Code running hedonometer.org.
The Hedonometer website at http://hedonometer.org is comprised of three main parts: (1) the web server processing including the base code in Python Django, (2) the data processing on the server, and (3) data processing on the VACC. The deployment of the webserver is done using templates and the Ansible tool. Settings and detailed instructions for deploying development and production servers are at github.com/andyreagan/hedonometer-vagrant-ansible-deployment. In the Figure below we diagram the web server side of the server, included the deployment settings mentioned above and the Django server linked in the caption.
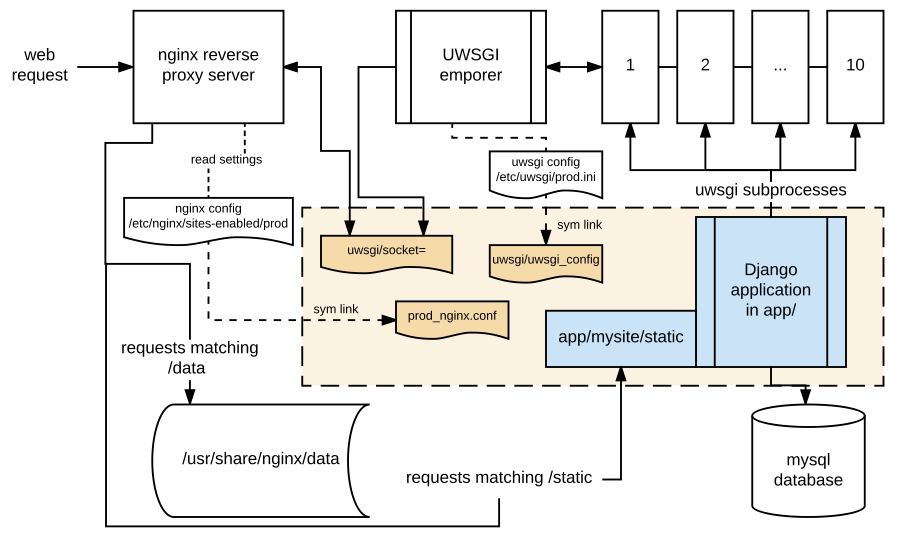 Schematic of the Hedonometer server architecture.
The section in orange is contained in the prod user account.
The settings files for UWSGI and Nginx are written by an Ansible playbook based on the user account under which the code is distributed (playbook, etc available over here).
Schematic of the Hedonometer server architecture.
The section in orange is contained in the prod user account.
The settings files for UWSGI and Nginx are written by an Ansible playbook based on the user account under which the code is distributed (playbook, etc available over here).
The data side of the server is run separately from the web server side.
Nginx serves all files in the /data URL ending at Hedonometer, and the files can be browsed at http://hedonometer.org/data/.
The files here are used in the front end visualizations across the site, and represent files that loaded for the details-on-demand, as well as the overview files.
The structure is optimized for front end performance.
The code base is on GitHub at https://github.com/andyreagan/hedonometer-data-munging.
As seen in the overall schematic of the server, these files are all inside of /usr/share/nginx and they are managed by the root user.
Every hour on the hour, these files are updated by a cascade of processes through the cron scheduler.
The process is simple enough to do without a diagram: cron calls cronregions.sh every hour, which simply calls regions.py with Python.
The regions.py loops over dates, looks for files in the word-vectors folders for each region, and uses \verb|rsync| to copy over the missing files.
Once whole days are downloaded in the 15-minute pieces, it creates the daily summary files (e.g., word-vectors/vacc/2017-04-07-sum.csv) and updates the overall summary at http://hedonometer.org/data/word-vectors/vacc/sumhapps.csv (being wary of duplicates, and keeping the most recent).
The copy of files from the VACC uses rsync, which operates of ssh and relies on the public key of the server being present on the VACC for seamless access.
The files on the VACC are created by a separate process, which is managed in much the same way as the keyword searches in the previous appendix.
The cron scheduler runs every hour on the hour, and submits jobs to the PBS queue that turn 15-minute zipped JSON Tweet files into length 10,222 word vectors.
The full code for this process is available at https://github.com/andyreagan/hedonometer-VACC-processing.
For more details on the motivation and the science, see the about page
- Start a virtualenv
virtualenv pyenv
- Install the frozen requirements
pyenv/bin/pip install -r requirements-freeze.txt
- Source the dummy config
source local_config.sh
- Start the webserver
pyenv/bin/python manage.py runserver
- (optional) Mount the remote data directory
sshfs linderoot:/usr/share/nginx/data data