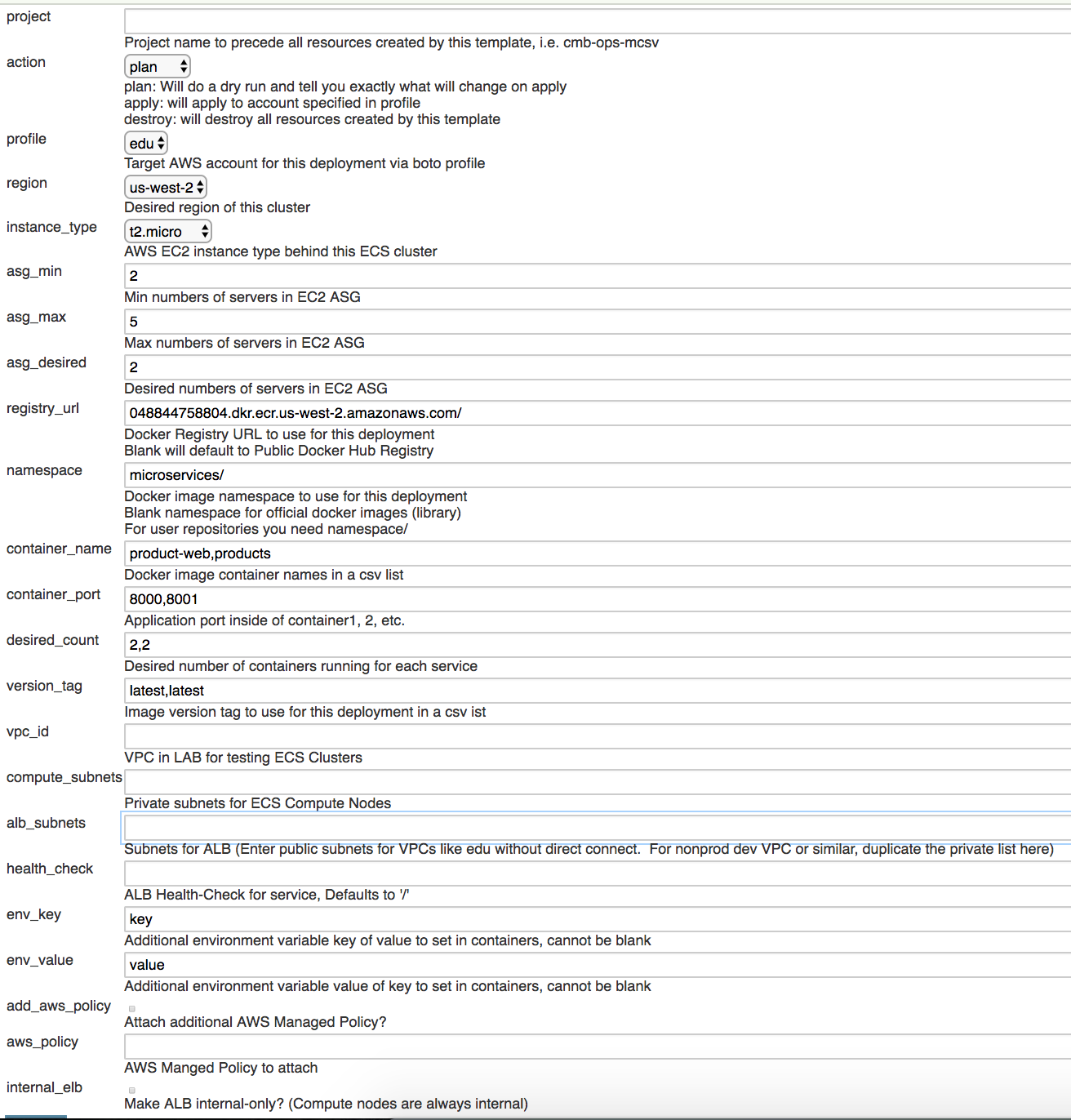
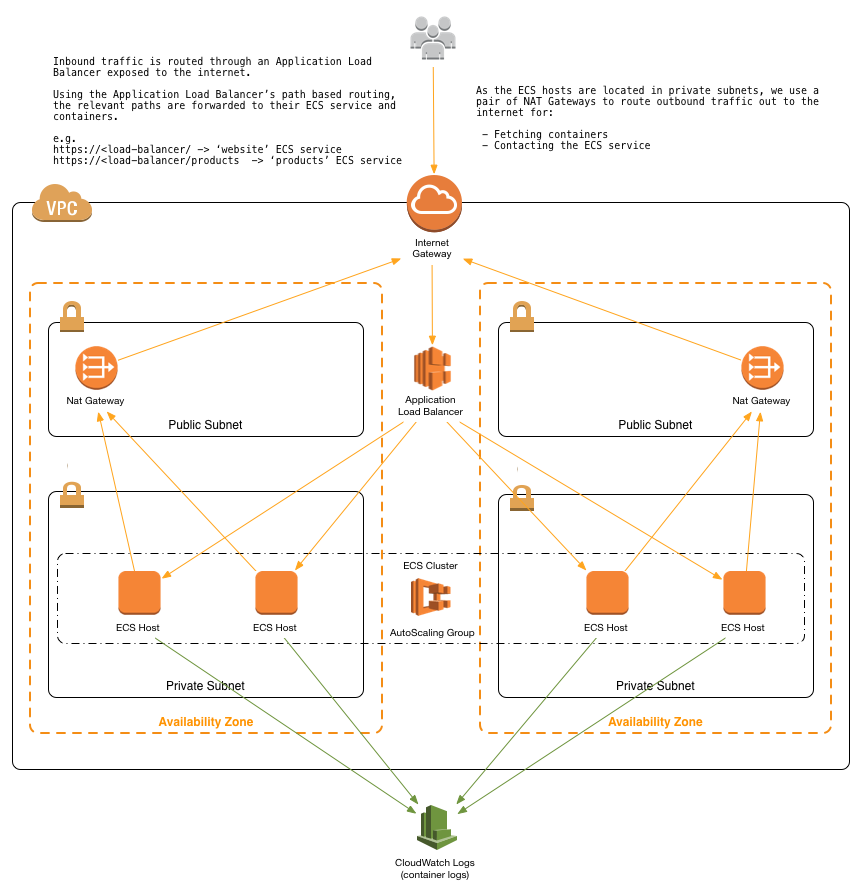
This project was created to provide a pipeline for ECS cluster deployments at scale. If you have microservices in containers that could benefit from ALB architecture, this template will be able to configure and deploy them, using the latest ECS-Optimized Amazon Linux AMIs to take advantage of IAM roles for tasks.
A few production-ready efforts are implemented:
- Compute/container nodes are in a private VPC (with NAT Gateway) where only ALB is publicly accessible. ALB can be made private by setting the
internal_elbvar to true add_aws_policywill set IAM policy at the container-level, not at the instance-level- A log group will be created for each ECS service you specify in the container vars, which are easily filtered in CloudWatch Logs
- Persistent storage is available out of the box with EFS which is available on the container's
/mnt- EFS is now encrypted both at REST and at transit
- Upon deployment, the latest ECS-Optimized AMI will be used. On update of the stack, releases of newer AMIs will not force new instances. (which can be disabled)
- Protip: Set
env_keyorenv_valuefor container environment variables like DB endpoints. The ALB endpoint is in all containers by default at $ENDPOINT.
Default container image variables are set in container_vars.tf to deploy some example microservices.
If you're not using the [default] aws cli profile, make sure the correct profile in ~/.aws/(config|credentials) is configured in aws_vars.tf.
# provider.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.aws_region}"
profile = "${var.profile}"
}
# vars.tf
variable "profile" {
description = "Boto/AWS profile to use for this deployment"
default = "edu"
}
The path is slightly different for Windows: https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/
Always run this first for syntax or logic check
terraform init is now required before running these commands the first time
ip="$(dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com)" && \
terraform plan \
-var admin_cidr_ingress="${ip}/32" \
-var key_name=aws_key_namekey_name: Key in AWS you would like to use to access your instances
terraform apply \
-var admin_cidr_ingress="${ip}/32" \
-var key_name=aws_key_nameOnce the stack is created, wait a minute or two for positive health checks and test the stack by launching a browser with the ALB url.
- First service listed in container_name var will be available at / (i.e. product-web)
- Each subsequent service will be available at /container_name (i.e. /products)
terraform destroy \
-var admin_cidr_ingress="${ip}/32" \
-var key_name={your_key_name}Source: https://github.com/awslabs/ecs-refarch-cloudformation
deployment_minimum_healthy_percent overrides a cli default of 100% a rolling deployment policy of 50% at a time. When you update a task definition, check out the ALB target to see old connections draining. Task Definition updates to any service are available almost immediately, thanks to the dynamic port mapping. However, the previous task definition will continue running for a few minutes as it can take a while to drain connections and the previous task to disappear.
ec2-user@ip-10-10-0-197 ~ $ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
a0982396ab51 048844758804.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/microservices/product-web:latest "/app" 33 minutes ago Up 33 minutes 0.0.0.0:32775->8000/tcp MCSV-POC-product-web-bebfeacdf189b8c76600
4035e05cdfd3 048844758804.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/microservices/products:latest "/app" About an hour ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:32768->8001/tcp MCSV-POC-products-aeefddc3aaf080c2bc01
66cd74ae81cf amazon/amazon-ecs-agent:latest
The generated ALB Endpoint is set as an environment variable in each container, $ENDPOINT
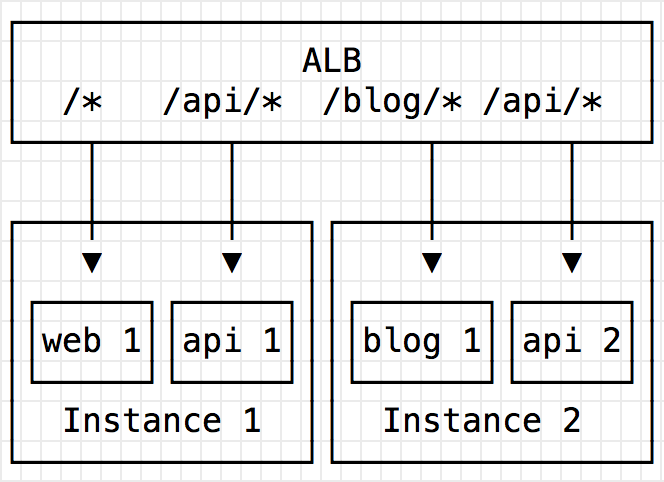 Source: https://convox.com/blog/alb/
Source: https://convox.com/blog/alb/
Health check are done via target groups for each container:
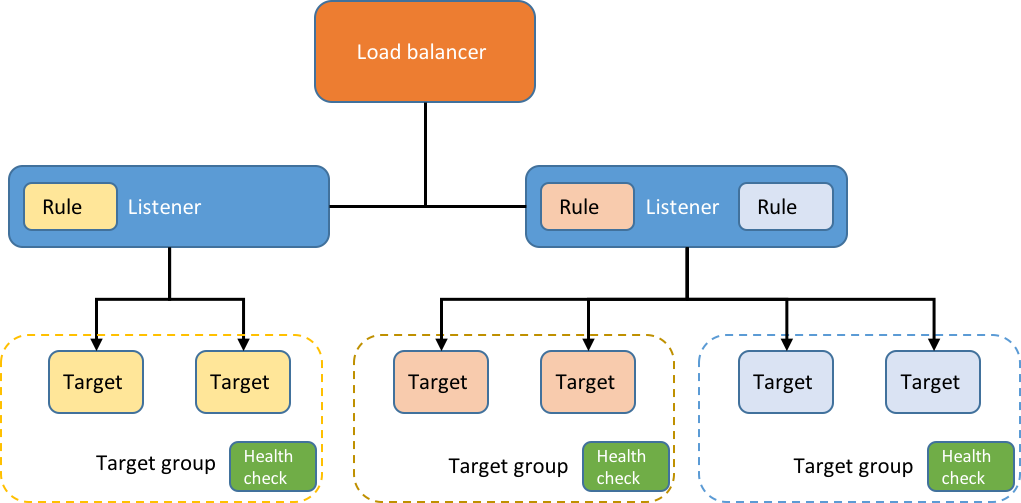 Source: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/microservice-delivery-with-amazon-ecs-and-application-load-balancers/
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/microservice-delivery-with-amazon-ecs-and-application-load-balancers/
As pictured, they can all share a listener. The health check looks for /target.
[Container's /mnt] >> [ EFS_mnt/container_name ] #bestartwork
Examples borrowed from: https://github.com/awslabs/ecs-refarch-cloudformation/tree/master/services.
Product web (2 containers) talks to a product api (2 containers) for products listing. 4 containers total running on only two ECS instances.
For continuous delivery of this stack we can set up a Jenkins project that will check out this repository and add an execute shell step with a script like this:
Until we can add a Jenkinsfile
rm -rf .terraform
bash -x tfstate/configure-remote-state.sh
echo "yes" | terraform ${action} \
-var key_name=${key_name} \
-var resource_tag=${project} \
-var profile=${profile} \
-var aws_region=${region} \
-var instance_type=${instance_type} \
-var asg_min=${asg_min} \
-var asg_max=${asg_max} \
-var asg_min=${asg_min} \
-var asg_desired=${asg_desired} \
-var admin_cidr_ingress=${admin_cidr_ingress} \
-var registry_url=${registry_url} \
-var namespace=${namespace} \
-var container_name=${container_name} \
-var container_port=${container_port} \
-var desired_count=${desired_count} \
-var version_tag=${version_tag} \
-var health_check=${health_check} \
-var env_key=${env_key} \
-var env_value=${env_value} \
-var add_aws_policy=${add_aws_policy} \
-var aws_policy=${aws_policy} \
-var internal_elb=${internal_elb}Note that "Variables specified with the TF_VAR_ environment variables will be literal string values, just like -var." So it's possible to clean up the script a bit with some expections
/usr/local/sbin/terraform init
/usr/local/sbin/terraform refresh \
-var profile=${ACCOUNT} \
-var add_aws_policy=${add_aws_policy} \
-var aws_policy=${aws_policy}
echo "yes" | /usr/local/sbin/terraform ${action} \
-var profile=${ACCOUNT} \
-var add_aws_policy=${add_aws_policy} \
-var aws_policy=${aws_policy}'Build with parameters' would look similar to the following: